Unlock Efficiency: The Complete Guide to Type-A Plug (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for type-a plug
In today’s interconnected world, sourcing the right type A plug for your business needs can be a daunting task. With varying electrical standards across continents, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe often face challenges in ensuring compatibility and safety. This guide is designed to illuminate the complexities of the global market for type A plugs, providing actionable insights to streamline your purchasing process.
We will explore the intricacies of type A plugs, including their design specifications, applications in diverse industries, and the critical importance of supplier vetting. Additionally, this guide will cover pricing strategies, regulatory compliance, and safety considerations that can significantly impact your procurement decisions. With comprehensive information at your fingertips, you can confidently navigate the landscape of electrical components, ensuring that your business operations remain efficient and reliable.
By empowering international buyers with the knowledge to make informed choices, this guide aims to mitigate risks associated with incompatible electrical systems and subpar products. Whether you’re a distributor looking to stock type A plugs or a manufacturer seeking reliable components, understanding these key aspects will enhance your purchasing strategy, ultimately driving success in your global operations.
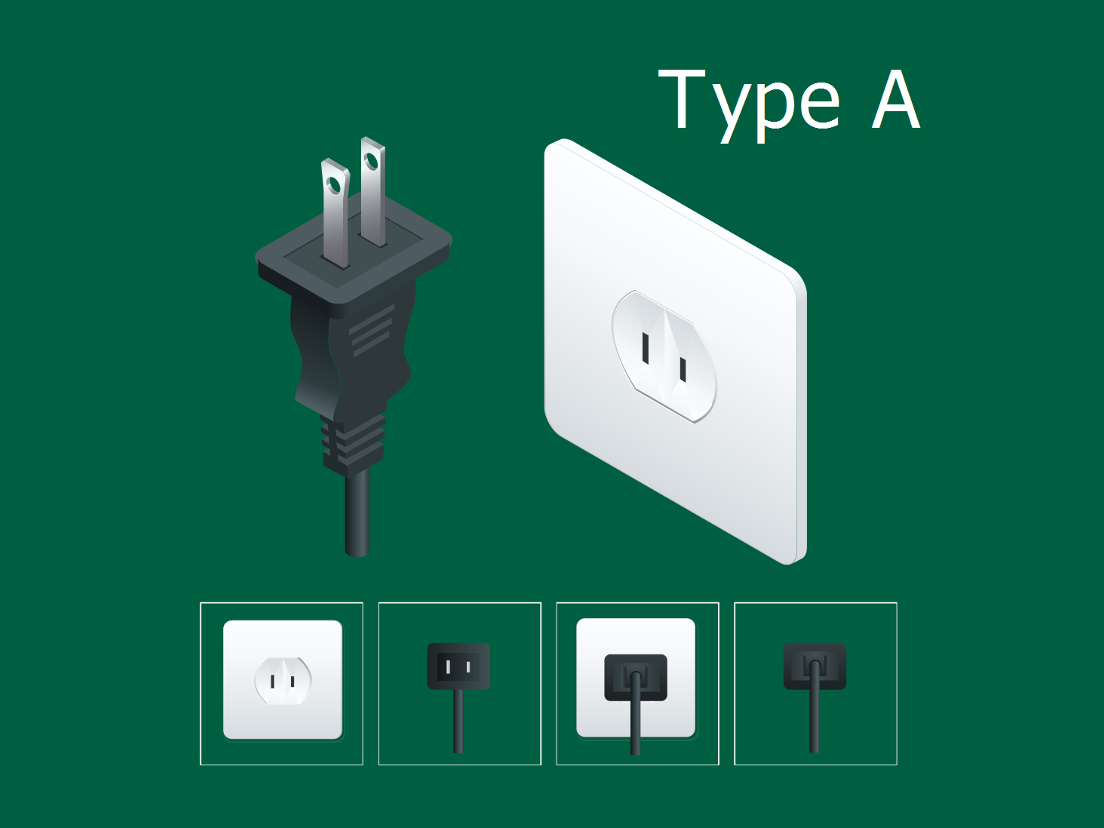
Understanding type-a plug Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA 1-15 | Ungrounded, two flat parallel prongs, polarized | Consumer electronics, appliances in North America | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: No ground protection, less safe for high-power devices. |
| NEMA 5-15 | Grounded, two flat parallel prongs plus a round earth pin | Commercial and industrial equipment, appliances | Pros: Enhanced safety with grounding, versatile. Cons: May not fit into older sockets without modification. |
| Type A (Japanese variant) | Similar to NEMA 1-15 but with equal-width prongs | Electronics, small appliances in Japan | Pros: Compatibility with US outlets, widely used. Cons: Limited grounding, less robust for heavy-duty applications. |
| Type A with locking features | Includes additional features for securing the plug | Vending machines, outdoor equipment | Pros: Prevents accidental disconnections, ideal for high-use environments. Cons: More complex installation, potentially higher cost. |
| Type A with enhanced grip | Features holes in prongs for a tighter fit | Consumer electronics, portable devices | Pros: Better connection stability, reduces wear on sockets. Cons: Not universally compatible, may require specific socket types. |
What are the Key Characteristics of NEMA 1-15 Plugs?
The NEMA 1-15 plug, commonly known as the ungrounded Type A plug, features two flat parallel prongs that are polarized for safety. This plug is primarily used in consumer electronics and small appliances across North America and parts of Central America. When considering B2B purchases, companies should weigh the cost-effectiveness and availability against the lack of grounding, which makes it less suitable for high-power devices or sensitive electronics.
How Does the NEMA 5-15 Plug Enhance Safety?
The NEMA 5-15 plug is the grounded version of the Type A plug, featuring an additional round earth pin. This plug is widely utilized in commercial and industrial settings due to its safety features, allowing for the grounding of devices. B2B buyers should consider this plug for applications where safety is paramount, as it significantly reduces the risk of electrical shock. However, compatibility with older sockets may require modifications, which could entail additional costs.
What Makes the Japanese Type A Plug Unique?
The Japanese variant of the Type A plug closely resembles the NEMA 1-15 plug but features prongs of equal width. This design allows for compatibility with US outlets, making it a versatile choice for businesses operating in both regions. However, like its North American counterpart, it lacks grounding, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. B2B buyers should consider the specific electrical requirements of their devices before opting for this plug.
Why Choose Type A Plugs with Locking Features?
Type A plugs equipped with locking mechanisms are designed for high-usage environments, such as vending machines and outdoor equipment. These plugs prevent accidental disconnections, ensuring a stable power supply. While they provide enhanced security, the installation process may be more complex and could increase initial costs. Businesses should evaluate their operational needs to determine if the investment in locking features is justified.
What Advantages Do Enhanced Grip Type A Plugs Offer?
Enhanced grip Type A plugs include holes in the prongs that allow for a tighter fit in compatible sockets. This feature improves connection stability and reduces wear on both the plug and socket over time. While these plugs are advantageous for portable devices and consumer electronics, their compatibility is not universal, requiring specific socket types. B2B buyers should assess their existing infrastructure to ensure compatibility before purchasing these enhanced grip plugs.
Key Industrial Applications of type-a plug
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of type-a plug | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Powering small appliances and gadgets | Facilitates the use of a wide range of devices | Ensure compliance with local voltage and current ratings |
| Retail and Vending | Connecting vending machines and kiosks | Provides reliable power for self-service solutions | Look for durability in high-traffic environments |
| Office Equipment | Supplying power to computers and peripherals | Enhances productivity by ensuring device functionality | Consider cable length and flexibility for workspace design |
| Hospitality Industry | Charging stations for guests’ devices | Improves guest experience with accessible charging | Focus on safety and compatibility with various devices |
| Manufacturing | Powering light machinery and tools | Increases operational efficiency in production areas | Evaluate the plug’s load capacity and environmental ratings |
What are the Key Applications of Type-A Plugs in Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, type-A plugs are commonly used for powering small appliances and gadgets such as chargers, radios, and laptops. The ungrounded nature of these plugs makes them suitable for devices that do not require a grounding connection. For international B2B buyers, ensuring compliance with local voltage and current ratings is crucial to avoid damage and ensure safety. Additionally, understanding the compatibility of type-A plugs with various devices can streamline procurement processes.
How is the Type-A Plug Utilized in Retail and Vending Applications?
Type-A plugs are essential for connecting vending machines and kiosks, which are prevalent in retail environments. These plugs provide a reliable power source for self-service solutions, enhancing customer convenience. For businesses in Africa and South America, sourcing durable plugs that can withstand high-traffic conditions is vital. Buyers should consider the operational environment, ensuring that the plugs can handle the electrical demands of vending machines while maintaining safety standards.
Why is the Type-A Plug Important for Office Equipment?
In office environments, type-A plugs are often used to supply power to computers and peripherals such as printers and scanners. This plug type enhances productivity by ensuring that essential devices are always functional. B2B buyers should pay attention to cable length and flexibility to accommodate various workspace layouts. Additionally, ensuring that the plugs meet local safety regulations will mitigate risks associated with electrical faults.
What Role Does the Type-A Plug Play in the Hospitality Industry?
The hospitality sector utilizes type-A plugs for charging stations that allow guests to recharge their devices conveniently. This application significantly improves the guest experience, as accessibility to power sources is a critical factor in hotel satisfaction. When sourcing these plugs, businesses should focus on safety and compatibility with a wide range of devices, ensuring that they can accommodate various electronics guests may bring.
How is the Type-A Plug Applied in Manufacturing Settings?
In manufacturing, type-A plugs power light machinery and tools, contributing to increased operational efficiency. These plugs are beneficial in environments where equipment requires a straightforward power connection without the need for grounding. B2B buyers in this sector should evaluate the plug’s load capacity and environmental ratings to ensure they meet the operational demands of their facilities, particularly in regions with varying electrical standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘type-a plug’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Incompatibility with Local Outlets
The Problem: Many B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East often encounter issues with equipment that uses Type A plugs. Due to the prevalence of different plug standards globally, these buyers may find that their devices cannot be plugged into local outlets without an adapter. This creates challenges in operational efficiency, increases downtime, and can lead to potential damage if an incompatible connection is forced.
The Solution: To mitigate compatibility issues, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing products with universal compatibility or consider using Type A plugs in conjunction with high-quality, certified adapters. When making purchases, verify that the devices adhere to international standards and check the voltage requirements to avoid damaging sensitive equipment. It is also advisable to create a centralized inventory of adapters that can be used across various devices, ensuring ease of access and minimizing delays during critical operations. Establishing relationships with reliable suppliers who understand the local electrical standards can further streamline this process.
Scenario 2: Safety Risks with Ungrounded Connections
The Problem: The ungrounded nature of Type A plugs poses significant safety risks, particularly in commercial settings. B2B buyers may find themselves in situations where equipment is at risk of electrical shock due to improper grounding. This is especially concerning in regions with fluctuating electrical currents, as the absence of a ground connection can lead to equipment failure and increase liability for workplace safety.
The Solution: To enhance safety, B2B buyers should consider investing in equipment that either features a grounded Type B plug or utilize plug converters that provide grounding options. It is crucial to conduct a risk assessment of all equipment used in the workplace, focusing on the electrical safety standards in the respective country. Additionally, training employees on the importance of using grounded plugs and the potential hazards of ungrounded connections can promote a culture of safety. Engaging with local electrical safety consultants can also provide insights into best practices for grounding and wiring in commercial environments.
Scenario 3: Voltage Compatibility Issues
The Problem: Voltage discrepancies can severely impact the functionality of devices using Type A plugs. Many buyers importing equipment from regions like North America may overlook that their local voltage standards differ—often being higher in countries across Europe and Africa. This oversight can lead to equipment failure, warranty voids, and costly repairs, especially when equipment is not rated for the local voltage.
The Solution: Before making any purchase, B2B buyers should thoroughly research the voltage requirements of all devices and ensure they are compatible with local standards. Utilizing voltage converters can be an effective short-term solution, but it is best to procure equipment designed for the specific voltage of the operating region. Establishing a checklist for voltage and plug type compatibility during the procurement process can help avoid errors. Furthermore, partnering with suppliers who have a deep understanding of international electrical standards can provide added assurance and access to reliable equipment suited for the buyer’s specific needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for type-a plug
What Are the Key Materials for Type-A Plugs?
When selecting materials for type-A plugs, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of type-A plugs: thermoplastics, thermosetting plastics, copper, and brass.
How Do Thermoplastics Affect Type-A Plug Performance?
Key Properties: Thermoplastics, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or nylon, exhibit excellent electrical insulation properties, high impact resistance, and good thermal stability. They can withstand temperatures up to 85°C (185°F) and are resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of thermoplastics is their lightweight nature and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for mass production. However, they may not be as durable as other materials under extreme conditions, leading to potential wear over time.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are ideal for residential use where moderate electrical loads are expected. However, they may not be suitable for industrial applications requiring higher durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure compliance with local electrical safety standards, such as IEC or ASTM, when selecting thermoplastic components.
What Role Does Thermosetting Plastic Play in Plug Manufacturing?
Key Properties: Thermosetting plastics, like epoxy and phenolic resins, offer superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 150°C (302°F). They are also highly resistant to deformation and chemical corrosion.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of thermosetting plastics is their durability and stability under high temperatures, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, they are more expensive and complex to manufacture compared to thermoplastics.
Impact on Application: These materials are particularly beneficial in environments where plugs are subjected to high electrical loads or extreme temperatures, such as industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like DIN or JIS is crucial, especially for buyers in regions with stringent electrical safety regulations.
Why Are Copper and Brass Commonly Used in Type-A Plugs?
Key Properties: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, with high thermal and electrical conductivity. Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers good corrosion resistance and strength.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of using copper and brass is their superior conductivity, which ensures efficient power transfer. However, these metals can be more expensive and may require additional treatments to prevent corrosion.
Impact on Application: Copper and brass are ideal for high-performance applications where efficient electrical conduction is critical. They are commonly used in plugs designed for heavy-duty electrical equipment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for metal components in different regions. For instance, compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is essential in Europe.
Summary of Material Selection for Type-A Plugs
When selecting materials for type-A plugs, international B2B buyers must weigh the benefits and limitations of each material against their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements. Understanding these factors will aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for type-a plug | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastics | Residential plugs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
| Thermosetting Plastics | Industrial plugs | High heat resistance | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Copper | Heavy-duty electrical equipment | Superior electrical conductivity | Higher cost and potential corrosion | Med |
| Brass | High-performance applications | Good corrosion resistance | Expensive and requires treatment | Med |
This table provides a concise overview of the materials analyzed, helping B2B buyers make strategic decisions tailored to their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for type-a plug
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Type-A Plugs?
The manufacturing of Type-A plugs involves several critical stages that ensure both the functionality and safety of the final product. This process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
A stock image related to type-a plug.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves selecting high-quality materials such as thermoplastic for the casing and copper for the prongs. These materials are essential for durability and conductivity. Suppliers should verify that the raw materials meet international standards to ensure safety and performance.
-
Forming: The forming stage includes processes like stamping and injection molding. Stamping machines cut the copper into the required shapes for the prongs, while injection molding machines shape the plastic casing. Precision in this stage is crucial to maintain uniformity and compliance with specifications.
-
Assembly: During assembly, the prongs are inserted into the plastic casing, and internal components like springs and contacts are added. Automated assembly lines are often used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves quality checks and surface finishing processes such as plating to prevent corrosion. Aesthetic aspects, including branding and labeling, are also applied during this phase.
How Is Quality Assurance Ensured in Type-A Plug Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of Type-A plugs to guarantee safety and compliance with international standards. Key QA practices include adherence to international standards like ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific certifications such as CE and UL.
-
International Standards: ISO 9001 sets the framework for a quality management system (QMS) that ensures consistent product quality. Manufacturers should maintain documented procedures and records to demonstrate compliance.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) indicate that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. For B2B buyers, verifying these certifications is essential for ensuring that the plugs can be legally sold in their respective markets.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints During the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects and ensure adherence to specifications. These include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should conduct tests to verify that materials meet specified criteria, such as conductivity and thermal resistance.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC checks are performed at various stages to monitor quality. This may involve measuring dimensions, checking assembly integrity, and testing for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before the products are packaged and shipped. This includes electrical testing to ensure that the plugs meet safety standards and function as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Type-A Plugs?
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality and safety of Type-A plugs:
-
Electrical Testing: Tests such as dielectric strength and insulation resistance are conducted to ensure that the plugs can handle the required voltage and prevent electrical shocks.
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes pull tests to measure the strength of the prongs and casing. Manufacturers often conduct durability tests to simulate wear over time.
-
Temperature and Humidity Testing: Plugs are subjected to extreme temperature and humidity conditions to assess their performance under various environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control measures of suppliers. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, equipment, and quality control practices in real-time. This can provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s performance history. These reports should outline testing results, defect rates, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and final products. This is particularly important for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where local regulations may differ.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing Type-A plugs, international B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have specific regulatory requirements. For example, products sold in Europe must comply with CE marking, while those in North America may require UL certification. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with these regulations.
-
Documentation: Buyers should request comprehensive documentation, including certificates of compliance, test reports, and manufacturing process details. This information is crucial for demonstrating compliance to local authorities.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can help facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships. Buyers should be aware of varying expectations regarding quality assurance and communication styles.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for Type-A plugs is essential. By focusing on key manufacturing stages, quality control checkpoints, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes and ensure product safety and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘type-a plug’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing Type A plugs effectively, this checklist outlines essential steps to follow. These actions will ensure you procure quality products that meet your specific needs while navigating the complexities of international trade.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin sourcing, it’s crucial to clearly outline your technical requirements for Type A plugs. Consider factors such as voltage, current rating (typically 15A for Type A), and the specific design features you require, such as polarized prongs. Knowing these specifications upfront helps in filtering suppliers who can meet your needs.
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure that the plugs are suitable for the voltage in your target market (generally 120V in the US).
- Material Requirements: Decide whether you need plastic or metal housing, which can affect durability and safety.
Step 2: Research Market Standards and Regulations
Understanding the regulatory landscape is essential when sourcing electrical components. Each country may have specific standards for safety and performance that Type A plugs must meet.
- Compliance Certification: Look for certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or CE (Conformité Européenne) that indicate compliance with safety standards.
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local electrical codes in your target regions, especially if you are importing into Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This step mitigates risks associated with quality and reliability.
- Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews and ratings to gauge the supplier’s reliability.
- Production Capacity: Ensure the supplier can meet your volume needs without compromising quality.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of the Type A plugs you intend to purchase. This allows you to assess the quality and functionality firsthand.
- Quality Assessment: Inspect the samples for build quality, compliance with specifications, and any safety features.
- Testing: If possible, conduct electrical tests to ensure they meet the required performance standards.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms that suit both parties. Discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery timelines to avoid potential misunderstandings.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures based on order volume to optimize your costs.
- Payment Security: Consider payment methods that offer protection, such as letters of credit or escrow services.
Step 6: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once negotiations are complete, ensure that all agreements are documented in a formal contract. This should include all terms discussed, including warranties and return policies.
- Legal Review: Have a legal expert review the contract to ensure compliance with international trade laws.
- Clear Terms: Specify delivery timelines, quality assurance processes, and penalties for non-compliance.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Consider the logistics involved in shipping Type A plugs from the supplier to your location. This includes shipping methods, customs clearance, and warehousing.
- Shipping Options: Evaluate various shipping methods (air, sea, land) based on cost and urgency.
- Customs Regulations: Ensure that you understand and comply with the customs requirements in your country to avoid delays.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for Type A plugs, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for type-a plug Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Type-A Plug Sourcing?
When sourcing Type-A plugs, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary materials used in Type-A plug production include high-quality plastic for insulation, copper for the prongs, and sometimes brass for better conductivity. The choice of materials affects both performance and durability, impacting overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region of production. Countries with lower labor costs may offer cheaper plugs, but this might compromise quality. In contrast, manufacturers in regions like Europe may charge more due to higher labor standards and wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient factories can reduce overhead costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial costs for molds and tooling can be high, especially for custom designs. Buyers should consider these costs when assessing the overall price, particularly for large orders or unique specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the plugs meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Certifications such as UL or CE can add to the price but are crucial for ensuring compliance, especially in regulated markets.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location, the shipping method, and current freight rates. Understanding these factors can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their risks and profit. The margin can vary based on the supplier’s reputation, market demand, and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Type-A Plug Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of Type-A plugs, and understanding these can help buyers negotiate better deals:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to optimize order sizes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as additional safety measures or branding, can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate if these enhancements justify the additional expense.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can lead to higher prices. Buyers need to balance quality with cost, especially for applications requiring high reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities play a significant role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for determining who bears the costs and risks during transportation. This knowledge can influence the total landed cost of the plugs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing a long-term partnership can lead to better deals over time.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, warranty, and replacement costs to assess the true value of the plugs.
-
Stay Informed About Pricing Nuances: Keep abreast of market trends and fluctuations in raw material prices, which can directly impact plug costs. Being informed allows for better timing in purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Regional Differences: Different regions may offer varying prices for similar products. Assessing potential suppliers across different countries can yield significant savings.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for Type-A plugs can fluctuate based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotations to ensure they are getting the best deal suited to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing type-a plug With Other Solutions

A stock image related to type-a plug.
When evaluating the Type-A plug, it’s crucial for international B2B buyers to consider alternative solutions that may better fit their specific operational needs. This analysis will compare the Type-A plug with other viable options, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses make informed decisions when sourcing electrical solutions for their operations.
| Comparison Aspect | Type-A Plug | Alternative 1: Type-C Plug | Alternative 2: Universal Socket |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited to 15A, ungrounded | Supports up to 16A, grounded | Supports various plug types |
| Cost | Low manufacturing cost | Slightly higher cost | Higher initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple design, widely available | Requires specific sockets | Requires adapters for some plugs |
| Maintenance | Minimal, but safety concerns | Low, generally safe | Moderate, depends on plug types |
| Best Use Case | Basic household devices | Appliances needing grounding | Multi-national operations |
What Are the Benefits of Using Type-C Plugs as an Alternative?
The Type-C plug, commonly used in Europe and other regions, is a notable alternative to the Type-A plug. It supports higher current ratings (up to 16A) and features a grounding pin, enhancing safety for users and devices. The design is more robust, and it accommodates a wider range of appliances, making it suitable for international businesses that operate in regions with different standards. However, the initial cost for Type-C sockets can be higher, and their installation may require more effort, especially in older buildings.
How Do Universal Sockets Compare with Type-A Plugs?
Universal sockets offer a flexible solution that can accommodate various plug types, including Type-A, Type-C, and others. This versatility is particularly beneficial for businesses with multinational operations, as it reduces the need for multiple adapters. However, the upfront investment for universal sockets is higher, and they may require more maintenance due to their complexity. Additionally, the performance can vary based on the type of plug used, which may lead to concerns about compatibility and safety.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Plug Solution?
When selecting the right plug solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, the types of devices they will be using, and the regions in which they operate. While the Type-A plug is cost-effective and simple, alternatives like the Type-C plug and universal sockets may provide enhanced safety and flexibility. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation and maintenance, alongside the operational requirements will guide buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business strategies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for type-a plug

A stock image related to type-a plug.
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Type-A Plugs?
Understanding the technical properties of Type-A plugs is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from or supplying to regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are the key specifications:
What Are the Key Specifications of Type-A Plugs?
-
Material Composition
Type-A plugs are typically made from high-grade thermoplastics and metal alloys. The thermoplastics provide durability and insulation, while the metal components ensure reliable conductivity. Choosing plugs made from robust materials is essential for minimizing electrical failures and enhancing product longevity. -
Pin Dimensions and Configuration
The Type-A plug features two flat parallel pins, each measuring approximately 1.5 mm thick and 15.9 to 18.3 mm long. The design is often polarized, with one pin wider than the other to ensure correct insertion. This configuration is vital for safety and operational efficiency, as it prevents incorrect connections that could lead to electrical hazards. -
Current Rating
Type-A plugs are rated for a maximum current of 15 A. This rating indicates the plug’s capability to handle electrical loads without overheating. For businesses, understanding current ratings is crucial for ensuring compatibility with electrical devices and avoiding potential damages or safety risks. -
Voltage Compatibility
These plugs are designed to operate with voltages typically around 120V, common in North America. Buyers must ensure that the voltage ratings of the plugs match their intended application to prevent equipment failure and maintain operational safety. -
Polarization and Safety Features
The polarized design of Type-A plugs enhances safety by ensuring that the live and neutral connections are correctly aligned. This feature is particularly important for devices that are sensitive to electrical polarity, thus reducing the risk of shock and equipment damage.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation effectiveness in B2B transactions involving Type-A plugs. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of Type-A plugs, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source reliable products tailored to specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to plan their inventory and budget accordingly, especially when dealing with specialized electrical components like Type-A plugs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products. For international buyers, preparing an RFQ for Type-A plugs ensures they receive competitive pricing and can compare offers from multiple suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risk management, and delivery timelines when purchasing Type-A plugs across borders. -
CE Marking
CE marking indicates that a product complies with European safety standards. For buyers in Europe, ensuring that Type-A plugs have CE marking is critical for legal compliance and product safety. -
RoHS Compliance
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) compliance ensures that electrical products do not contain harmful materials. This is increasingly important for buyers looking to meet regulatory standards and promote sustainability in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring that they acquire Type-A plugs that meet both safety and performance standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the type-a plug Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Type-A Plug Sector?
The global market for Type-A plugs is influenced by several key drivers, including the rapid expansion of the electronics sector and increased demand for international compatibility in power supplies. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in technology adoption, which translates into a higher need for reliable and versatile power connections. International B2B buyers are particularly focused on sourcing Type-A plugs that not only meet local standards but also ensure compatibility with devices manufactured in regions that utilize this plug type, such as North America and Japan.
Emerging trends include the growing emphasis on smart technology integration within electrical components. With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), buyers are looking for Type-A plugs that can accommodate smart features, such as energy monitoring and remote control capabilities. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a significant factor in purchasing decisions, with many companies seeking suppliers who can offer eco-friendly options without compromising on quality and safety standards.
Furthermore, the competitive landscape is shifting, with an increasing number of manufacturers in emerging markets offering competitive pricing and innovative designs. This trend presents a dual challenge and opportunity for international buyers: while they can benefit from lower costs, they must also ensure that these products meet the required safety and performance standards to avoid potential liabilities.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Type-A Plugs?
The environmental impact of electrical components, including Type-A plugs, is gaining attention from international B2B buyers. The production of plugs often involves materials that can be harmful to the environment if not sourced and disposed of responsibly. As a result, buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is crucial, as companies face pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to ensure their supply chains are environmentally friendly. Buyers should look for manufacturers that utilize recyclable materials, adhere to stringent waste management practices, and have certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, certifications related to energy efficiency can be beneficial, as they indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to reducing the carbon footprint of their products.
Incorporating ‘green’ materials into the production of Type-A plugs not only addresses environmental concerns but can also enhance brand reputation. Buyers who emphasize sustainability can appeal to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers and businesses, positioning themselves as leaders in responsible sourcing practices.
What is the Historical Context of Type-A Plugs Relevant to B2B Buyers?
Type-A plugs have a rich history that dates back to their invention by Harvey Hubbell II in 1904. Initially designed for use in North America, these plugs were created to facilitate the growing demand for electrical appliances. Over the decades, the Type-A plug has evolved to meet the changing needs of consumers and technological advancements.
Significantly, the introduction of regulations has shaped the design and safety features of Type-A plugs. For instance, the ungrounded nature of Type-A plugs (NEMA 1-15) has led to concerns regarding safety in modern applications, prompting manufacturers to innovate. This historical context is important for B2B buyers as it highlights the ongoing need for compliance with safety standards and the potential for new designs that incorporate grounding features, thus enhancing safety and usability in diverse applications.
Understanding the evolution of Type-A plugs enables buyers to make informed decisions about sourcing products that not only meet current market demands but also anticipate future trends in electrical safety and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of type-a plug
-
How do I solve compatibility issues with Type-A plugs in international markets?
When sourcing Type-A plugs for international distribution, ensure that you understand the specific electrical standards and plug configurations of the target countries. Different regions may have variations in voltage and amperage ratings. Utilize plug adapters or invest in multi-standard products that can accommodate various types of sockets. Additionally, consider partnering with local distributors who have a thorough understanding of the market, as they can provide insights into customer preferences and regulatory compliance. -
What is the best way to vet suppliers for Type-A plugs?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation and certifications. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications or compliance with relevant electrical safety standards, such as UL or CE markings. Request samples to evaluate product quality and assess their ability to meet your specifications, including customization options. Additionally, seek references from other businesses that have previously worked with the supplier to gauge reliability and responsiveness. -
What customization options are available for Type-A plugs?
Customization options for Type-A plugs can include variations in color, branding, and specific electrical specifications like voltage ratings and prong designs. Some manufacturers may offer the ability to add features such as surge protection or waterproofing, depending on the intended use of the plugs. Discuss your requirements early in the negotiation process to understand the supplier’s capabilities and limitations regarding customization. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for Type-A plugs?
Minimum order quantities for Type-A plugs can vary significantly by supplier and the complexity of the product. Typically, MOQs range from 1,000 to 10,000 units, especially for customized orders. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about the possibility of smaller trial orders or bulk discounts to optimize your inventory management and reduce upfront costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing Type-A plugs internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s location and your relationship with them. Common terms include full payment upfront, a deposit followed by a balance on delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days). Consider using secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to mitigate financial risk. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for Type-A plugs?
To ensure quality assurance, implement a multi-step inspection process that includes pre-production samples, in-process inspections, and final product evaluations. Collaborate with suppliers who have established quality management systems and are willing to provide inspection reports. Additionally, consider third-party quality control services to conduct audits and checks before shipment, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing Type-A plugs?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Determine whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable based on your urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with the customs requirements of the importing country, including tariffs and duties. Partnering with a reliable logistics provider can streamline the shipping process, ensuring that your products arrive on time and in compliance with local regulations. -
How do I handle after-sales support for Type-A plugs?
After-sales support is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction. Establish clear communication channels for customers to report issues or seek assistance. Provide detailed product manuals and warranty information to facilitate troubleshooting. Additionally, consider setting up a dedicated customer service team or outsourcing support to manage inquiries effectively. Proactively addressing potential problems can enhance your brand reputation and foster long-term customer loyalty.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for type-a plug
In summary, strategic sourcing for Type A plugs presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the unique specifications and applications of Type A plugs—such as their ungrounded design and compatibility with various devices—can enhance procurement strategies. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable manufacturers to ensure compliance with safety standards and to mitigate risks associated with ungrounded electrical connections.
As markets evolve, the demand for reliable and efficient electrical solutions will continue to grow. Buyers are encouraged to leverage partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate innovation in product development and reliability in delivery. By adopting a strategic sourcing approach, businesses can not only enhance their operational efficiency but also position themselves for future growth in a competitive landscape.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for international buyers to stay informed about global sourcing trends and regulatory changes affecting the use of Type A plugs. Engaging with industry experts and participating in trade forums can provide invaluable insights that drive informed decision-making. Take action today to optimize your sourcing strategy and secure a competitive edge in your market.