Top 8 Seal Manufacturers List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario 1:…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for seal manufacturers
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, sourcing high-quality sealing solutions can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets like Germany and Nigeria) strive for operational efficiency, understanding the complexities of the global seal manufacturing market is essential. This guide aims to streamline the process of finding the right seal manufacturers by providing an in-depth exploration of various types of seals, their applications across different industries, and critical insights into supplier vetting.
The comprehensive scope of this guide covers not only the diverse range of sealing products, such as O-rings, hydraulic seals, and custom solutions, but also delves into factors influencing cost and quality. With a focus on practical strategies for effective supplier selection, buyers will gain valuable knowledge about evaluating manufacturers based on performance, reliability, and service capabilities.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide serves as a vital resource for making informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in the oil and gas sector or the pharmaceutical industry, understanding the nuances of seal manufacturing will help you mitigate risks, enhance product performance, and ultimately drive business success in a competitive global market.
Top 10 Seal Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Wyatt Seal – Custom Sealing Solutions
Domain: wyattseal.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
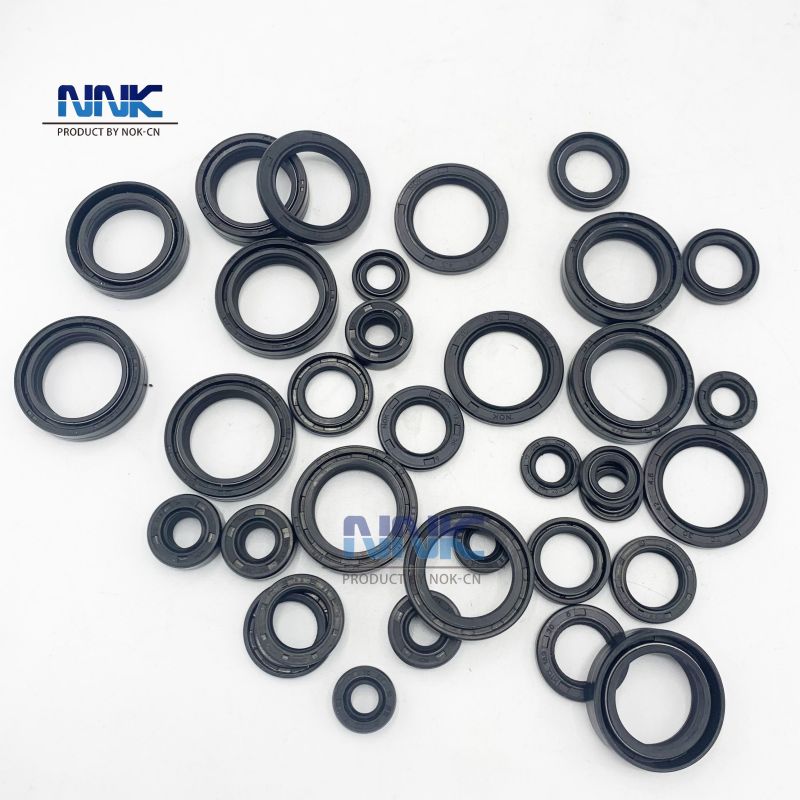
Introduction: Custom Seal Manufacturers & Sealing Solutions including O-rings, Hydraulics & Pneumatics, Rotary Seals, Custom Molded Gaskets, Machined Rubber & Plastics, Extruded Shapes & Profiles, and Specialty Products. O-rings available in Custom and Standard (AS568) sizes, by brands such as Parker and Freudenberg, and materials including Nitrile, FKM, EPDM, FFKM, Silicone, Fluorosilicone, PTFE, Polyurethane,…
2. Seal Company – Sealing Solutions
Domain: sealcompany.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Seal Company is an authorized distributor and manufacturer of high-quality sealing solutions including o-rings, seals, gaskets, packings, and custom-engineered products. They offer services such as Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) programs, bar-coding, custom packaging, kitting, and EDI order management. Their fabrication capabilities include computer-aided design & manufacturing (CAD/CAM) and rever…
3. US Seal Mfg – Mechanical Seals
Domain: ussealmfg.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: US Seal Mfg offers a wide variety of mechanical seals suitable for various applications. Their products represent 95% of the replacement seal market, promising long life, reduced maintenance, and automatic self-adjustment. The seals are available in different materials, allowing customers to choose the correct combination of elastomer, metallurgy, and sealing faces for their specific needs.
4. PSI Seal – Custom High Pressure Seals
Domain: psiseal.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: High Pressure Seal Manufacturer – Custom Polymer Seals & Sealing Solutions. Products include: Spring Energized PTFE Seals, Hydraulic Seals, PTFE Rotary Lip Seals, Self-Lubricating Polymer Bearings, High Pressure Seals, High Temperature Seals, Low Friction Seals, Cryogenic Seals, Chemical Resistant Seals, High Speed Rotary Seals, Vacuum Seals. Applications include Aerospace, Medical, Energy, Oil & …
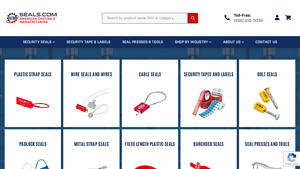
5. Seals.com – Security Seals
Domain: seals.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Security Seals include: Plastic Security Seals, Fixed Length Plastic Seals, Bolt Seals, Cable Seals, Metal Strap Seals, Padlock Seals, Wire Seals, High Security Seals (C-TPAT and ISO17712 compliant), Barcoded Seals, Cup Seals for screw and bolt protection, Security Tape & Labels, Seal Presses & Tools. Products are categorized by industry including Agriculture, Airlines, Auto Racing, Cargo & Logist…
6. Stein Seal Company – Precision Seals
Domain: steinseal.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Stein Seal Company manufactures a variety of precision seals including Circumferential Seals, Face Seals, Bushing Seals, Bellows Seals, Film Riding Seals, API 682 Seals, and Inter Shaft Seals. Their products are used across multiple markets such as Aerospace, Industrial, Marine, Nuclear, Power Generation, and Process Industry. Specific applications include Main Shaft Seals, Gearbox Seals, APU Seal…
7. Seal & Design – Custom Sealing Solutions
Domain: sealanddesign.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Seal & Design manufactures and distributes a variety of custom sealing products, including: O-Rings (available in standard and specialty varieties for static and dynamic applications, made from materials like silicone rubber, Nitrile, and fluorosilicone), Gaskets (made from rubber, metallic, sponge, and foam, with styles including die-cut, water-jet cut, beaded, and PSA laminated parts), Seals (in…
8. Real Seal – Specialty Seals & O-Rings
Domain: real-seal.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Real Seal is a manufacturer and distributor of seal products and mechanical component goods, specializing in performance-oriented rubber and plastic materials. Key products include: Specialty Seals, Rubber Polyurethane, O-rings, Gasket Seals, Polyurethane O-Rings & Seal Systems, Engineered Thermoplastic Mechanical Components, and Engineered Rubber Components. The company offers a wide array of sea…
Understanding seal manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Seal Manufacturers | Specialize in bespoke sealing solutions tailored to specific needs. | Aerospace, Oil & Gas, Automotive | Pros: Tailored solutions, high precision. Cons: Longer lead times, potentially higher costs. |
| Standard Seal Suppliers | Offer a wide range of pre-manufactured seals for general use. | Manufacturing, Construction, Hydraulics | Pros: Quick delivery, lower costs. Cons: Limited customization, may not fit unique applications. |
| Specialty Seal Manufacturers | Focus on niche markets with unique materials or designs. | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals | Pros: High performance in specific conditions. Cons: Limited product range, higher prices. |
| Multi-Product Distributors | Provide a variety of sealing products along with related services. | General Industry, Maintenance Services | Pros: One-stop shop, diverse inventory. Cons: Variable quality, may lack specialization. |
| Engineering Service Firms | Combine sealing solutions with design and engineering support. | R&D, Custom Manufacturing | Pros: Integrated solutions, expert guidance. Cons: Potentially higher costs, longer project timelines. |
What Are the Characteristics of Custom Seal Manufacturers?
Custom seal manufacturers are known for their ability to create tailored sealing solutions that meet specific operational requirements. They excel in producing seals that fit unique applications, often utilizing advanced materials and manufacturing techniques. B2B buyers in sectors such as aerospace, oil and gas, and automotive find these manufacturers invaluable when standard options do not suffice. However, while they provide precise and effective solutions, the lead times and costs associated with custom seals can be higher compared to off-the-shelf alternatives.
How Do Standard Seal Suppliers Operate?
Standard seal suppliers focus on delivering a broad range of pre-manufactured seals that cater to general applications. These suppliers are ideal for industries such as manufacturing and construction, where quick turnaround and cost-effectiveness are paramount. Buyers benefit from reduced lead times and lower prices, but they may face limitations in customization. Standard seals may not always meet specific operational demands, which could lead to performance issues in critical applications.
What Makes Specialty Seal Manufacturers Unique?
Specialty seal manufacturers target niche markets by offering products designed for specific conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments. Industries like food and beverage and pharmaceuticals often require these specialized seals to ensure compliance with strict regulations and performance standards. While these manufacturers provide high-performance solutions, their limited product range and higher prices can be a consideration for buyers looking for more versatile options.
What Are the Benefits of Multi-Product Distributors?
Multi-product distributors serve as one-stop shops for a variety of sealing products and related services. They cater to general industry and maintenance services, making them ideal for businesses that require diverse sealing solutions without the need for specialization. The primary advantage is the convenience of sourcing multiple products from a single supplier; however, buyers must be cautious about variable quality and the potential lack of specialized expertise in certain sealing applications.
How Do Engineering Service Firms Enhance Sealing Solutions?
Engineering service firms combine sealing solutions with comprehensive design and engineering support. They are particularly valuable for research and development projects and custom manufacturing where expert guidance is essential. These firms can provide integrated solutions that address complex sealing challenges. However, buyers should be prepared for potentially higher costs and longer project timelines due to the extensive services offered.
Key Industrial Applications of seal manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of seal manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Seals for drilling equipment and pipelines | Enhanced safety and efficiency, reducing downtime | Material compatibility with harsh environments, certification standards |
| Automotive | Seals for engines and transmission systems | Improved performance and longevity of vehicle components | Customization options, temperature and pressure ratings |
| Pharmaceuticals & Food & Beverage | Sealing solutions for processing equipment | Compliance with hygiene standards and contamination prevention | Regulatory certifications, material safety data sheets (MSDS) |
| Aerospace | Seals for fuel systems and hydraulic applications | Reliability in extreme conditions, ensuring safety | Weight considerations, resistance to extreme temperatures |
| Renewable Energy | Seals for wind turbines and solar panel systems | Increased operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Durability against environmental factors, custom solutions |
What Are the Key Applications of Seal Manufacturers in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, seal manufacturers provide critical sealing solutions for drilling equipment and pipelines. These seals are essential for preventing leaks of hazardous materials, thereby enhancing safety and operational efficiency. Buyers in this industry must consider the material compatibility with harsh environments, as well as the necessary certifications to meet regulatory standards. The ability to customize seals for specific applications can also significantly impact performance and reliability.
How Are Seals Used in the Automotive Sector?
Seal manufacturers play a vital role in the automotive industry by supplying seals for engines and transmission systems. These seals help to contain fluids and gases, which improves the overall performance and longevity of vehicle components. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing seals that meet temperature and pressure ratings is crucial. Additionally, customization options may be necessary to fit unique vehicle designs and specifications.
What Sealing Solutions Are Essential for Pharmaceuticals and Food & Beverage Industries?
In the pharmaceuticals and food & beverage sectors, seal manufacturers provide sealing solutions for processing equipment that must comply with strict hygiene standards. These seals prevent contamination, ensuring product safety and quality. Buyers need to focus on sourcing materials that meet regulatory certifications and have clear material safety data sheets (MSDS). The ability to deliver custom solutions tailored to specific processing requirements can also be a significant advantage.
How Do Aerospace Applications Benefit from Seal Manufacturers?
Seal manufacturers supply seals for fuel systems and hydraulic applications in the aerospace industry, where reliability is paramount. These seals must withstand extreme conditions, ensuring operational safety and efficiency. International buyers in this sector should prioritize weight considerations and the seals’ resistance to extreme temperatures. Understanding the specific requirements for aerospace applications can lead to better performance and compliance with industry standards.
What Role Do Seals Play in Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, seal manufacturers provide sealing solutions for wind turbines and solar panel systems. These seals are designed to enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs by preventing leaks and environmental damage. Buyers should consider the durability of seals against various environmental factors, as well as the availability of custom solutions to meet specific energy applications. Investing in high-quality seals can significantly contribute to the sustainability and effectiveness of renewable energy projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘seal manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Challenge of Custom Sealing Solutions
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties when searching for sealing solutions that meet specific requirements for unique applications. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals may require seals that have custom dimensions, materials, or configurations not readily available in the market. This need for customization can lead to frustrating delays in production timelines, increased costs due to trial and error, and potential project setbacks if the right seals cannot be sourced quickly.
The Solution: To effectively address the need for custom sealing solutions, buyers should partner with seal manufacturers that offer robust design and engineering services. Start by clearly defining your requirements, including dimensions, material compatibility, and performance specifications. Engaging in a collaborative design process with the manufacturer can streamline the creation of prototypes tailored to your specific application. Utilize tools such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) to visualize and refine your requirements before moving to production. Establish clear communication channels to ensure that your manufacturer understands the nuances of your needs, leading to faster iterations and more effective solutions.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Timely Deliveries in Sealing Solutions
The Problem: Delays in the delivery of seals can significantly disrupt production schedules and lead to costly downtime. Many B2B buyers face the challenge of unreliable shipping timelines, which may stem from inadequate inventory management or logistical issues from the manufacturer. This uncertainty can create a ripple effect, causing project delays and affecting the overall supply chain.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of delivery delays, buyers should prioritize working with seal manufacturers that have a proven track record of on-time deliveries and robust inventory management practices. Before placing an order, inquire about the manufacturer’s inventory levels and lead times for your required seals. Consider implementing a Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) program, where the manufacturer takes responsibility for maintaining optimal stock levels based on your usage patterns. This proactive approach can help ensure that you always have the necessary seals on hand, thus minimizing production downtime and keeping your projects on track.
Scenario 3: Navigating Material Selection for Sealing Applications
The Problem: The wide array of sealing materials available can overwhelm B2B buyers, particularly when specific applications demand unique properties such as chemical resistance, temperature stability, or flexibility. Incorrect material selection can lead to seal failures, resulting in costly repairs and operational disruptions.
The Solution: To effectively navigate material selection, buyers should engage directly with seal manufacturers who possess expertise in material science and application requirements. Begin by providing detailed information about the operating conditions of your application, including the types of fluids or gases involved, temperature ranges, and environmental factors. Manufacturers with a diverse portfolio can offer insights into which materials are best suited for your specific needs. Additionally, request samples for testing before finalizing your order to ensure compatibility and performance. Leverage the manufacturer’s technical resources, such as material compatibility charts and case studies, to inform your decision-making process and reduce the likelihood of future failures.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for seal manufacturers
What Are the Key Properties of Common Seal Materials for Manufacturers?
Seal manufacturers often utilize a variety of materials, each with distinct properties that influence their performance in different applications. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable sealing solutions.
1. Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Nitrile rubber, also known as Buna-N, is a synthetic rubber widely used for seals due to its excellent resistance to oils and fuels.
- Key Properties: NBR can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to +100°C and offers moderate resistance to abrasion and tearing.
- Pros & Cons: It is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. However, its performance can degrade in extreme temperatures and with exposure to ozone, which limits its use in certain environments.
- Impact on Application: NBR is particularly suitable for automotive and industrial applications where oil resistance is critical. It is not recommended for applications involving strong oxidizing agents or high-temperature steam.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials, as NBR may not meet all regulatory requirements in certain industries.
2. Fluoroelastomer (FKM)
Fluoroelastomers, commonly referred to as FKM, are known for their exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature stability.
- Key Properties: FKM can operate effectively in temperatures from -20°C to +200°C and is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including fuels, oils, and solvents.
- Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of FKM is its durability and long service life, making it ideal for demanding applications. However, it is more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to process, which may lead to higher manufacturing costs.
- Impact on Application: FKM is ideal for use in the aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries, where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and South America should be aware of the high cost and ensure that the benefits justify the investment, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
3. Silicone Rubber
Silicone rubber is known for its versatility and ability to maintain its properties over a wide temperature range.
- Key Properties: It can withstand temperatures from -60°C to +200°C and offers excellent resistance to UV light and ozone.
- Pros & Cons: Silicone is highly flexible and can be molded into complex shapes, making it suitable for custom applications. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to other materials and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
- Impact on Application: Silicone is often used in food and beverage applications due to its non-toxic properties and is also common in medical devices.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with FDA regulations is crucial for buyers in the food and medical industries, particularly in Europe, where stringent standards apply.
4. Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane seals are known for their high resilience and resistance to wear and tear.
- Key Properties: PU can withstand temperatures from -40°C to +80°C and has excellent abrasion resistance.
- Pros & Cons: The material is highly durable and can be formulated for specific applications, but it can be more expensive and complex to manufacture than other rubber materials.
- Impact on Application: Polyurethane is often used in hydraulic applications and in environments where high wear resistance is required.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific formulation of PU, as not all grades are suitable for contact with certain chemicals. Compliance with local standards is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Seal Manufacturers
| Material | Typical Use Case for seal manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Automotive and industrial seals | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited temperature and ozone resistance | Low |
| Fluoroelastomer (FKM) | Aerospace and chemical processing | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Silicone Rubber | Food and medical applications | Versatile and UV resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Hydraulic applications | High durability and wear resistance | More expensive and complex to manufacture | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of common sealing materials, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regulatory environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for seal manufacturers
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Seals?
The manufacturing process of seals involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the stringent requirements of various applications. Understanding these stages can provide B2B buyers with insight into the reliability and performance of the sealing solutions they procure.
-
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of seals is material preparation. This stage involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which may include elastomers, thermoplastics, metals, or composites, depending on the application. Suppliers often utilize advanced material characterization techniques to ensure the selected materials have the right mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. This is crucial, as the performance of the seal largely depends on the quality of the materials used. -
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This can involve several techniques, such as injection molding, compression molding, extrusion, or machining. For instance, injection molding is widely used for producing complex shapes with high precision, while extrusion is ideal for continuous profiles like O-rings and gaskets. During this stage, manufacturers must adhere to specific tolerances to ensure the seals fit properly in their intended applications. -
Assembly of Components
In cases where seals consist of multiple parts, the assembly process is essential. This stage may involve bonding, welding, or mechanically joining different components to create a complete sealing solution. Advanced automation and robotics are often employed to enhance efficiency and precision during assembly, which can be particularly beneficial for high-volume production. -
Finishing Processes
The finishing stage includes various treatments that enhance the seal’s performance and durability. This may involve surface treatments, coatings, or secondary machining processes to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy. For instance, seals might be treated to improve their resistance to wear, abrasion, or chemical degradation, which is critical for applications in demanding environments such as oil and gas, automotive, or aerospace sectors.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing of Seals?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of seal manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer specifications. A robust QA process typically includes several checkpoints and adherence to recognized standards.
-
Adherence to International Standards
Many seal manufacturers comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification signifies that the manufacturer has established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications or CE marking for products sold in Europe further ensure compliance with safety and performance standards. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These include:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to verify that they meet specifications before production begins.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify any deviations from quality standards in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all seals meet the required specifications, including dimensional checks and functional testing. -
Testing Methods for Seal Performance
Common testing methods employed in the QC process include:
– Pressure Testing: Evaluates the seal’s ability to withstand pressure without leaking.
– Temperature Testing: Assesses performance under varying temperature conditions.
– Chemical Resistance Testing: Determines the seal’s durability against specific fluids or gases it may encounter in application.
– Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to ensure reliability over the product’s lifespan.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control Processes of Seal Suppliers?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential seal suppliers to ensure they receive high-quality products. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits
Performing on-site audits of potential suppliers can provide deep insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. During the audit, buyers can review documentation, observe manufacturing practices, and assess the overall quality management system in place. -
Request Quality Assurance Documentation
Suppliers should be able to provide documentation detailing their quality assurance processes, including certificates of compliance with relevant standards (e.g., ISO, API, CE). This documentation serves as evidence of the supplier’s commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards. -
Third-Party Inspection Reports
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. Independent inspectors can evaluate the manufacturing processes and conduct tests on samples, providing unbiased feedback on quality and compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances in quality control should be considered:
-
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements and standards for sealing products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure that the products they procure are compliant and suitable for their markets. -
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
Quality assurance does not end with manufacturing; it extends to the logistics and supply chain processes as well. Buyers should evaluate how suppliers manage inventory, shipping, and delivery to minimize risks of damage or delays that could affect product quality. -
Cultural and Language Barriers
Communication is vital in ensuring quality standards are met. Buyers should consider potential cultural and language barriers that may affect understanding quality requirements and specifications. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can mitigate misunderstandings.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of seal manufacturers, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that the sealing solutions they procure are reliable, high-quality, and suited to their specific applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘seal manufacturers’
Introduction
Sourcing high-quality seals for your industrial applications can be a complex process. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your procurement efforts, ensuring you select the right seal manufacturer that meets your specific needs. By following these steps, you can mitigate risks, enhance efficiency, and secure reliable sealing solutions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to potential suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Specify the type of seals needed—O-rings, hydraulic seals, or custom solutions—along with dimensions, materials, and performance characteristics. This step is crucial to ensure that suppliers can meet your exact needs and avoid costly delays later in the process.
- Consider environmental factors: Identify conditions such as temperature, pressure, and media compatibility that may affect seal performance.
- Document standards: Include any industry-specific standards or certifications required for your application.
Step 2: Research Potential Manufacturers
Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers that specialize in the types of seals you need. Look for companies with a solid reputation and a proven track record in your industry. This foundational step helps ensure that you engage with suppliers capable of delivering quality products on time.
- Utilize online resources: Explore manufacturer websites, industry publications, and trade shows to gather information.
- Check reviews and testimonials: Seek feedback from other businesses that have worked with potential suppliers to gauge reliability and service quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and quality management systems. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry-related certifications indicate a commitment to quality and compliance with international standards.
- Request documentation: Ask for copies of relevant certifications and ensure they are up to date.
- Understand the implications: Compliance with industry standards can affect product performance and safety, particularly in sectors like oil and gas or pharmaceuticals.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Investigate the manufacturing capabilities of potential suppliers. A manufacturer with advanced technology and in-house capabilities can offer custom solutions and quicker turnaround times. Understanding their production processes helps ensure they can meet your volume and quality requirements.
- Explore customization options: Check if the supplier can accommodate unique specifications, such as custom sizes or materials.
- Inquire about lead times: Knowing production timelines is essential for planning your inventory and operations.
Step 5: Request Samples and Test Products
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the seals you intend to buy. Testing these samples in your application can reveal potential performance issues and ensure compatibility with your systems.
- Conduct performance tests: Evaluate the seals under real-world conditions to assess their durability and effectiveness.
- Analyze feedback: Gather input from your engineering team to make informed decisions based on practical testing.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a preferred supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing clear terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
- Discuss volume discounts: If you plan to order large quantities, inquire about bulk pricing options.
- Clarify delivery expectations: Ensure that both parties agree on delivery timelines and responsibilities to avoid supply chain disruptions.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Partnership
Consider building a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. This partnership can lead to better pricing, enhanced service, and a more streamlined procurement process over time. Regular communication and feedback will help foster a collaborative environment.
- Schedule regular reviews: Periodically assess the supplier’s performance and address any concerns promptly.
- Explore additional services: Ask about value-added services, such as inventory management or technical support, that can further benefit your operations.
By following this checklist, you can ensure a structured and efficient approach to sourcing seal manufacturers, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes and reduced risks.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for seal manufacturers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Seal Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure for seal manufacturers is essential for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials for seals, such as rubber, silicone, and PTFE, vary in cost based on quality and availability. Specialized materials, like those resistant to extreme temperatures or chemicals, command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing and quality control processes. Regions with higher labor costs may affect the overall price of seals, making it essential to consider the geographical context when sourcing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs, allowing for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often required for specific seal designs, which can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should consider whether they need custom solutions, as this can influence initial costs and lead times.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that seals meet industry standards and client specifications incurs costs related to testing and certification. High-quality seals often require more rigorous QC processes, which can increase the final price.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are crucial, especially for international shipments. Factors like shipping method, distance, and import/export regulations can all contribute to the overall cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers gauge whether the pricing is fair based on quality and service.
What Influences Pricing for Seal Manufacturers?
Several factors can influence pricing, making it essential for buyers to understand the nuances:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ): Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom seals tailored to specific applications can increase costs due to the need for specialized materials and tooling. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against standard options.
-
Material Choices: The type and quality of materials used can significantly affect pricing. High-performance materials may offer better longevity and efficiency but come at a premium.
-
Quality and Certifications: Seals that meet stringent industry standards (like ISO certifications) often carry higher price tags. Buyers should evaluate the importance of certifications relative to their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of a supplier can influence pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer companies might offer lower prices to attract business.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can impact total costs, especially for international shipments. Buyers should be aware of responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs to avoid unexpected expenses.
How Can Buyers Negotiate Effectively?
To maximize cost-efficiency, buyers should adopt strategic negotiation tactics:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consider consolidating orders or collaborating with other businesses to increase order volume and negotiate better pricing.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term benefits of quality seals, such as reduced maintenance and failure rates, which can justify a higher initial price.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Comparing quotes from various manufacturers can reveal pricing discrepancies and provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing trends and economic factors that may influence costs, such as currency fluctuations and local tariffs.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time, as trust and reliability develop.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for sealing solutions can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. Buyers should request tailored quotes from manufacturers to obtain accurate pricing reflective of their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing seal manufacturers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Seal Manufacturers: What Are the Options?
When considering sealing solutions, businesses often evaluate multiple options to determine the best fit for their specific applications. Seal manufacturers provide tailored products designed to meet unique sealing requirements, but alternative solutions may also offer viable benefits. This section explores how traditional seal manufacturing compares to other approaches, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Seal Manufacturers | 3D Printing of Seals | Pre-Manufactured Sealing Kits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-performance, custom solutions available | Varies based on printer quality and materials | Standardized performance for common applications |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to customization | Lower initial investment, but material costs can add up | Often lower cost due to mass production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires consultation and order processing | Requires technical expertise to operate printers | Simple to use, ready-to-install solutions |
| Maintenance | Offers ongoing support and replacement options | Maintenance of printers and material handling required | Minimal maintenance needed, ready to use |
| Best Use Case | Complex, unique applications needing precision | Rapid prototyping and low-volume production | Common applications with standardized sizes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing for Seals?
3D printing presents an innovative alternative to traditional seal manufacturing. This method allows for rapid prototyping and on-demand production, which can significantly reduce lead times. However, the quality of the seals produced largely depends on the printer’s capabilities and the materials used. While initial costs may be lower, businesses must consider the expenses associated with maintaining 3D printers and sourcing appropriate materials. This solution is ideal for companies looking to quickly iterate designs or produce low-volume, customized seals.
How Do Pre-Manufactured Sealing Kits Compare to Custom Seal Manufacturing?
Pre-manufactured sealing kits are another alternative that offers convenience and cost-effectiveness. These kits include a variety of standard seals that can be easily installed in common applications. Their primary advantage is the lower cost due to economies of scale in production, making them accessible for many businesses. However, they lack the customization that seal manufacturers provide, which can be a drawback for companies with unique sealing requirements. These kits are best suited for businesses that deal with standard applications and prioritize quick installation.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Sealing Solution?
When selecting the right sealing solution, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs against the strengths and weaknesses of each option. If precision and customization are critical, working with a seal manufacturer may be the best choice. On the other hand, if cost and speed are more pressing, 3D printing or pre-manufactured kits may serve as suitable alternatives. Understanding the application requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities will guide buyers toward the most effective sealing solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for seal manufacturers
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for Seal Manufacturers?
Understanding the technical properties of seals is vital for B2B buyers to make informed decisions. Here are several key specifications that significantly impact the performance and reliability of sealing solutions:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of a seal determines its compatibility with various fluids and gases, as well as its resistance to temperature and pressure variations. Common materials include rubber (e.g., Nitrile, Viton), plastics, and metals. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and preventing seal failure, which can lead to costly downtime in operations. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a seal’s dimensions. It is essential for ensuring that seals fit properly in their designated applications. Tight tolerances are often necessary for high-pressure or precision applications, while looser tolerances may be acceptable in less demanding environments. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers avoid assembly issues that could compromise functionality. -
Durometer Hardness
– This property measures a material’s hardness, typically on a scale from 0 to 100. A higher durometer indicates a harder material, which may be suitable for applications requiring durability and abrasion resistance. Conversely, softer materials provide better flexibility and sealing capability. Buyers must assess the durometer to match the seal’s performance with the application’s requirements. -
Temperature Range
– Each sealing material has a specified temperature range in which it can operate effectively. Exceeding these limits can result in material degradation and seal failure. Buyers must ensure that the seals chosen can withstand the operational temperatures of their applications to maintain reliability and safety. -
Pressure Rating
– The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure a seal can withstand without failing. This specification is vital for applications in hydraulic systems or high-pressure environments. Understanding the pressure rating helps buyers select seals that will not only perform effectively but also enhance the overall safety of the system. -
Chemical Resistance
– Different materials exhibit varying levels of resistance to chemicals. Knowing the chemical compatibility of seals is crucial for applications involving aggressive fluids or gases. This property helps prevent material degradation, leaks, and potential hazards, ensuring that the sealing solution remains effective throughout its operational life.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Seal Manufacturing Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication between buyers and manufacturers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the sealing industry, OEMs often require custom seals to meet specific design criteria. Understanding this term helps buyers identify potential suppliers that can fulfill unique sealing requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases more effectively and avoid excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Buyers use RFQs to compare prices and terms from different manufacturers, ensuring they make cost-effective decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is essential for smooth cross-border purchases of sealing solutions. -
VMI (Vendor Managed Inventory)
– VMI is a supply chain initiative where the supplier manages the inventory levels of their products at the buyer’s location. This approach helps streamline inventory management and reduces the risk of stockouts, ensuring that critical sealing components are always available. -
CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
– CAD refers to software used by engineers and designers to create detailed drawings and specifications for parts, including seals. Understanding CAD capabilities allows buyers to collaborate effectively with manufacturers on custom designs, enhancing the chances of getting the exact sealing solutions they need.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the seal manufacturing landscape more effectively, ensuring they select the right products for their applications while fostering better communication with suppliers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the seal manufacturers Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Seal Manufacturers?
The seal manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global trends. A key factor is the rapid technological advancement in materials and manufacturing processes, which has led to the development of high-performance seals. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide custom solutions tailored to specific applications, reflecting the need for adaptability in diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy. Additionally, the rise of digital tools for inventory management and supply chain optimization is reshaping sourcing strategies, allowing buyers to streamline procurement processes and enhance operational efficiency.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America present unique opportunities for seal manufacturers. As industries in these regions expand, demand for reliable sealing solutions grows. Buyers are looking for manufacturers who can ensure on-time delivery and maintain robust inventory levels to prevent production delays. In Europe, particularly in Germany, there is a strong focus on compliance with stringent quality standards, prompting manufacturers to invest in certifications that assure product reliability and safety.
The global push for sustainability is another critical trend influencing the market. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to eco-friendly practices and materials. This shift not only impacts sourcing decisions but also drives innovation in seal design and manufacturing processes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Seal Manufacturing Industry?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has become a central concern for B2B buyers in the seal manufacturing sector. Ethical sourcing practices are now a prerequisite for many companies, particularly those operating in regions with strict environmental regulations. Buyers are actively seeking manufacturers who utilize sustainable materials and demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
The adoption of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001, signals to buyers that a manufacturer adheres to recognized environmental management standards. Additionally, the use of biodegradable and recyclable materials in seal production is gaining traction. This trend is particularly relevant for industries such as food and beverage, where product safety and sustainability are paramount.
Furthermore, transparency in supply chains is becoming increasingly important. Buyers are demanding to know the origins of materials and the ethical practices of suppliers. This includes ensuring that labor practices meet ethical standards and that suppliers are not contributing to environmental degradation. Manufacturers who can provide clear documentation and certification of their sourcing practices will have a competitive edge in attracting conscientious buyers.
What Is the Historical Evolution of the Seal Manufacturing Sector?
The seal manufacturing sector has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from simple rubber seals to sophisticated sealing solutions tailored for a myriad of applications. Initially, seals were primarily made from natural rubber, but advancements in material science have introduced synthetic options that offer enhanced durability and performance in extreme conditions.
In the 1970s and 1980s, the introduction of advanced polymers and composites revolutionized the industry, allowing for the production of seals that could withstand higher pressures and temperatures. This evolution was further accelerated by the digital transformation in manufacturing, which has enabled precision engineering and custom solutions. Today, seal manufacturers leverage cutting-edge technologies such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) to meet the complex needs of global industries, positioning themselves as essential partners in innovation and efficiency.
In conclusion, international B2B buyers in the seal manufacturing sector must navigate a landscape shaped by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and evolving market dynamics to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of seal manufacturers
-
How do I solve sealing performance issues in my machinery?
To resolve sealing performance issues, first, identify the root cause of the failure. Common problems include improper material selection, incorrect installation, or inadequate maintenance. Collaborate with a trusted seal manufacturer to assess your application requirements, including pressure, temperature, and media compatibility. They can recommend the right sealing materials and designs tailored to your specific needs. Regular inspections and maintenance schedules can further mitigate performance issues and prolong the lifespan of seals. -
What is the best seal type for high-pressure hydraulic applications?
For high-pressure hydraulic applications, O-rings and hydraulic seals made from materials like Nitrile (Buna-N) or Fluoroelastomer (Viton) are often recommended. These materials offer excellent resistance to pressure and temperature variations while maintaining their sealing integrity. It’s crucial to consult with a seal manufacturer who can evaluate your specific application parameters and suggest the most suitable seal type that meets the required pressure ratings and environmental conditions. -
How can I ensure the seals I order meet my quality standards?
To ensure the seals meet your quality standards, request certifications and documentation from the manufacturer, such as ISO 9001 or specific material certifications. Conduct audits or site visits if possible, and consider suppliers who offer quality assurance programs, including testing and validation processes. Establish clear specifications and requirements upfront, and maintain open communication with the manufacturer throughout the production process to address any potential issues promptly. -
What factors should I consider when customizing seals for my application?
When customizing seals, consider factors like the operating environment (temperature, pressure, and media), material compatibility, and design specifications. Collaborate with the manufacturer to identify critical dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements. It’s also essential to discuss lead times and prototyping options to test the custom seals before full-scale production, ensuring they will perform as expected in your specific application. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for seal manufacturers?
Minimum order quantities vary by manufacturer and are influenced by factors such as material type, complexity of the seal design, and production capabilities. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for standard products, while custom seals typically have higher MOQs due to the setup and tooling costs involved. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to find flexible options that accommodate your purchasing volume and budget constraints. -
How do international shipping and logistics work for seal manufacturers?
International shipping for seals typically involves selecting a reliable freight forwarder who understands the specific requirements of your products. Factors to consider include customs regulations, shipping costs, and delivery times. Ensure that the manufacturer provides proper documentation, including invoices and packing lists, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Discuss shipping terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to clarify responsibility for costs and risks during transit. -
What payment terms are common when dealing with seal manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary widely among seal manufacturers but often include options like net 30, net 60, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may require a deposit for custom orders, while others might offer credit terms based on your business relationship. Discuss payment options early in negotiations and ensure they are documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. Be aware of any additional fees for international transactions, including currency conversion and bank charges. -
How can I evaluate potential seal manufacturers before placing an order?
To evaluate potential seal manufacturers, consider their industry experience, client testimonials, and product range. Request samples of their products and assess their quality and performance. Look for manufacturers with robust quality management systems, certifications, and a commitment to customer service. Engaging in preliminary discussions about your specific needs can also provide insight into their expertise and willingness to collaborate on solutions tailored to your application.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for seal manufacturers
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Sealing Solutions?
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical component for businesses looking to optimize their sealing solutions. By fostering strong relationships with reputable seal manufacturers, companies can ensure access to high-quality products tailored to their specific needs. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Key takeaways for international buyers include the importance of evaluating manufacturers based on their capabilities, responsiveness, and inventory management practices. Engaging with suppliers who offer custom solutions and robust support can lead to improved performance and reduced downtime. Furthermore, leveraging partnerships that prioritize on-time delivery and quality assurance will significantly impact your bottom line.
As we look to the future, the sealing industry is poised for innovation, particularly in sectors like renewable energy and advanced manufacturing. Embrace the opportunity to collaborate with forward-thinking manufacturers who can provide cutting-edge solutions for evolving market demands. Take the next step towards optimizing your supply chain and securing your sealing solutions by initiating conversations with trusted seal manufacturers today. Your operational excellence awaits.