Unlock Efficiency: The Complete Fanuc M Code List (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fanuc m code list
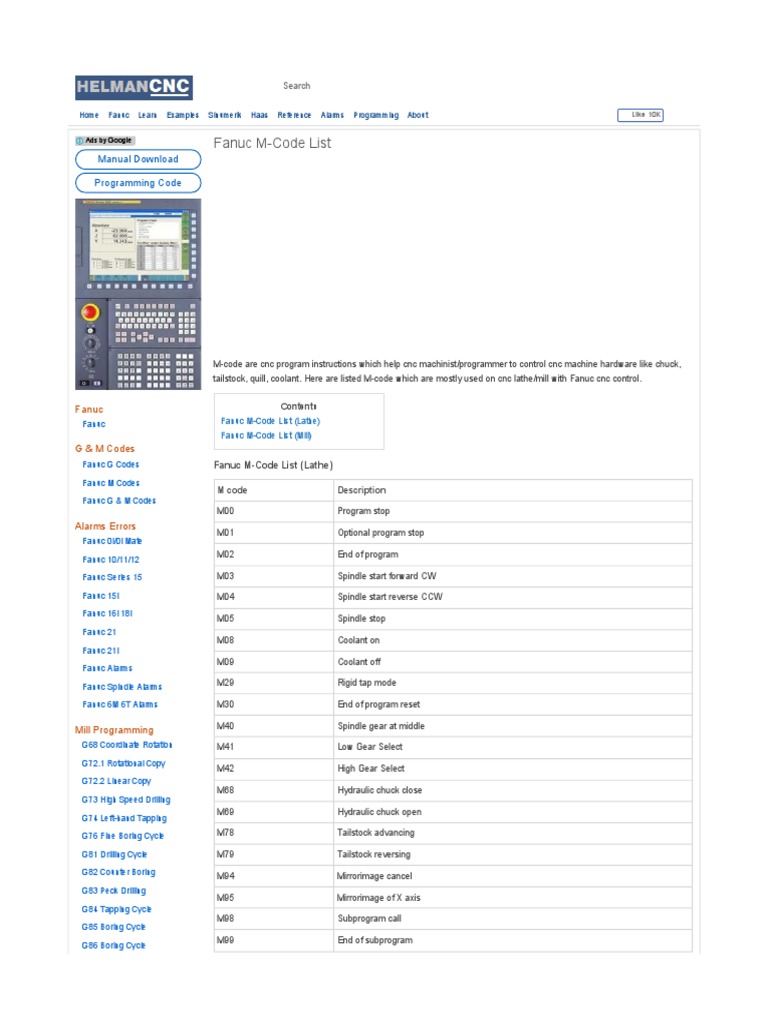
Navigating the global market for the Fanuc M code list can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing advanced CNC machinery and components in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. One of the primary challenges faced by these buyers is understanding the complexities of M codes and their various applications in optimizing CNC machining processes. This guide aims to demystify the Fanuc M code list by providing a comprehensive overview that includes types of codes, their specific applications, and crucial considerations for supplier vetting.
In this guide, you will find an extensive breakdown of the M codes essential for efficient machine operation, including commands that control everything from spindle speed to tool changes and coolant activation. Additionally, we will discuss how to evaluate suppliers based on their expertise and reliability, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions. Cost considerations will also be addressed, allowing buyers to compare options effectively while remaining within budget constraints.
By leveraging the insights and detailed information presented in this guide, international B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of the CNC market, enhance their operational efficiencies, and ultimately drive greater productivity in their manufacturing processes. Whether you are in Saudi Arabia, Spain, or beyond, this resource is tailored to empower your strategic sourcing decisions in the competitive landscape of CNC machining.
Understanding fanuc m code list Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard M Codes | Basic commands for machine operation (e.g., M00, M03, M08) | General CNC machining and milling | Pros: Simple to understand; widely supported. Cons: Limited functionality for advanced tasks. |
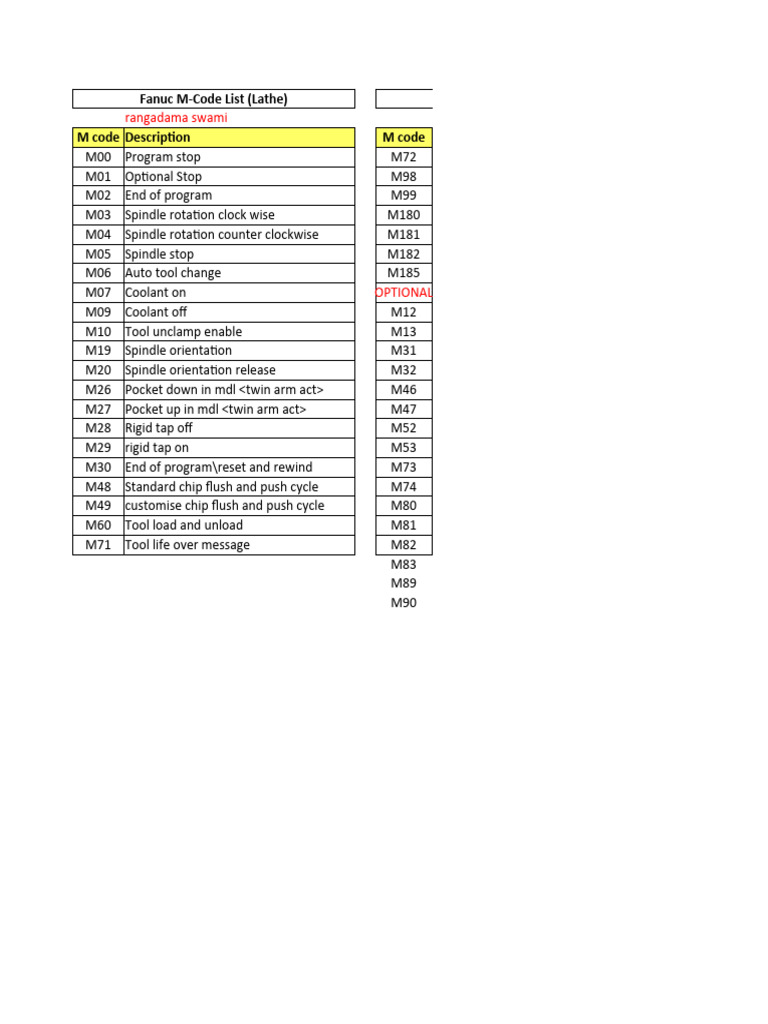
| Lathe M Codes | Specialized for lathe operations (e.g., M29, M40, M41) | Precision turning and threading | Pros: Optimized for lathe tasks; enhances efficiency. Cons: May require specific machine configurations. |
| Mill M Codes | Tailored for milling processes (e.g., M01, M06, M30) | Complex part manufacturing | Pros: Versatile for various milling operations. Cons: Complexity may confuse inexperienced operators. |
| Macro M Codes | Allows for custom programming and repetitive tasks (e.g., M98) | Automated production and CNC programming | Pros: Increases productivity; customizable. Cons: Requires advanced programming skills. |
| Coolant Control M Codes | Manage coolant flow during operations (e.g., M08, M09) | Essential for heat management in machining | Pros: Protects tools and workpieces; enhances machining quality. Cons: Improper use can lead to machine damage. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard M Codes and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Standard M codes are fundamental commands that control the essential functions of CNC machines, such as starting and stopping the spindle, pausing operations, and managing coolant flow. These codes are widely applicable across various CNC machines, making them suitable for general machining and milling operations. B2B buyers should consider investing in equipment that supports these codes for ease of integration and operation, especially if they are new to CNC machining.
How Do Lathe M Codes Enhance Precision in B2B Applications?
Lathe M codes are specifically designed to optimize the performance of lathe machines, focusing on tasks such as threading and turning. These codes, like M29 for rigid tapping and M40 for spindle gear selection, enhance operational efficiency and precision in manufacturing. For B2B buyers in industries requiring high accuracy, such as aerospace or automotive, investing in lathe machines with comprehensive M code support can significantly improve production quality and speed.
What Benefits Do Mill M Codes Offer for Complex Part Manufacturing?
Mill M codes cater to the unique requirements of milling processes, facilitating tasks such as tool changes and program resets. They are essential for manufacturers dealing with complex parts that demand precision and versatility. B2B buyers should evaluate their machining needs and opt for milling machines that incorporate these codes to streamline their operations. However, the complexity of these codes may pose challenges for less experienced operators, so adequate training is recommended.
Why Are Macro M Codes Valuable for Automated Production?
Macro M codes enable advanced programming capabilities, allowing users to create custom routines and automate repetitive tasks. This flexibility can lead to significant productivity gains in a B2B environment, particularly for companies focused on high-volume production. However, buyers should be aware that utilizing macro M codes requires a certain level of programming expertise, which may necessitate additional training or hiring skilled personnel.
How Do Coolant Control M Codes Contribute to Machining Quality?
Coolant control M codes are crucial for managing coolant flow during machining processes, which helps to reduce heat buildup and prolong tool life. Proper coolant management is vital for maintaining machining quality, especially in high-speed operations. B2B buyers should prioritize machines that offer reliable coolant control features to enhance the longevity of their tools and improve overall production efficiency. However, incorrect coolant usage can lead to adverse effects, making it essential to implement proper training and maintenance protocols.
Key Industrial Applications of fanuc m code list
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fanuc m code list | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Manufacturing | Precision machining of aircraft components | High accuracy and repeatability in complex part production | Certification of suppliers and compliance with aviation standards |
| Automotive Industry | Production of engine components and assemblies | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced cycle times | Availability of skilled technicians and after-sales support |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Assembly of circuit boards and electronic enclosures | Improved precision in high-volume production | Compatibility with existing machinery and software |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Fabrication of surgical instruments and implants | Ensures safety and compliance with medical regulations | Quality assurance certifications and traceability |
| Energy Sector | Manufacturing of turbine parts and components | Increased reliability and performance in energy production | Robust supply chain management and logistics capabilities |
What Are the Key Applications of the Fanuc M Code List in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace industry, the Fanuc M code list is crucial for the precision machining of aircraft components. M codes like M06 (tool change) and M03 (spindle on clockwise) enable the automation of complex machining operations, ensuring high accuracy in producing intricate parts such as turbine blades and fuselage components. International buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must prioritize suppliers with certifications in aerospace standards, ensuring that the components meet stringent safety and performance regulations.
How is the Fanuc M Code List Utilized in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive sector extensively employs the Fanuc M code list for the production of engine components and assemblies. M codes facilitate automated processes, such as M08 (coolant on) for efficient machining and M30 (end of program) for seamless operation. This leads to enhanced production efficiency and reduced cycle times, crucial for meeting market demands. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider sourcing from manufacturers that can provide both skilled technicians and robust after-sales support to ensure operational continuity.
What Role Does the Fanuc M Code List Play in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, the Fanuc M code list is essential for the assembly of circuit boards and electronic enclosures. The precise control offered by M codes allows for improved accuracy in high-volume production, which is vital given the miniaturization of electronic components. International B2B buyers must ensure that the machinery they source is compatible with existing systems and software, which can significantly enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
How is the Fanuc M Code List Important in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Medical device manufacturing relies heavily on the Fanuc M code list for fabricating surgical instruments and implants. The use of M codes ensures that machining processes adhere to safety standards, addressing critical regulatory requirements. Buyers from regions such as Africa and Europe should focus on suppliers that provide quality assurance certifications and traceability, as these factors are vital for compliance in the medical sector.
Why is the Fanuc M Code List Relevant in the Energy Sector?
In the energy sector, the Fanuc M code list is used for the manufacturing of turbine parts and components, where precision and reliability are paramount. M codes facilitate the automation of machining processes, enhancing performance and ensuring the durability of energy production equipment. Buyers should evaluate the robustness of the supply chain and logistics capabilities of potential suppliers, as these elements are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in energy production environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘fanuc m code list’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Understanding Machine-Specific M Codes
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face confusion due to the variability of M codes across different Fanuc CNC machine models. For example, a manufacturer in Saudi Arabia might find that the M codes they learned for their Fanuc 0i model differ significantly from those on a Fanuc 21i. This inconsistency can lead to operational errors, increased downtime, and costly mistakes when programming machines, as a lack of understanding can hinder effective communication between operators and technicians.
The Solution:
To mitigate this issue, buyers should prioritize sourcing comprehensive documentation directly from the machine tool builder or authorized distributors. A detailed M code list that specifically pertains to their machine model should be provided during the purchase process. Additionally, investing in training sessions or workshops led by experienced technicians can empower operators to become proficient in using the correct M codes. Utilizing simulation software that mirrors the machine’s functionality can also provide a safe environment for operators to practice and understand the nuances of their specific M codes before actual implementation.
Scenario 2: Incompatibility with Existing Software Systems
The Problem:
B2B buyers from regions like Europe and South America may encounter challenges when integrating their Fanuc M code lists with existing manufacturing execution systems (MES) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. This incompatibility can create workflow disruptions, resulting in inefficiencies and a misalignment between production scheduling and actual machine capabilities. For instance, a factory in Spain might find that their CAD/CAM software does not fully support the M codes required for their newly acquired Fanuc machines, leading to delays in production.
The Solution:
To address this challenge, businesses should conduct a thorough compatibility assessment before purchasing any CNC machinery. It’s crucial to consult with both the CNC machine supplier and the software vendors to ensure that the M codes can be seamlessly integrated into the existing systems. If incompatibilities arise, consider investing in custom software solutions or middleware that can bridge the gap between the CNC machines and the existing software. Regular updates and maintenance of both the CNC firmware and software applications will also ensure ongoing compatibility, which is vital for maintaining operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Lack of Standardization in Programming Practices
The Problem:
In diverse manufacturing environments, particularly in the Middle East and Africa, companies often deal with multiple operators who use varying programming practices for Fanuc M codes. This lack of standardization can lead to inconsistent machining results and quality issues, which can be detrimental to businesses relying on precision engineering. For example, a machining facility in South Africa may find that different operators use different M codes for similar tasks, causing variability in the final products.
The Solution:
Establishing a standardized programming protocol is essential to overcome this hurdle. Companies should develop a comprehensive M code guide that outlines best practices for all operators, ensuring consistency in programming. Regular training sessions should be implemented to reinforce these standards and provide updates on any changes in M codes or programming techniques. Furthermore, integrating a centralized programming system that allows for the storage and sharing of verified M code programs can streamline operations and ensure all operators are on the same page. This approach not only enhances product quality but also fosters a more collaborative work environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fanuc m code list
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Fanuc M Code Applications?
Aluminum is a widely used material in CNC machining due to its excellent properties. It boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where reducing weight is critical. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity, which is beneficial for dissipating heat generated during machining processes. Furthermore, it exhibits corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized, which enhances its durability in various environments.
Pros & Cons of Using Aluminum in CNC Machining
The advantages of aluminum include its lightweight nature, which facilitates faster machining speeds and reduced energy consumption. It is also relatively easy to machine, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries. However, aluminum can be more expensive than other materials like steel, and its lower hardness may lead to wear in high-friction applications. Additionally, while aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it may not be suitable for environments with highly corrosive media without proper treatment.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Fanuc M Code Applications?
Steel is another popular choice for CNC machining, known for its exceptional hardness and tensile strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel is also available in various grades, allowing for tailored properties to meet specific application requirements.
A stock image related to fanuc m code list.
Pros & Cons of Using Steel in CNC Machining
The primary advantage of steel is its durability and resistance to deformation under stress, which is crucial for high-load applications. It is also generally more cost-effective compared to aluminum, particularly in bulk. However, steel is heavier, which can increase machining times and energy costs. Additionally, it is prone to rust if not properly treated, necessitating protective coatings or finishes.
Why is Stainless Steel a Preferred Material for Certain Applications in Fanuc M Code?
Stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. It combines the strength of steel with enhanced resistance to oxidation and staining, which is particularly beneficial in food processing and medical applications.
Pros & Cons of Using Stainless Steel in CNC Machining
The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance requirements due to its corrosion resistance. It is also highly durable and can maintain its integrity under extreme conditions. However, stainless steel is more challenging to machine than aluminum or carbon steel, often leading to higher manufacturing costs and longer lead times. Additionally, its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where reducing mass is essential.
What Are the Considerations for Using Plastics in Fanuc M Code Applications?
A stock image related to fanuc m code list.
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in CNC machining due to their lightweight and versatile properties. They can be engineered to exhibit specific characteristics, such as impact resistance or flexibility, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons of Using Plastics in CNC Machining
The advantages of plastics include their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion, which can be beneficial in specific environments. They are also generally less expensive than metals and can be machined quickly. However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures or loads as well as metals, limiting their application scope. Additionally, they can be more susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Summary Table of Material Properties for Fanuc M Code Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for fanuc m code list | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty machinery parts | Exceptional durability and strength | Heavier, leading to increased machining time | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | More challenging to machine | High |
| Plastics | Non-structural components | Lightweight and versatile | Limited load and temperature resistance | Low |
This analysis provides international B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials most commonly associated with Fanuc M code applications, enabling informed decision-making tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fanuc m code list
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for the Fanuc M Code List?
The manufacturing process for products utilizing the Fanuc M code list involves several critical stages. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to ensure quality and efficiency in their procurement processes.
How Is Material Preparation Conducted in CNC Machining?
The first stage of the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which could range from metals to plastics, depending on the final product specifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers use high-quality materials that meet industry standards, as the integrity of the material directly impacts the final product’s performance and durability.
After selecting the material, it undergoes initial processes such as cutting to size, which can include sawing or shearing. This stage is crucial because any defects in the material can lead to increased waste and additional costs in later stages.
What Techniques Are Used for Forming Components in CNC Machining?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming, where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines take center stage. Using the Fanuc M code list, operators program the machines to execute precise movements along designated axes—typically three to five axes.
Key techniques include:
- CNC Milling: This technique involves the removal of material using rotary cutters. The M codes facilitate operations such as tool changes (M06) and coolant control (M08), ensuring smooth and efficient milling processes.
- Turning: For cylindrical components, turning operations are utilized, where the workpiece rotates against a cutting tool. The M code commands ensure that the spindle operates correctly (M03 for clockwise, M04 for counter-clockwise).
- Drilling and Tapping: Specific M codes are used to manage drilling cycles and tapping operations, allowing for the creation of holes and threads with precision.
How Is Assembly Managed in the Manufacturing Process?
In the assembly stage, components produced through CNC machining are fitted together. This process may involve manual labor or additional automated systems, depending on the complexity of the assembly.
Buyers should be aware of the assembly techniques used by suppliers, as well as any M codes relevant to assembly operations. For example, M codes may be employed to control automated systems that facilitate the assembly of parts, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
What Finishing Techniques Are Essential for Quality Assurance?
Finishing techniques are crucial in enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the final product. These techniques can include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing, plating, or painting may be employed to improve corrosion resistance and appearance.
- Quality Inspection: Before final packaging, products must be inspected for dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
The M code list plays a role here, as certain commands can dictate processes that lead to quality enhancements, such as controlling spindle speeds during finishing operations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA processes in place can significantly impact procurement decisions.
What International Standards Should Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are critical for maintaining quality management systems. Compliance with ISO standards signifies that a manufacturer adheres to best practices in quality assurance, which can lead to fewer defects and higher customer satisfaction.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in oil and gas, can indicate compliance with safety and performance requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC stages include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line. Buyers should request documentation that demonstrates IQC practices, ensuring materials meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor processes and ensure that they conform to specifications. This includes monitoring the execution of M codes to guarantee that machining operations are performed correctly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After the production is complete, final inspections assess whether the finished products meet quality standards. This can involve dimensional checks and functional tests.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s QC practices is essential. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to standards. These audits should assess both manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that demonstrate compliance with international standards. This documentation can include test results, inspection checklists, and certifications.
-
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality assurance practices. These inspectors can verify that the manufacturing processes align with the agreed standards and specifications.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various nuances regarding quality control. Differences in regulatory standards, cultural practices, and logistical challenges can impact the procurement process.
For example, buyers in Saudi Arabia may encounter specific local regulations that differ from those in Spain, necessitating an understanding of regional compliance requirements. Additionally, language barriers can complicate communication with suppliers, making it essential to establish clear specifications and expectations upfront.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their quality standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘fanuc m code list’
In the competitive landscape of B2B manufacturing, sourcing an accurate and comprehensive Fanuc M Code List is essential for optimizing CNC machining operations. This practical guide provides a step-by-step checklist to aid international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe in their procurement process. Following these steps will ensure you select the right resources that align with your technical requirements and operational standards.
1. Identify Your Specific Needs
Before diving into supplier options, clearly define what you need from the Fanuc M Code List. Consider factors such as the type of CNC machines you operate, the complexity of your machining tasks, and any industry-specific requirements. This clarity will help you filter suppliers effectively.
2. Research Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in providing Fanuc M Code Lists. Look for companies that specialize in CNC machinery and have a history of serving clients in your region. Utilize platforms like industry forums, trade associations, and LinkedIn to gather insights and recommendations.
3. Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Verify that potential suppliers meet industry standards and possess relevant certifications. Look for ISO certifications or other quality management systems that indicate a commitment to quality and reliability. This step is crucial as it ensures that you are sourcing from reputable vendors who adhere to best practices.
4. Request Detailed Product Information
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request comprehensive information about their M Code Lists. This should include:
– Compatibility: Ensure that the codes are compatible with your specific Fanuc CNC models.
– Updates: Inquire about how frequently the code lists are updated to reflect new developments in CNC technology.
5. Assess Customer Support and Technical Assistance
A reliable supplier should offer robust customer support. Evaluate their willingness to provide technical assistance, such as troubleshooting or training on using the M Codes effectively. This is particularly important for complex operations where precision is vital.
6. Review Pricing and Payment Terms
Discuss pricing structures and payment terms with potential suppliers. While cost is a significant factor, consider the value offered, including support services and the quality of the M Code List. Ensure that the payment terms align with your financial processes and capabilities.
7. Gather Feedback from Existing Clients
Before making a final decision, reach out to existing clients of the suppliers you are considering. This feedback can provide invaluable insights into the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and customer service. Look for testimonials or case studies that highlight successful implementations of their M Code Lists.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for a Fanuc M Code List, ensuring that they select the best possible options for their CNC machining needs. Making informed decisions will enhance operational efficiency and contribute to long-term success in the manufacturing sector.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fanuc m code list Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a Fanuc M Code List?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing a Fanuc M Code list, several components need to be taken into account:
-
Materials: The cost of materials primarily involves the software and documentation needed to effectively utilize the Fanuc M Codes. While the M Codes themselves are generally part of the machine’s control system, associated training materials, manuals, and software updates may incur additional costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the expenses related to the programming and operation of CNC machines. Skilled machinists or programmers are essential for effective implementation, and their wages can vary significantly by region. For instance, hiring skilled labor in Europe may be more expensive compared to Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and depreciation. Overhead can fluctuate based on the operational scale of the facility and its geographical location. In regions like the Middle East, where energy costs may vary, overhead can significantly influence overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are pertinent to the equipment required to execute the CNC processes dictated by the M Codes. This can include specialized tools for particular tasks or general-purpose tools used across multiple jobs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control measures is crucial to ensure that the outputs meet specified tolerances and standards. The costs associated with QC can include inspection equipment, testing procedures, and potential rework.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs associated with acquiring the necessary materials and tools must be factored in. Incoterms can also influence logistics costs, especially when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on the competitive landscape, volume of orders, and relationships with buyers. Understanding the typical margin in your region can provide leverage during negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Costs for Fanuc M Codes?
Several factors can influence pricing in the sourcing of Fanuc M Codes:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can be beneficial for cost efficiency. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger volumes, which is particularly advantageous for businesses with ongoing CNC machining needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized M Codes or specific programming requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly outline their specifications to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Quality and Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications may come at a premium. Ensure that the supplier’s quality assurance processes align with your operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can also impact pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but can offer superior service and support.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect the final cost. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties is crucial for accurate budgeting.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices on Fanuc M Codes?
International B2B buyers should consider the following tips to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing Fanuc M Codes:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate not just the price, but also payment terms, delivery schedules, and service agreements. This can lead to better overall value.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider long-term costs associated with training, maintenance, and potential downtime due to equipment failures.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing structures due to local market conditions, tariffs, and currency fluctuations. Familiarizing yourself with these nuances can provide a competitive edge during negotiations.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Engage with multiple suppliers to foster competition, which may result in better offers.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of sourcing a Fanuc M Code list requires a comprehensive understanding of cost components and price influencers. By leveraging strategic negotiation techniques and considering the total cost of ownership, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remain aware of the indicative nature of pricing, as costs can fluctuate based on market dynamics and specific buyer requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing fanuc m code list With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to the Fanuc M Code List?
In the world of CNC machining, the Fanuc M Code List is widely recognized as a standard for programming and controlling various machining operations. However, various alternatives exist that may better suit specific operational needs, particularly for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section will explore these alternatives, comparing their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases to help you make an informed decision.
Comparison Table of Fanuc M Code List Against Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Fanuc M Code List | Siemens Sinumerik M Codes | Haas M Code List |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and reliability | Comparable precision; robust features | Good performance; user-friendly |
| Cost | Generally moderate; premium features may increase cost | Similar pricing; cost-effective for large operations | Typically lower initial costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate complexity; requires training | Requires specific training; user manuals available | User-friendly; easy to learn |
| Maintenance | Regular software updates; moderate | Requires trained personnel for maintenance | Low maintenance; easy troubleshooting |
| Best Use Case | Complex machining operations; high volume | Advanced applications; automation | Small to medium-sized enterprises; versatile machining |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Siemens Sinumerik M Codes: A Strong Competitor
Siemens Sinumerik M Codes are an alternative that offers comparable performance to the Fanuc M Code List. These codes are renowned for their advanced features, making them suitable for complex machining tasks that require automation. However, the downside is that they often require specific training and understanding of Siemens systems, which could increase implementation time. For businesses focused on high-end manufacturing, the investment in training may be justified.
Haas M Code List: Cost-Effective and User-Friendly
The Haas M Code List is a popular alternative, especially among small to medium-sized enterprises. Known for its user-friendly interface, the Haas system allows operators to quickly learn and implement machining operations. While the performance may not match the high precision of Fanuc or Siemens, it offers a cost-effective solution for versatile machining needs. Maintenance is typically low, making it a practical choice for businesses looking to minimize downtime. However, for operations that require intricate details and high-volume production, it might fall short.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating alternatives to the Fanuc M Code List, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements and the technical expertise available within their teams. If your operations demand high precision and automation, Siemens Sinumerik M Codes may be the best fit, despite the need for more extensive training. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a cost-effective, user-friendly option, the Haas M Code List could serve your needs well. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing performance, cost, and ease of implementation to meet your unique business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fanuc m code list
A stock image related to fanuc m code list.
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of the Fanuc M Code List?
Understanding the technical specifications of the Fanuc M Code List is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially when evaluating CNC machining capabilities. Here are some of the critical specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Precision and Accuracy
– Definition: Precision refers to the repeatability of a machining process, while accuracy indicates how close the machined part is to the intended design.
– B2B Importance: High precision and accuracy are essential for producing intricate components that meet stringent quality standards. This is particularly vital for industries such as aerospace and automotive, where tolerances are critical. -
Material Compatibility
– Definition: This specification indicates the types of materials that can be effectively machined using the Fanuc M Code protocols.
– B2B Importance: Buyers need to ensure that the CNC machines can handle the specific materials they intend to work with, such as metals, plastics, or composites. Understanding material compatibility helps in selecting the right machines and tools for specific applications. -
Tool Change Speed
– Definition: This property refers to the time taken for the CNC machine to change tools during the machining process.
– B2B Importance: A faster tool change speed leads to reduced cycle times and improved productivity. For businesses looking to optimize production efficiency, understanding this metric is crucial. -
Dwell Time
– Definition: Dwell time is the period for which the machine pauses at a specific point during the machining process.
– B2B Importance: Adjusting dwell time can significantly affect the quality of the final product, especially in operations like drilling or tapping. Buyers should be aware of how dwell time impacts their specific machining needs. -
Axis Configuration
– Definition: This refers to the number of axes available for movement in the CNC machine (e.g., 3-axis vs. 5-axis).
– B2B Importance: The complexity of parts that can be manufactured often depends on the axis configuration. Buyers should assess their production requirements to determine the necessary configurations for efficient machining.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to the Fanuc M Code List?
In addition to technical properties, understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Knowing the OEM can help buyers identify the source of the machinery and the reliability of parts, ensuring that they are acquiring high-quality equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Understanding MOQ is essential for budget management and supply chain efficiency. Buyers need to assess their production needs against the MOQ to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Using RFQs effectively can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and better understand the market rates for CNC machining services. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they define who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby minimizing disputes. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
– Definition: CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools by means of a computer.
– Relevance: Understanding CNC technology is fundamental for buyers as it impacts machining capabilities, quality, and efficiency.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they select the right machinery and suppliers for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the fanuc m code list Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Fanuc M Code List Sector?
The global CNC machining market, driven by increased automation and precision manufacturing, has seen significant growth, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key drivers include the rising demand for customized manufacturing solutions, technological advancements in CNC machinery, and the integration of Industry 4.0 principles. International B2B buyers must stay abreast of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, which enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Moreover, the trend towards collaborative manufacturing is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for partnerships with suppliers who can provide not just machinery but also comprehensive support, including training on Fanuc M codes and G codes. This collaboration is crucial for optimizing production processes, particularly in regions where skilled labor may be scarce.
Sourcing decisions are also influenced by geopolitical factors and economic fluctuations, with international buyers needing to navigate tariffs and trade agreements that affect machine imports. For example, buyers in Saudi Arabia and Spain should consider local regulations and standards when sourcing CNC machinery and components. Staying informed on these market dynamics enables buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Fanuc M Code List Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in B2B sourcing, particularly in the manufacturing sector. The environmental impact of CNC machining, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. Buyers should seek suppliers who prioritize energy-efficient machines and processes, as well as those who actively work to minimize their carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies face increasing scrutiny regarding their supply chains. B2B buyers are advised to partner with manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and possess certifications such as ISO 14001, which emphasizes effective environmental management. Additionally, sourcing materials that are recyclable or derived from sustainable practices can enhance a company’s brand image and appeal to environmentally conscious clients.
In the context of the Fanuc M code list, buyers should also consider the lifecycle of the machinery and the availability of spare parts to reduce overall waste. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, companies not only contribute to a healthier planet but also position themselves favorably in a competitive market increasingly driven by consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Fanuc M Codes and Their Importance in Modern CNC Machining?
The evolution of Fanuc M codes is rooted in the development of CNC technology, which revolutionized manufacturing processes beginning in the late 20th century. Fanuc, a pioneer in CNC technology, introduced M codes as part of their programming language to facilitate machine operations, allowing for enhanced control over various functions such as spindle speed, tool changes, and coolant management.
As CNC machining gained traction, the standardization of M codes enabled greater interoperability between different machine tools, fostering a more efficient production environment. Today, understanding the comprehensive Fanuc M code list is essential for operators and programmers, as it allows for precise control over machining processes, leading to improved accuracy and efficiency.
In the current landscape, where customization and rapid prototyping are paramount, the relevance of M codes continues to grow. As international B2B buyers engage with suppliers across various regions, a thorough understanding of these codes not only aids in operational efficiency but also ensures compliance with local manufacturing standards and practices. This historical context underscores the importance of M codes as foundational elements in the ongoing evolution of CNC machining.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fanuc m code list
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with the Fanuc M code list?
To address compatibility issues, it’s crucial to verify the specific M codes supported by your CNC machine model. Different manufacturers may customize M codes beyond the standard list, particularly for codes above M79. Always consult your machine’s manual or directly contact the manufacturer to confirm the correct M codes for your equipment. Additionally, using simulation software can help identify any discrepancies before executing programs on actual machinery. -
What is the best approach to sourcing Fanuc M code lists for my CNC operations?
The best approach to sourcing a Fanuc M code list is to obtain it directly from reliable suppliers or manufacturers of CNC machines. Consider working with authorized distributors who can provide the latest updates and comprehensive documentation. Additionally, joining industry forums or networks can help you connect with experienced users who may share insights or resources regarding specific M codes relevant to your operations. -
How can I customize M codes for specific machining tasks?
Customizing M codes typically involves programming subroutines or macros that extend the functionality of standard M codes. This requires familiarity with G-code programming and your machine’s capabilities. Consult your CNC machine’s programming manual for guidelines on creating and integrating custom M codes. Partnering with a skilled CNC programmer can also streamline this process, ensuring that your customized codes meet your operational needs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing Fanuc M code lists or related software?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of product. For software or digital resources, many suppliers may not impose an MOQ, allowing for single purchases. However, if you’re ordering physical manuals or training materials, it’s advisable to confirm with your supplier. Always negotiate terms upfront to ensure that your purchasing needs are met without excess inventory. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Fanuc M code lists internationally?
When sourcing internationally, payment terms can vary widely by supplier. Common options include advance payment, net 30/60 days, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to establish clear terms before finalizing any agreement. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks, especially when dealing with new suppliers from regions like Africa, South America, or the Middle East. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing CNC programming resources?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing CNC programming resources, it’s important to choose reputable suppliers with established track records. Request samples or trial periods to evaluate the resources before committing to larger orders. Additionally, consider certifications or endorsements from recognized industry organizations as indicators of quality. Regularly review the performance of the sourced materials in your operations to ensure they meet your standards. -
What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing Fanuc M code lists?
Logistical considerations for importing Fanuc M code lists include understanding customs regulations, shipping times, and associated costs. Ensure that your supplier can provide necessary documentation, such as invoices and customs declarations, to facilitate a smooth import process. Familiarize yourself with local regulations in your country regarding imported digital goods and software. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can also help navigate these logistics effectively. -
How do I verify the credibility of suppliers offering Fanuc M code lists?
Verifying supplier credibility can be accomplished by conducting thorough research. Check for online reviews, ratings, and testimonials from previous customers. Request references or case studies from the supplier to assess their track record. Additionally, ensure that the supplier is compliant with international standards and has relevant certifications. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their professionalism and responsiveness.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fanuc m code list
As global manufacturing continues to evolve, understanding the nuances of the Fanuc M code list becomes increasingly critical for B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Strategic sourcing not only facilitates access to high-quality CNC machinery but also enhances operational efficiency through precise programming capabilities. By leveraging the right M codes, businesses can optimize their machining processes, reduce downtime, and ultimately drive profitability.
International buyers should prioritize collaborating with reputable suppliers who offer comprehensive training and support on M codes to ensure seamless integration into their operations. This approach not only mitigates risks associated with machine operation but also empowers teams with the knowledge needed to maximize their equipment’s potential.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced CNC solutions will only increase. Companies must stay informed about the latest technological advancements and coding practices to remain competitive. Embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to innovation, and take proactive steps to align your purchasing strategy with the evolving landscape of CNC machining. The future is bright for those who adapt and invest wisely in their manufacturing capabilities.