Unlock Efficiency: The Ultimate Electric Motor Diagram Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric motor diagram
Navigating the complex landscape of the global market for electric motor diagrams can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the nuances of sourcing electric motor diagrams is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with operational needs and budget constraints. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the various types of electric motors, their applications across different industries, and essential supplier vetting processes.
By delving into the intricacies of electric motor diagrams, buyers will gain insights into how these components function and their significance in converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. We will also explore cost considerations, helping businesses in countries such as Argentina and Brazil to optimize their procurement strategies.
Arming international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide aims to enhance understanding and facilitate better decision-making in sourcing electric motor diagrams. Whether you are looking to upgrade existing equipment or invest in new technology, the information provided will empower you to navigate the global market with confidence and clarity, ensuring that you choose the right solutions for your operational goals.
Understanding electric motor diagram Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Motors | Operate on direct current; simple construction; speed control via voltage. | Robotics, automotive, and small appliances. | Pros: Easy to control speed; Cons: Less efficient for large-scale applications. |
| AC Motors | Use alternating current; more efficient for high power applications; can be synchronous or asynchronous. | Industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and pumps. | Pros: High efficiency; Cons: More complex control systems required. |
| Stepper Motors | Precise control of angular position; operate in discrete steps. | CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics. | Pros: High precision; Cons: Limited speed and torque. |
| Brushless DC Motors | No brushes; higher efficiency and longer lifespan; typically quieter. | Electric vehicles, drones, and HVAC fans. | Pros: Low maintenance; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Three-Phase Motors | Requires three-phase power supply; more power and torque; common in industrial settings. | Heavy machinery, conveyors, and compressors. | Pros: Higher efficiency and power output; Cons: Requires specialized wiring and setup. |
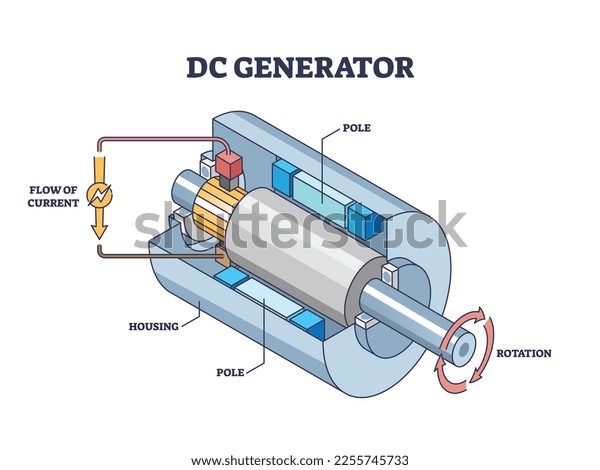
What Are the Characteristics of DC Motors?
DC motors are characterized by their simplicity and ease of speed control through voltage adjustments. They are commonly found in applications such as robotics and small appliances, making them ideal for businesses that require straightforward motion control solutions. When purchasing DC motors, buyers should consider their voltage requirements and whether they need a brushed or brushless design, as the latter offers greater efficiency and longevity.
How Do AC Motors Differ from Other Types?
AC motors utilize alternating current and are known for their efficiency in high-power applications, including industrial machinery and HVAC systems. They can be classified into synchronous and asynchronous types, which affects their performance in various scenarios. Buyers should evaluate their power supply capabilities and application needs, as AC motors often require more complex control systems but deliver superior efficiency for large-scale operations.
What Makes Stepper Motors Ideal for Precision Applications?
Stepper motors are distinct for their ability to achieve precise control over angular positions, making them suitable for applications like CNC machines and 3D printers. These motors operate in discrete steps, which allows for accurate positioning without the need for feedback systems. B2B buyers should assess the required precision and speed of their applications, as stepper motors may face limitations in high-speed scenarios.
Why Consider Brushless DC Motors?
Brushless DC motors stand out due to their lack of brushes, which enhances efficiency and extends lifespan while reducing noise levels. They are often used in electric vehicles and drones, where performance and reliability are critical. Buyers should weigh the higher initial costs against the long-term benefits of lower maintenance and operational costs, particularly in demanding applications.
What Are the Advantages of Three-Phase Motors?
Three-phase motors are designed for heavy-duty applications, providing more power and torque than single-phase motors. Commonly used in industrial settings, they require a three-phase power supply, which can complicate installation. For businesses involved in manufacturing or heavy machinery, investing in three-phase motors can lead to significant efficiency gains, but careful consideration of the power infrastructure is essential.
Key Industrial Applications of electric motor diagram
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Motor Diagram | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs. | Reliability of motor, energy efficiency ratings, and support services. |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Pumps | Ensures consistent water supply, improving crop yields. | Durability in harsh environments and compatibility with local power supply. |
| Transportation | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Reduces operational costs and environmental impact. | Compliance with international standards and availability of service parts. |
| HVAC Systems | Air Conditioning Units | Enhances energy efficiency, leading to cost savings. | Motor size, energy consumption ratings, and warranty terms. |
| Mining | Drilling Equipment | Increases extraction efficiency and reduces downtime. | Motor power ratings, resistance to extreme conditions, and after-sales support. |
How Is the Electric Motor Diagram Used in Manufacturing Conveyor Systems?
In manufacturing, electric motors are integral to conveyor systems, which facilitate the movement of materials and products. The electric motor diagram serves as a blueprint for understanding the motor’s components, including the rotor, stator, and power supply connections. This clarity helps manufacturers optimize their conveyor designs for efficiency and maintenance. By implementing reliable electric motors, companies can enhance production efficiency, minimize labor costs, and ensure smooth operational flow. For international buyers, it’s crucial to consider the motor’s reliability and energy efficiency ratings, as well as the availability of local support services.
What Role Do Electric Motors Play in Agriculture Irrigation Pumps?
Electric motors are vital in powering irrigation pumps, ensuring a consistent water supply for agricultural operations. The electric motor diagram assists farmers in comprehending the motor’s mechanics and how it integrates with the pump system. This understanding allows for better selection of motors that can withstand the rigors of agricultural environments. By utilizing efficient motors, farmers can significantly improve crop yields and optimize water usage. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize durability and compatibility with local power supplies when sourcing these motors.
How Are Electric Motors Utilized in Transportation Electric Vehicles?
In the transportation sector, electric motors are the heart of electric vehicles (EVs), converting electrical energy into mechanical power. The electric motor diagram helps engineers and manufacturers visualize the motor’s structure and operation, essential for developing efficient EVs. This application leads to reduced operational costs and a lower carbon footprint for businesses. International buyers must ensure compliance with regional standards and consider the availability of service parts to support long-term vehicle maintenance and efficiency.
How Do Electric Motors Enhance HVAC Systems?
Electric motors are crucial for HVAC systems, driving compressors and fans that regulate indoor climates. The electric motor diagram provides insight into the motor’s components and their functions, aiding in the design and troubleshooting of HVAC systems. Efficient motors contribute to lower energy consumption and operational costs, making them a key investment for businesses. Buyers should focus on motor size, energy consumption ratings, and warranty terms to ensure they are making informed decisions when sourcing motors for HVAC applications.
What Importance Do Electric Motors Hold in Mining Drilling Equipment?
In mining, electric motors power drilling equipment, significantly enhancing extraction efficiency. The electric motor diagram is essential for understanding the motor’s integration with drilling machinery, allowing for better maintenance and operational strategies. Efficient motors reduce downtime, which is critical in the high-stakes mining industry. For international buyers, sourcing considerations should include motor power ratings, resistance to extreme conditions, and the availability of after-sales support to ensure optimal performance in challenging environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric motor diagram’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Motor Performance Due to Wiring Misunderstandings
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter issues with electric motor performance stemming from misinterpretations of wiring diagrams. In complex setups, particularly with three-phase motors, incorrect wiring can lead to reduced efficiency, overheating, or even catastrophic failure. Buyers may struggle with understanding how to connect the motor correctly, especially when multiple diagrams are available for similar models. This confusion is particularly prevalent among teams with limited technical knowledge or in regions where training resources are scarce.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, it’s crucial to always refer to the wiring diagram provided on the motor nameplate. This diagram is tailored specifically for the motor in question and outlines the correct connections for optimal performance. Buyers should invest in training sessions for their technical teams to understand these diagrams thoroughly. Utilizing online resources, such as instructional videos or webinars that demonstrate the wiring process, can also enhance comprehension. Additionally, creating a standardized procedure for checking wiring against the nameplate diagram before installation can mitigate risks and ensure consistency in motor performance.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing High-Quality Electric Motor Diagrams
The Problem: International B2B buyers often struggle to find reliable and high-quality electric motor diagrams that match their specific requirements. This difficulty can stem from the vast array of motor types and manufacturers, leading to potential mismatches between diagrams and the actual motors used in their applications. In regions such as Africa and South America, where access to technical documentation can be limited, this can lead to miscommunications and increased downtime during installations or repairs.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing diagrams from reputable manufacturers or authorized distributors. Establishing a direct relationship with motor manufacturers can provide access to the most accurate and updated diagrams. Additionally, leveraging online platforms that specialize in industrial components can yield high-quality diagrams. It’s beneficial to maintain a database of these diagrams for easy access during projects. Encouraging collaboration with local engineering firms can also enhance the sourcing process, as these firms may already have established connections with manufacturers and can provide tailored assistance.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Understanding Electric Motor Diagrams for Maintenance
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face difficulties in interpreting electric motor diagrams during maintenance and troubleshooting. This can result in prolonged downtime and increased costs, especially if the maintenance staff lacks experience with reading and understanding these technical documents. In industries where electric motors are critical to operations, such as manufacturing or logistics, the inability to swiftly diagnose and fix issues can severely impact productivity.
The Solution: To address this pain point, companies should implement a structured training program focused on understanding electric motor diagrams. This training should include hands-on workshops where maintenance teams can practice interpreting diagrams in real-life scenarios. Additionally, creating a visual guide that breaks down common diagram symbols and their meanings can serve as a quick reference tool for technicians. Encouraging the use of digital tools, such as mobile apps that provide interactive diagrams, can also enhance understanding. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and providing accessible resources, companies can empower their teams to effectively maintain electric motors, thereby minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric motor diagram
What Are the Common Materials Used in Electric Motor Diagrams?
When selecting materials for electric motors, understanding the properties and applications of common materials is crucial for international B2B buyers. This guide analyzes several materials frequently used in electric motor diagrams, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Copper in Electric Motors?
Copper is one of the most widely used materials in electric motors, particularly for windings and electrical connections. Its excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 59.6 × 10^6 S/m) ensures minimal energy loss during operation. Additionally, copper has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C), making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Pros: Copper is durable and resistant to corrosion, which enhances the longevity of electric motors. Its high conductivity allows for efficient energy transfer, making it ideal for applications requiring high performance.
Cons: The primary drawback of copper is its cost, which is generally higher than alternatives like aluminum. Manufacturing complexity can also be an issue, as copper requires specialized techniques for winding and soldering.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media, including water and oil, and is essential for applications like pumps and industrial motors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of copper in their region, as fluctuations in market prices can affect procurement costs.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Electric Motors?
Aluminum is another popular choice for electric motor windings and casings. It has good electrical conductivity (approximately 37.7 × 10^6 S/m) and a lower density than copper, making it lighter and easier to handle.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness compared to copper. It is also corrosion-resistant, which is beneficial for outdoor applications.
Cons: While aluminum is lighter, it has a lower conductivity than copper, which can lead to higher energy losses in some applications. Additionally, aluminum may require thicker windings to achieve the same performance as copper.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for various environments but may not perform as well in high-temperature applications compared to copper.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet relevant standards and are suited for the specific environmental conditions of their applications.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Motor Construction?
Steel, particularly in the form of laminations, is commonly used for the stator and rotor cores in electric motors. Steel’s magnetic properties (with a permeability of around 1000 H/m) make it ideal for enhancing magnetic flux.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and provides excellent mechanical strength and durability. Its magnetic properties improve the efficiency of electric motors.
Cons: Steel can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, and its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where reducing mass is critical.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media and is often used in industrial applications where strength and durability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for steel that complies with international standards, particularly regarding corrosion resistance and magnetic properties.
What Are the Advantages of Using Plastic Components in Electric Motors?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in electric motors for non-load-bearing components like housings and insulators. Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: The primary advantage of plastics is their low cost and versatility. They are resistant to corrosion and can provide electrical insulation.
Cons: Plastics typically have lower thermal and mechanical strength compared to metals, which can limit their use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications where weight reduction is essential and where exposure to moisture or chemicals is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used meet relevant safety and performance standards for their specific applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Motor Diagram | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings, electrical connections | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Windings, casings | Cost-effective, lightweight | Lower conductivity, thicker windings | Medium |
| Steel | Stator and rotor cores | Mechanical strength, durability | Prone to corrosion, heavier weight | Low |
| Plastic | Housings, insulators | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Lower thermal/mechanical strength | Low |
This comprehensive analysis equips international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions regarding material selection for electric motors. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will enable buyers to optimize performance while considering cost-effectiveness and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric motor diagram
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Motors?
The manufacturing process of electric motors involves several critical stages that ensure the product meets quality and performance expectations. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing electric motors.
A stock image related to electric motor diagram.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Electric Motor Manufacturing?
The first step in manufacturing electric motors is material preparation. Common materials include:
- Copper Wire: Used for windings in both AC and DC motors due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Magnetic Steel: Utilized for the stator and rotor, providing the necessary magnetic properties.
- Insulation Materials: Essential for preventing electrical short circuits, often made of materials like polyester or epoxy.
- Commutators and Brushes: Usually manufactured from carbon or metal to ensure efficient electrical contact.
Proper selection and treatment of these materials are crucial, as they directly impact the motor’s efficiency and durability.
How Are Electric Motors Formed?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming the components. This includes:
- Winding the Coils: Copper wire is wound around the stator and rotor cores to create electromagnetic fields. Automated winding machines are often used to enhance precision and reduce labor costs.
- Stamping: The rotor and stator laminations are stamped from magnetic steel sheets. This process helps minimize energy loss through eddy currents.
- Machining: Components are machined to specific tolerances. This stage may involve CNC machining to ensure high precision in dimensions.
By utilizing advanced forming techniques, manufacturers can enhance the performance and lifespan of electric motors.
What Does the Assembly Process Look Like?
The assembly of electric motors is a critical phase where all components come together. Key steps include:
- Component Assembly: The rotor is inserted into the stator, and the winding connections are made. Proper alignment is essential to ensure efficient operation.
- Installation of Commutators and Brushes: These components are installed to facilitate current flow and motor functionality.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: In-process quality checks (IPQC) are conducted to ensure that each assembly step meets specified standards.
A well-organized assembly line can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce the likelihood of defects.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used for Electric Motors?
Finishing processes are vital for enhancing the durability and aesthetic quality of electric motors. Common techniques include:
- Coating: Components may be coated with protective materials to resist corrosion and wear.
- Balancing: Rotors are dynamically balanced to minimize vibrations during operation, which can extend the motor’s lifespan.
- Final Assembly and Testing: The final assembly is performed, followed by comprehensive testing to ensure that the motor operates within specified parameters.
Finishing touches can significantly impact the reliability and performance of electric motors in various applications.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process, ensuring that electric motors meet international standards and customer expectations.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
International standards such as ISO 9001 are crucial indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality management. Other relevant certifications include:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Important for motors used in oil and gas applications, ensuring adherence to industry-specific quality standards.
Buyers should verify that suppliers possess these certifications to ensure product reliability and safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Motor Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early in the production process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing is performed on finished products to verify performance and compliance with specifications.
These checkpoints help maintain high standards throughout the manufacturing process.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Electric Motors?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure electric motors meet performance and safety standards:
- Electrical Testing: Measures insulation resistance, winding resistance, and voltage testing to ensure electrical integrity.
- Mechanical Testing: Involves tests for vibration, noise levels, and thermal performance to assess operational efficiency.
- Load Testing: Simulates real-world operating conditions to evaluate performance under load.
These testing methods provide insights into the motor’s operational capabilities, helping buyers make informed decisions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should take proactive steps to verify supplier quality control:
What Steps Can Be Taken to Conduct Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. Key steps include:
- On-Site Visits: Schedule visits to the manufacturing facility to observe the production processes and quality control measures in place.
- Review of Quality Documentation: Request access to quality management system documentation, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products.
These measures can help ensure that suppliers adhere to high-quality standards and practices.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports?
Buyers should request and review quality reports from suppliers. These reports typically include:
- Inspection Results: Detailed findings from various quality checkpoints during production.
- Certification Copies: Documentation of compliance with international standards and any relevant industry certifications.
- Defect Rates: Historical data on defect rates can provide insights into the manufacturer’s reliability and quality consistency.
Having access to this information allows buyers to make more informed sourcing decisions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers need to be aware of certain nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations that affect product quality standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality can impact supplier relationships and negotiation strategies.
- Logistical Considerations: Quality control measures may vary based on the logistics of shipping and handling products across borders. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust processes to mitigate risks.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of international sourcing and ensure they partner with reliable manufacturers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric motor diagram’
To successfully procure an electric motor diagram, it’s essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide you through the key steps necessary to ensure that you are sourcing a high-quality and suitable electric motor diagram for your needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is the first step in sourcing an electric motor diagram. Consider the type of motor you need—AC, DC, or specialized motors for specific applications. Additionally, take into account the voltage, current rating, and any specific features like torque requirements or speed settings.
- Tip: Document your needs meticulously to facilitate better communication with suppliers.
Step 2: Research the Market for Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in electric motor diagrams. Look for manufacturers or distributors who have a proven track record in your industry and region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Tip: Utilize online directories and trade associations to find reputable suppliers. Reading reviews and testimonials can also provide insights into their reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions to understand their capabilities and reliability.
- Tip: Pay attention to their customer service and support, as this will be vital in case of any future issues or modifications needed.
Step 4: Request and Review Samples
Request samples of electric motor diagrams from shortlisted suppliers. This allows you to assess the quality and clarity of their diagrams, ensuring they meet your technical specifications.
- Tip: Evaluate the diagrams for accuracy, detail, and usability in your specific applications. A well-detailed diagram will facilitate better understanding and implementation.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the electric motor diagrams comply with relevant international standards and regulations. This is especially important if you are operating in regions with strict compliance requirements, such as Europe.
- Tip: Ask for documentation that proves compliance, such as certifications or test reports, to ensure the diagrams meet safety and performance standards.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and reviewed the diagrams, it’s time to negotiate the terms and conditions of the purchase. This includes pricing, delivery times, and payment terms.
- Tip: Be clear about your expectations regarding after-sales support and warranty terms, as these can be crucial for long-term satisfaction.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Monitor the Process
After reaching an agreement, finalize the purchase and keep an eye on the production and delivery process. Regular communication with your supplier can help address any issues that arise during this phase.
- Tip: Establish a timeline for delivery and set milestones to track progress. This proactive approach can prevent delays and ensure timely receipt of your electric motor diagrams.
By following this step-by-step checklist, you can effectively source high-quality electric motor diagrams that meet your specific business needs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in your operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric motor diagram Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Motor Diagram Sourcing?
When sourcing electric motor diagrams, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in electric motors significantly impact costs. Common materials include copper for windings, steel for the rotor and stator, and various plastics for housings. Opting for higher-quality materials can enhance performance but may increase initial costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, affecting the overall pricing. Skilled labor is essential for assembling motors and ensuring quality control. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but ensure that this does not compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, making the final product more competitive.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specific motor designs or configurations. This upfront investment can be substantial, but it is amortized over larger production runs, making it crucial to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure that motors meet industry standards and certifications. The costs associated with QC can vary, but they are essential for maintaining product reliability and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and weight. Understanding Incoterms is vital for negotiating logistics responsibilities and costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on market conditions and supplier relationships.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Motor Diagram Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric motor diagrams, and understanding these can help buyers make informed decisions:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often results in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer better pricing or discounts for bulk orders, so consider your needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized motors or specific technical specifications can lead to increased costs. Ensure that you communicate your requirements clearly to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Motors that meet specific quality certifications (like ISO or CE) may carry a premium price. While these certifications ensure reliability, they also contribute to higher costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record, while newer entrants may offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms can significantly impact total costs, including logistics and insurance. Clear agreements on responsibilities for shipping and customs can prevent hidden costs.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Negotiating Electric Motor Diagram Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management strategies are essential:
-
Negotiate Terms and Pricing: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating prices, especially for larger orders. Request quotes from multiple suppliers to establish a baseline for negotiations.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operational efficiency, and longevity. A higher upfront cost may be justified by lower operational costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the different pricing structures based on local market conditions. Prices may vary significantly depending on regional manufacturing capabilities and supply chain logistics.
-
Be Cautious with Indicative Prices: Always treat quoted prices as indicative, as fluctuations in raw material costs or currency exchange rates can impact final pricing. Ensure that your contracts include clauses for price adjustments based on market changes.
By understanding these components and strategies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric motor diagrams effectively, ensuring they secure quality products at competitive prices.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric motor diagram With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Electric Motor Diagrams
When considering the implementation of electric motor diagrams, it’s essential to evaluate viable alternatives that could achieve similar operational goals. This analysis will help international B2B buyers identify the most effective and cost-efficient solutions tailored to their specific needs. The alternatives discussed here include hydraulic systems and pneumatic systems, both of which can serve as substitutes for electric motors in various applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Motor Diagram | Hydraulic System | Pneumatic System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, precise control | Excellent power-to-weight ratio, high force output | Good for quick movements, limited force capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; low operational costs | High initial setup cost; ongoing fluid maintenance | Lower initial investment; compressed air costs can add up |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires technical understanding; straightforward wiring | Complex setup; needs skilled personnel for installation | Easier to set up; simpler components |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional wiring checks | Regular fluid checks and replacements required | Minimal maintenance; check for leaks periodically |
| Best Use Case | Robotics, HVAC systems, and automotive applications | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | Assembly lines, packaging machinery |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Systems?
Hydraulic systems utilize pressurized fluids to generate mechanical power, offering a high power-to-weight ratio. They excel in applications requiring significant force, such as construction equipment and industrial machinery. However, the initial investment can be steep, and ongoing maintenance of hydraulic fluids is necessary to ensure efficiency. Furthermore, hydraulic systems can be complex, requiring skilled technicians for installation and repair, which may not be feasible for all businesses.
How Do Pneumatic Systems Compare in Terms of Efficiency?
Pneumatic systems operate using compressed air to drive machinery, making them well-suited for tasks requiring quick, repetitive motion, such as in assembly lines. They are generally easier to set up compared to hydraulic systems and involve simpler components, which can reduce initial costs. However, their force capabilities are limited compared to hydraulic systems and electric motors, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications. Additionally, while maintenance is minimal, companies must consider the ongoing costs associated with air compression.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
In selecting the appropriate technology, international B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and the skill level of their workforce. Electric motor diagrams offer a balance of performance and efficiency for many applications, but alternatives like hydraulic and pneumatic systems provide viable options depending on the context. By weighing the pros and cons of each solution, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and operational demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric motor diagram
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Motors?
Understanding the technical properties of electric motors is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing components for various applications in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and energy. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
The materials used in electric motor construction, such as copper for windings and steel for the rotor and stator, significantly affect performance. High-grade materials ensure better conductivity, durability, and efficiency. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer motors made from verified material grades to ensure longevity and reliability.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For electric motors, tight tolerances are crucial to ensure proper fitting and functioning of components like bearings and rotors. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to increased wear and tear, reducing the motor’s lifespan. Buyers should request tolerance specifications to ensure compatibility with their machinery.
3. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings indicate how well an electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, often expressed as a percentage. Higher efficiency ratings reduce operational costs and environmental impact, making them vital for industries focused on sustainability. Buyers should compare efficiency ratings across different models to select the most cost-effective option.
4. Power Output
Power output, measured in horsepower or kilowatts, determines the motor’s capability to perform work. Understanding the required power output for specific applications helps buyers select the right motor size and type, preventing underperformance or excess energy consumption. Analyzing power requirements based on intended use is crucial for optimal performance.
5. Torque Characteristics
Torque is the rotational force produced by an electric motor, essential for driving machinery. Different applications may require specific torque characteristics, such as starting torque or maximum torque. Buyers should assess their operational needs to choose motors that deliver the required torque efficiently.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Electric Motor Transactions?
Familiarity with trade terminology is equally important for B2B buyers when negotiating contracts or sourcing electric motors. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the electric motor industry, OEMs often provide components that meet specific standards for original equipment. Buyers should consider partnering with reputable OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs without overcommitting to excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific quantities of products. This process allows buyers to compare offers from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best deal. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline procurement and lead to better pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they dictate who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Buyers should be familiar with relevant Incoterms to avoid unexpected costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In electric motor procurement, shorter lead times can significantly impact project timelines. Buyers should discuss lead times with suppliers to ensure timely delivery and minimize disruptions in production.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, enhance their procurement processes, and ultimately improve their operational efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric motor diagram Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends for Electric Motors?
A stock image related to electric motor diagram.
The electric motor market is witnessing significant growth driven by the global push towards renewable energy and sustainable technologies. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for efficient electric motors is surging, fueled by industrial automation and electric vehicle adoption. Key trends include a shift toward high-efficiency motors, advancements in motor design and materials, and the integration of smart technologies that enhance performance and energy management.
International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific applications. This includes considerations for size, power output, and compatibility with existing systems. Emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) applications are transforming electric motor functionality, enabling predictive maintenance and energy optimization. Additionally, the expansion of e-commerce platforms has streamlined sourcing processes, allowing buyers from diverse regions to access a broader range of products and suppliers more efficiently.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Electric Motor Procurement?
A stock image related to electric motor diagram.
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal factor for B2B buyers in the electric motor sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials and manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, with a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or renewable energy in their manufacturing processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses face pressure to ensure transparency in their supply chains. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management are becoming prerequisites for suppliers aiming to engage with conscientious buyers. Furthermore, the use of “green” materials in electric motor construction not only supports sustainability goals but can also enhance product performance. Buyers are encouraged to seek out suppliers that provide eco-friendly options, as this can improve marketability and compliance with emerging regulations.
What Is the Historical Context of Electric Motors in B2B Sourcing?
The evolution of electric motors dates back to the 19th century, with significant advancements in design and efficiency over the decades. Initially, electric motors were primarily used in industrial applications, but their adoption has expanded to various sectors, including automotive, consumer electronics, and renewable energy systems. As technology progressed, the development of brushless motors and the introduction of variable frequency drives (VFDs) revolutionized performance, allowing for greater control and energy savings.
Today, the market is characterized by rapid innovation and adaptation to changing energy standards, making it essential for international B2B buyers to stay informed about historical trends and technological advancements. Understanding the evolution of electric motors can provide valuable insights into current sourcing strategies and future opportunities for competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric motor diagram
-
How do I choose the right electric motor diagram for my application?
Selecting the right electric motor diagram involves understanding your specific application needs, including the type of motor (AC or DC), power requirements, and load characteristics. Consider factors such as torque, speed, and efficiency. Consult with suppliers who can provide detailed diagrams and technical specifications tailored to your application. Ensure the diagrams include all necessary components such as the rotor, stator, commutator, and brushes for clarity in installation and maintenance. -
What are the essential components depicted in an electric motor diagram?
An electric motor diagram typically includes key components such as the stator, rotor, commutator, brushes, and power supply connections. Each component plays a crucial role in the motor’s operation: the stator provides a magnetic field, the rotor converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, and the commutator ensures the flow of current is properly managed. Familiarity with these elements can help in troubleshooting and optimizing motor performance. -
What is the best way to source electric motor diagrams from international suppliers?
The best approach to sourcing electric motor diagrams is to establish relationships with reputable suppliers who specialize in your required motor type. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or TradeKey to find verified suppliers. Request detailed product catalogs and technical drawings to ensure they meet your specifications. Additionally, consider suppliers from regions known for motor manufacturing, such as Europe and Asia, as they often provide high-quality diagrams and support. -
How can I ensure the quality of electric motor diagrams I receive from suppliers?
To ensure quality, always request samples of diagrams and any accompanying technical documentation. Verify the supplier’s certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management systems. Conduct a thorough vetting process, including checking references and previous client reviews. If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to assess their production processes and quality control measures firsthand. -
What customization options should I consider when ordering electric motor diagrams?
Customization options can include alterations in voltage, power ratings, or specific configurations to suit unique applications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Ensure the supplier can provide custom diagrams that reflect these changes, including any modifications to wiring layouts or component placements. This will help in seamless integration into your existing systems. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric motor diagrams?
Minimum order quantities for electric motor diagrams can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the diagrams. Generally, established manufacturers may have MOQs ranging from 50 to 100 units for standard diagrams. For custom diagrams, MOQs might be higher. It’s advisable to negotiate with suppliers to find a balance that meets your needs while also considering your budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric motor diagrams internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, it’s wise to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the remainder upon receipt. Always ensure that payment terms are clearly outlined in your purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric motor diagrams?
When importing electric motor diagrams, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Work with logistics providers experienced in international trade to ensure smooth transportation. Be aware of import regulations in your country to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in the potential need for local representation in the supplier’s country for any on-site inspections or approvals before shipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric motor diagram
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Electric Motors?
In summary, understanding the intricacies of electric motor diagrams is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Electric motors are integral to a multitude of applications, from industrial machinery to household appliances, thus emphasizing the importance of selecting the right type based on specific operational needs.
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential in the Electric Motor Market?
Strategic sourcing enables buyers to identify reliable suppliers who can deliver high-quality electric motors while optimizing costs. By leveraging data and market insights, businesses can secure favorable terms and ensure the sustainability of their supply chain. Additionally, with advancements in technology and production methods, staying abreast of innovations can lead to enhanced efficiency and performance in motor applications.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Trends in Electric Motors?
As the demand for electric motors continues to grow, fueled by shifts towards automation and renewable energy sources, international buyers should proactively engage with suppliers. This engagement can foster partnerships that prioritize innovation and sustainability. By anticipating market trends and consumer demands, B2B buyers can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape.
In conclusion, the journey towards effective procurement in the electric motor sector is ongoing. Buyers are encouraged to take actionable steps today by exploring diverse sourcing strategies and fostering supplier relationships that will drive long-term success.