Unlock Efficiency: The Ultimate Electrical Motor Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electrical motor
Navigating the global market for electrical motors can be a daunting task for B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing the right products that meet specific operational needs. With a myriad of options available—including AC motors, DC motors, and fractional horsepower motors—the challenge lies in identifying the most suitable type for your application while ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource, addressing key aspects such as the different types of electric motors, their applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and pricing considerations.
International B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Turkey and Poland—will find actionable insights tailored to their unique market conditions. By understanding the intricacies of electrical motors, including their construction and operational principles, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and reduce downtime. This guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of the electrical motor market, enabling you to source products that align with your business objectives while optimizing your supply chain. Whether you’re looking to upgrade existing machinery or invest in new technology, this resource is designed to facilitate smart purchasing decisions that drive your business forward.
Understanding electrical motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Induction Motors | Utilizes alternating current, robust design, low maintenance | Manufacturing, HVAC systems, pumps | Pros: Cost-effective, reliable; Cons: Less efficient at low speeds. |
| DC Motors | Operates on direct current, offers precise speed control | Robotics, automotive applications | Pros: High torque at low speeds; Cons: Requires more maintenance. |
| Synchronous Motors | Rotates in sync with the supply current frequency | Industrial machinery, renewable energy systems | Pros: High efficiency, constant speed; Cons: More complex control systems. |
| Stepper Motors | Moves in discrete steps for precise control | 3D printers, CNC machinery | Pros: Accurate positioning; Cons: Limited speed. |
| Servo Motors | Provides precise control of angular position and speed | Robotics, automation, aerospace | Pros: High precision and control; Cons: Higher cost. |
What Are the Characteristics of AC Induction Motors?
AC Induction Motors are among the most widely used types of electric motors in industrial applications. They operate using alternating current and are known for their robustness and reliability. These motors are suitable for applications like manufacturing and HVAC systems, where consistent performance is crucial. When purchasing AC Induction Motors, buyers should consider the motor’s efficiency ratings, operating environment, and load requirements to ensure optimal performance.
How Do DC Motors Differ in Functionality?
DC Motors are characterized by their ability to provide high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications in robotics and automotive sectors. They require direct current for operation and are advantageous for tasks that demand precise speed control. Buyers should evaluate the maintenance requirements and the motor’s compatibility with their existing systems when considering DC Motors, as these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency.
What Are the Advantages of Synchronous Motors?
Synchronous Motors are designed to rotate in sync with the frequency of the supply current, making them highly efficient for industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. Their ability to maintain a constant speed under varying loads is a key advantage. However, the complexity of their control systems can be a drawback for some buyers. It’s essential to assess the application requirements and the available infrastructure before investing in synchronous motors.
Why Choose Stepper Motors for Precision Applications?
Stepper Motors are unique in that they move in discrete steps, providing exceptional precision for applications such as 3D printing and CNC machinery. Their ability to achieve accurate positioning makes them a popular choice in automation. However, their limited speed can be a disadvantage for high-speed applications. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects to determine if the precision of stepper motors outweighs their speed limitations.
What Makes Servo Motors Suitable for Automation?
Servo Motors are engineered for high precision and control, making them a preferred choice in robotics, automation, and aerospace applications. They can provide accurate control of angular position and speed, which is crucial for modern manufacturing processes. While they tend to be more expensive than other types, the investment is often justified by the enhanced performance and efficiency they offer. Buyers should consider the specific control requirements and budget constraints when evaluating servo motors for their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of electrical motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electrical Motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Conveyor Systems | Enhances efficiency in material handling and production | Motor type (AC/DC), torque requirements, energy efficiency |
| Agriculture | Irrigation Pumps | Increases crop yield through reliable water supply | Power ratings, durability in harsh environments, maintenance support |
| Mining | Ventilation Systems | Improves air quality and worker safety | Explosion-proof standards, energy consumption, reliability |
| Transportation | Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint | Battery compatibility, motor efficiency, regulatory compliance |
| HVAC | Air Conditioning Units | Ensures energy efficiency and comfort in buildings | Noise levels, energy ratings, compatibility with existing systems |
How Are Electrical Motors Used in Manufacturing Conveyor Systems?
In the manufacturing sector, electrical motors are integral to conveyor systems, which transport materials across production lines. These motors provide the necessary mechanical energy to move products efficiently, thereby enhancing productivity and minimizing labor costs. For international B2B buyers, sourcing requires attention to motor type—whether AC or DC—as well as torque requirements to match the load. Energy efficiency is also critical, especially in regions where electricity costs are high.
What Role Do Electrical Motors Play in Agriculture Irrigation Pumps?
Electrical motors are essential for irrigation pumps in agriculture, enabling farmers to deliver water to crops efficiently. By automating the irrigation process, these motors help increase crop yield and optimize water usage, which is vital in arid regions. Buyers should consider power ratings and the motor’s durability in harsh environments, as well as the availability of maintenance support to ensure long-term operation.
How Are Electrical Motors Utilized in Mining Ventilation Systems?
In mining, electrical motors power ventilation systems that circulate air in underground operations. This is crucial for maintaining air quality and ensuring the safety of workers. When sourcing motors for this application, B2B buyers must prioritize explosion-proof standards due to the hazardous environment. Additionally, energy consumption and reliability are important factors, as downtime can lead to significant operational losses.
How Do Electrical Motors Contribute to Electric Vehicles (EVs)?
Electric motors are the heart of electric vehicles, converting electrical energy from batteries into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. This application not only reduces operational costs but also contributes to a lower carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals. Buyers in this sector need to consider compatibility with battery systems, motor efficiency, and compliance with regional regulations, particularly in Europe, where stringent emissions standards exist.
What Importance Do Electrical Motors Have in HVAC Air Conditioning Units?
In HVAC systems, electrical motors drive compressors and fans in air conditioning units, ensuring energy-efficient climate control in buildings. They are key to maintaining comfort levels while minimizing energy consumption. When sourcing these motors, businesses should evaluate noise levels and energy ratings, as well as their compatibility with existing systems to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance in diverse environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electrical motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficient Motor Performance Leading to Increased Costs
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges with electrical motors that underperform, leading to inefficiencies in production lines. For example, a manufacturing facility may use motors that are not properly matched to the load requirements of their machinery. This mismatch can result in excessive energy consumption, overheating, and ultimately a shorter lifespan for the motors. Companies in regions like Africa and South America, where energy costs are high, particularly feel the strain of such inefficiencies.
The Solution: To combat this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough load analysis before purchasing electrical motors. This analysis should include understanding the torque requirements, speed variations, and duty cycles of the equipment they intend to power. When sourcing motors, consider the use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) which can adjust motor speed to match actual demand. Additionally, selecting high-efficiency motors that meet or exceed IE3 or IE4 efficiency ratings can significantly reduce energy costs over time. Collaborating with suppliers who provide detailed performance data and efficiency ratings can also guide better purchasing decisions, ensuring optimal alignment with operational needs.
Scenario 2: Frequent Motor Failures Resulting in Downtime
The Problem: Frequent motor failures can be a major pain point for businesses, particularly in sectors like mining or heavy manufacturing where machinery is under constant strain. Buyers often encounter issues with motors that fail unexpectedly due to factors such as inadequate cooling, improper installation, or unsuitable environmental conditions. This downtime not only disrupts production but also incurs additional costs for repairs and lost revenue.
The Solution: Implementing a predictive maintenance strategy can greatly alleviate the risk of unexpected motor failures. This involves using condition monitoring tools to assess motor health through vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and regular inspections. Establishing a relationship with reliable suppliers who offer after-sales service and technical support can also provide valuable insights into proper installation and maintenance practices. Additionally, investing in motors designed for specific environments—such as explosion-proof or waterproof models—can enhance durability and reliability, thereby reducing overall failure rates.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Type of Motor for Specific Applications
The Problem: International buyers, especially from diverse regions such as the Middle East and Europe, often struggle to find the right electrical motors that meet their specific application requirements. This can be due to a lack of local suppliers offering a wide range of motor types, such as synchronous, induction, or brushless DC motors, tailored for unique operational needs. The complexity of different motor technologies can lead to confusion and suboptimal purchasing decisions.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, buyers should invest time in understanding the different types of electric motors available and their specific applications. Engaging with technical experts or consultants who specialize in electrical motors can provide tailored recommendations based on the intended use. Moreover, leveraging online platforms and databases that catalog various motor specifications can streamline the sourcing process. Establishing partnerships with manufacturers that offer customizable solutions can also ensure that the motors meet precise operational requirements. By fostering strong communication with suppliers, buyers can clarify their needs and receive guidance on the most suitable motor types for their applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electrical motor
What Are the Key Materials for Electrical Motors?
When selecting materials for electrical motors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including performance characteristics, manufacturing complexities, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electrical motors: copper, aluminum, steel, and plastic composites. Each material has unique properties and implications for specific applications.
How Does Copper Impact Electrical Motor Performance?
Copper is widely recognized for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for windings in both AC and DC motors. Its high thermal conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation, which is crucial in high-performance applications. Copper also exhibits good corrosion resistance, particularly when treated, enhancing its longevity in various environments.
Pros: Copper’s durability and performance make it ideal for high-efficiency motors. It is relatively easy to work with, allowing for complex winding designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is higher than aluminum. Additionally, copper is heavier, which may not be suitable for lightweight applications.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various media, including water and oil, but care must be taken in highly corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, especially when sourcing copper from different suppliers.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Electrical Motors?
Aluminum is another common material, particularly for motor casings and rotor structures. It is lightweight, which contributes to overall motor efficiency and performance. Aluminum also has good corrosion resistance and can be anodized for additional protection.
Pros: The lower cost of aluminum compared to copper makes it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Its lightweight nature can lead to lower shipping costs and easier handling during installation.
Cons: While aluminum has decent conductivity, it is not as efficient as copper. Additionally, its mechanical strength is lower, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for environments where weight is a critical factor, but it may not perform as well in high-temperature applications without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet relevant standards for strength and durability, particularly in regions with stringent regulations like Europe.
How Does Steel Contribute to Electrical Motor Design?
Steel is primarily used for the motor frame and magnetic components due to its magnetic properties and structural strength. It is crucial for induction motors, where the rotor and stator require robust materials to withstand operational stresses.
Pros: Steel’s high tensile strength and magnetic permeability make it ideal for applications requiring durability and efficiency in magnetic fields.
Cons: Steel is heavier than both copper and aluminum, which can impact the overall weight of the motor. It is also prone to rust if not properly coated or treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various environments, but it may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion in humid or saline conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local availability of specific steel grades and compliance with international standards, especially in regions like the Middle East where environmental conditions can be harsh.
What Advantages Do Plastic Composites Offer for Electrical Motors?
Plastic composites are increasingly used in non-load-bearing components of electrical motors, such as housings and insulators. They offer good insulation properties and can be engineered to be lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Pros: The versatility of plastic composites allows for innovative designs and reduced weight, which can enhance motor efficiency.
Cons: They generally have lower mechanical strength compared to metals and can be less suitable for high-temperature applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are ideal for applications where insulation and weight reduction are priorities, but they may not withstand extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure that plastic composites meet fire safety and environmental regulations, particularly in Europe, where standards can be stringent.
Summary of Material Selection for Electrical Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electrical Motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in AC/DC motors | Excellent conductivity and durability | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Motor casings and rotor structures | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity and strength | Medium |
| Steel | Frames and magnetic components | High strength and magnetic properties | Heavier and prone to rust | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Housings and insulators | Lightweight and good insulation | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electrical motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electrical Motors?
Manufacturing electrical motors involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets performance and quality standards. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing electrical motors is material preparation. This typically involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as copper for windings, iron or steel for the stator and rotor, and various insulating materials. The quality of these materials directly affects the motor’s efficiency and lifespan. Suppliers should provide Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) to ensure compliance with international standards.
2. Forming Techniques in Electrical Motor Production
In the forming stage, the raw materials are shaped into the required components. Key techniques include:
- Stamping and Machining: Stamping is used to create flat components like stator laminations, while machining is employed for precise dimensions in rotor shafts and end bells.
- Winding: Coils are wound using automated machines, ensuring uniformity and precision in the number of turns and wire tension, which is critical for performance.
- Casting: For some motor types, components such as the housing may be produced through casting, allowing for complex shapes and improved strength.
Each of these techniques requires skilled operators and well-maintained machinery to maintain quality.
3. Assembly Processes in Electrical Motor Manufacturing
The assembly stage involves the integration of all components into a complete motor. Key processes include:
- Component Integration: The stator, rotor, and other parts are assembled, often using robotic systems to ensure precision.
- Alignment and Balancing: Proper alignment of the rotor and stator is crucial to minimize vibrations. Balancing the rotor helps achieve smooth operation.
- Electrical Connections: These connections must be robust and insulated to prevent short circuits and ensure safety.
Effective assembly processes can significantly reduce the likelihood of defects and increase the motor’s operational reliability.
4. Finishing Touches in Electrical Motor Production
Finishing processes enhance the durability and performance of electrical motors. This includes:
- Coating: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and improve thermal management.
- Testing: Each motor undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets operational specifications before leaving the factory. This includes functional tests, load tests, and insulation resistance tests.
Investing in high-quality finishing processes can lead to longer-lasting products, which is a significant consideration for B2B buyers.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electrical Motor Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of electrical motors to ensure compliance with both international standards and specific industry requirements.
Relevant International Standards for Electrical Motors
International standards such as ISO 9001 play a vital role in guiding quality management systems in manufacturing. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers follow a systematic approach to quality, focusing on continuous improvement.
Industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are also essential, particularly for motors used in hazardous environments or specialized applications. These certifications indicate that the products meet stringent safety and environmental regulations.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in Electrical Motor Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter production. Suppliers must provide documentation and test results for materials.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing, IPQC checks the production line for adherence to specifications. This can include monitoring machine settings and component dimensions.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished motor. This may include performance tests, noise level measurements, and thermal imaging to identify potential issues.
These checkpoints help identify defects early, reducing costs associated with rework or product recalls.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits
Regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s quality management system. Buyers should assess whether suppliers are compliant with ISO standards and industry-specific certifications. This includes evaluating the supplier’s processes, documentation, and employee training.
2. Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. These reports can help assess the reliability of the supplier’s quality assurance measures.
3. Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. Independent auditors can provide unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing processes and quality control measures, helping buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (e.g., Turkey, Poland), understanding regional standards and practices is crucial. Here are some considerations:
- Cultural Differences in Quality Perception: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality. Buyers should communicate their specific requirements clearly and understand the local practices of their suppliers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that products comply with the regulatory requirements of the buyer’s country. This may involve additional certifications or testing.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should demand transparency in the supply chain to ensure that all components meet the required quality standards. This may involve tracing the origin of materials and components used in the manufacturing process.
By understanding these nuances, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing electrical motors and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electrical motor’
To successfully procure electrical motors, international B2B buyers must follow a structured approach to ensure they select the right product that meets their operational needs and compliance standards. This checklist serves as a practical guide for evaluating suppliers and products effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the electrical motors you need. This includes determining the type of motor (AC, DC, induction, synchronous, etc.), power rating, voltage, and application requirements. A well-defined specification helps in communicating your needs to suppliers and ensures compatibility with your existing systems.
- Consider Application Needs: Different applications may require specific motor features such as speed control, torque requirements, or environmental considerations.
- Power Efficiency: Look for motors that comply with energy efficiency standards to reduce operational costs.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in electrical motors. Use industry directories, trade associations, and online platforms to compile a list of manufacturers.
- Check for Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with a strong track record in your region, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Read Reviews and Testimonials: Customer feedback can provide insight into the supplier’s reliability and product performance.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with international standards. This is crucial for ensuring product safety and reliability.
- ISO Certifications: Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate a commitment to quality management.
- Local Compliance: Ensure that the motors meet local regulations and standards specific to your region.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Request detailed quotations from shortlisted suppliers. The quotation should include product specifications, pricing, lead times, and payment terms.
- Compare Offers: Analyze the quotations not only for pricing but also for the included warranties, support services, and delivery timelines.
- Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms to achieve a more favorable deal.
Step 5: Evaluate Product Quality
Assess the quality of the electrical motors through samples or technical documentation. Request test reports or certifications related to performance and efficiency.
- Performance Metrics: Look for data on efficiency ratings, torque curves, and load capabilities.
- Durability and Maintenance: Inquire about the expected lifespan and maintenance requirements of the motors.
Step 6: Check After-Sales Support
Inquire about the after-sales support provided by the supplier. Reliable support can significantly impact your operations, especially in case of technical issues.
- Technical Assistance: Ensure that the supplier offers technical support and has a responsive customer service team.
- Spare Parts Availability: Check if spare parts are readily available and how quickly they can be supplied if needed.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract
Once you have chosen a supplier, finalize the contract detailing all terms agreed upon. Ensure that it includes clauses on delivery schedules, payment milestones, and warranty terms.
- Legal Review: Consider having the contract reviewed by a legal expert to safeguard your interests.
- Clear Communication: Maintain open lines of communication with the supplier throughout the process to address any concerns promptly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for electrical motors, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electrical motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electrical Motor Sourcing?
When sourcing electrical motors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary components contributing to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly impacts costs. For instance, copper, steel, and rare earth magnets are common in electric motor manufacturing. Fluctuations in raw material prices can affect your sourcing budget, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where material sourcing may be subject to local market conditions.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In Europe, for example, labor costs are typically higher than in many parts of Africa or South America. Understanding the labor landscape in your supplier’s location can help in negotiating better pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Buyers should inquire about these costs, as they can vary widely based on the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling required for specific motor designs can add to initial costs but may lead to efficiencies in production. It’s vital to factor in these expenses when considering custom motor specifications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control processes ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards. While this may incur additional costs, it can prevent expensive failures and recalls, making it a worthwhile investment.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier to the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these logistics can help optimize the total cost.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can fluctuate based on competition and market demand. Buyers should compare quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they are receiving a fair price.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electrical Motor Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electrical motors:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk often leads to discounts. Buyers should negotiate Minimum Order Quantities (MOQs) to maximize savings, particularly when sourcing from suppliers in regions like Turkey or Poland.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can significantly increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether standard models meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may come at a premium but can enhance performance and longevity, reducing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can impact pricing. Researching potential suppliers can provide insights into their pricing structures and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can influence overall costs.
What Are Some Tips for Buyers to Negotiate Better Prices?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing electrical motors:
-
Negotiate Early and Often: Establishing open lines of communication with suppliers early in the sourcing process can lead to better pricing. Regular negotiations can help in adjusting terms based on changing market conditions.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and lifespan to make informed decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have distinct pricing structures due to local market conditions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these nuances to avoid overpaying.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to favorable pricing and better service. Consider loyalty discounts or long-term contracts as part of your sourcing strategy.
Are Prices Indicative and What Should Buyers Keep in Mind?
Prices for electrical motors can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It’s essential for buyers to approach pricing with flexibility and an understanding that fluctuations in material costs, labor, and logistics can all affect the final price. Always ask for detailed quotes and consider multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electrical motor With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Electrical Motors
In the quest for efficient and reliable power transmission, businesses often explore alternatives to traditional electrical motors. While electrical motors are widely used for their versatility and efficiency, alternatives such as pneumatic actuators and hydraulic systems can also provide effective solutions depending on specific application requirements. This analysis will compare electrical motors against these alternatives to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison of Electrical Motors with Alternative Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Electrical Motor | Pneumatic Actuator | Hydraulic System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, good torque at various speeds | Fast response, limited torque | High torque and power output |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Lower initial cost, higher operational costs | Higher initial investment, but lower operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires electrical infrastructure | Easier to install, less complex | Complex installation, requires hydraulic infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance, but air quality can affect performance | Regular checks required, risk of leaks |
| Best Use Case | General machinery, HVAC systems | Quick actuation, packaging, and assembly | Heavy machinery, lifting and pressing applications |
Analyzing Pneumatic Actuators as an Alternative
Pneumatic actuators utilize compressed air to create motion, making them suitable for applications requiring rapid response and high speed. Their simplicity in design allows for easier installation and lower initial costs, appealing to industries where budget constraints are significant. However, they may not provide the same level of torque as electrical motors and can incur higher operational costs due to air compression needs. Furthermore, the performance can be impacted by air quality and pressure fluctuations.
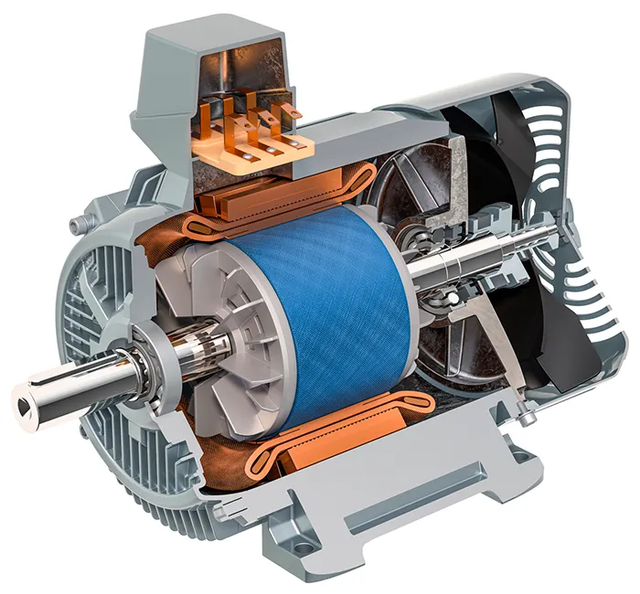
A stock image related to electrical motor.
Evaluating Hydraulic Systems as an Alternative
Hydraulic systems operate by using pressurized fluid to transmit power, delivering exceptional torque and force. They are particularly effective in heavy-duty applications such as construction and manufacturing, where substantial power is required. While the initial setup costs are higher and the installation process is more complex, hydraulic systems can offer lower operational costs over time, especially in applications that require sustained power. Maintenance is crucial, as leaks in the hydraulic lines can lead to performance issues and increased downtime.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate power transmission solution, B2B buyers must carefully consider the specific needs of their applications, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Electrical motors are often the go-to choice for versatility and efficiency, particularly in general machinery. However, for applications requiring rapid actuation or substantial lifting power, pneumatic actuators or hydraulic systems may be more suitable. Evaluating these alternatives against your operational demands will ensure a more informed decision, ultimately enhancing productivity and reducing costs in the long run.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electrical motor
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electrical Motors?
Understanding the technical properties of electrical motors is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some of the key specifications that should be considered:
1. Power Rating (Horsepower or Kilowatts)
The power rating indicates the motor’s output capability and is typically measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). This specification is vital because it determines whether the motor can handle the intended load. When negotiating purchases, knowing the required power rating can help buyers ensure they select motors that meet their operational needs without overpaying for unnecessary capacity.
2. Efficiency Class
Efficiency refers to how effectively the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Motors are often classified into efficiency classes (e.g., IE1, IE2, IE3). Higher efficiency motors consume less energy, reducing operating costs over time. For buyers, selecting energy-efficient motors can lead to significant long-term savings, making this a critical factor in procurement decisions.
3. Torque Rating
Torque is the rotational force produced by the motor and is typically measured in Newton-meters (Nm). Understanding torque ratings is essential for applications requiring specific performance characteristics. Buyers should ensure that the selected motor can deliver sufficient torque for their machinery, especially in industries such as manufacturing and agriculture where performance reliability is crucial.
4. Operating Voltage and Frequency
Electrical motors are designed to operate at specific voltage and frequency levels (e.g., 230V/50Hz or 460V/60Hz). Compatibility with local electrical supply standards is essential to avoid operational issues. Buyers must verify these specifications to ensure seamless integration into their existing systems, especially when sourcing motors from different regions.
5. Material Grade and Construction
The materials used in motor construction can significantly impact durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum and cast iron, which affect weight, heat dissipation, and resistance to corrosion. Buyers should consider the environment in which the motor will operate; for instance, motors used in harsh conditions may require higher-grade materials for longevity.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electrical Motor Industry?
Understanding industry jargon can greatly facilitate communication and negotiations in the B2B marketplace. Here are some commonly used trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. For B2B buyers, working with OEMs can provide access to high-quality motors tailored for specific applications, ensuring reliability and performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers, as understanding MOQ can help in budget planning and inventory management. High MOQs may require buyers to adjust their purchasing strategies or negotiate terms.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other relevant information for specific products or services. Buyers should craft detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate quotations that reflect their needs, aiding in effective decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that delineate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly impact total procurement costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the product. This term is particularly important in international trade, where delays can occur due to customs or logistics. Buyers should always inquire about lead times to manage project timelines effectively.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terminology, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electrical motors, ensuring they meet their operational requirements while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electrical motor Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electrical Motor Sector?
The electrical motor sector is currently experiencing robust growth, driven by increased demand for energy-efficient solutions across industries. Key global drivers include the push for automation in manufacturing, growth in renewable energy projects, and the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these trends present both opportunities and challenges in sourcing and procurement.
Emerging technologies such as smart motors and IoT-enabled electric motors are transforming traditional applications, allowing for better monitoring and control. This trend is particularly significant in regions like Turkey and Poland, where industrial modernization is a priority. B2B buyers should consider investing in motors that incorporate advanced features like real-time data analytics, which can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime.

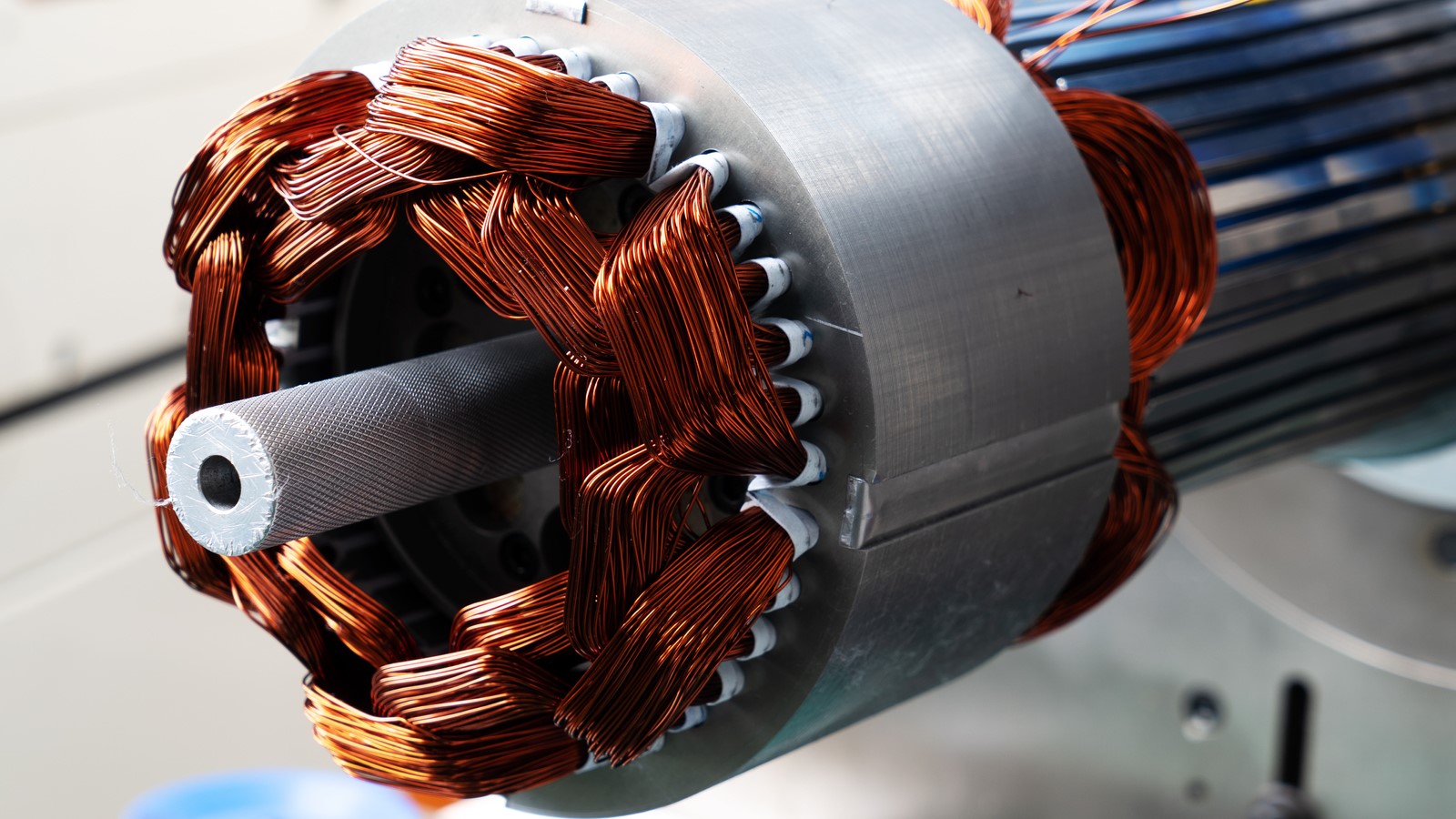
A stock image related to electrical motor.
Moreover, the increasing emphasis on local sourcing and supply chain resilience is shaping market dynamics. International buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers not only on price but also on their ability to deliver consistent quality and innovative solutions. Collaborating with local suppliers can lead to shorter lead times and lower transportation costs, making it a strategic advantage in the competitive landscape.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Electrical Motor Industry?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the electrical motor sector, influencing sourcing decisions across the globe. The environmental impact of production processes and product lifecycle is now a key consideration for international B2B buyers. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprints, sourcing electrical motors made from sustainable materials is increasingly important.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Energy Star ratings for energy-efficient products. Additionally, opting for motors designed for recyclability can contribute to a circular economy, minimizing waste and promoting sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital, as transparency in supply chains helps mitigate risks associated with labor practices and material sourcing. Buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate responsible sourcing practices, ensuring that their supply chains align with global ethical standards. This not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters long-term partnerships built on trust and shared values.
What is the Evolution of Electric Motors and its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of electric motors dates back to the early 19th century, with significant advancements leading to the diverse range of motors available today. Early developments focused on direct current (DC) motors, which were widely used in industrial applications. However, the introduction of alternating current (AC) motors revolutionized the sector, offering greater efficiency and versatility.
As electric motors have evolved, so too have their applications. Modern electric motors are integral to various sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial in recognizing the potential for innovation and the importance of selecting the right type of motor for specific applications.
In conclusion, staying informed about market dynamics, prioritizing sustainability, and understanding the historical evolution of electric motors can significantly enhance the strategic sourcing decisions of international B2B buyers. By aligning with current trends and ethical standards, companies can ensure they are well-positioned in a competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electrical motor
-
How do I solve compatibility issues when sourcing electrical motors?
To address compatibility issues, start by clearly defining your application requirements, including voltage, frequency, and power output. Consult with suppliers to verify that their motors meet your specifications. It’s also beneficial to understand the standards and certifications relevant to your region (e.g., IEC for Europe, NEMA for the U.S.) to ensure compliance. Additionally, consider sourcing motors that offer customizable features, allowing for adjustments based on your equipment. -
What is the best type of electrical motor for industrial applications?
The best type of electrical motor for industrial applications often depends on the specific use case. For high torque and variable speed, AC induction motors are commonly preferred due to their robustness and efficiency. For precision control in automation systems, servomotors or stepper motors are ideal. It’s essential to assess factors such as load characteristics, operational environment, and energy efficiency when making your selection. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for electrical motors?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, which can indicate product quality and safety. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who understand your regional market can also enhance communication and service delivery. -
How can I customize electrical motors to fit my specific needs?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for electrical motors, including changes to voltage ratings, speed configurations, and physical dimensions. When seeking customization, communicate your specific requirements clearly to the supplier. Discuss aspects such as environmental conditions, operational cycles, and integration with existing systems. Be aware that customization may affect lead times and pricing, so factor these into your planning. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electrical motors?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly by supplier and product type. Generally, standard models may have lower MOQs, while customized motors often require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to communicate directly with suppliers about your needs and negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and project timeline. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electrical motors internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases typically range from upfront payment to 30-90 days after delivery, depending on the supplier’s policy and your relationship with them. Options like letters of credit can provide security for both parties. Ensure to clarify payment terms upfront and consider discussing installment payments if the order is significant. Understanding currency exchange rates and potential tariffs is also crucial. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for the electrical motors I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and test reports from suppliers. Look for motors that meet international quality standards, such as ISO 9001 or IEC certifications. Additionally, consider conducting factory audits or third-party inspections before shipment. Establishing a clear return policy and warranty terms can also protect your investment in case of defects or performance issues. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing electrical motors?
When importing electrical motors, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your region. Ensure that the motors are packaged securely to prevent damage during transit. Work with logistics providers experienced in handling industrial equipment to streamline the process. Additionally, be aware of lead times and plan for potential delays due to customs clearance or transport issues, especially when sourcing from distant regions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electrical motor
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Electrical Motors?
In the dynamic landscape of electrical motors, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types of motors—AC, DC, and fractional horsepower—enables businesses to select the most suitable technology tailored to their operational needs. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate reliability and offer comprehensive support, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of motor systems.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Competitive Advantage?
Investing in strategic sourcing not only streamlines procurement processes but also fosters partnerships that can lead to innovation and cost savings. For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging local suppliers can mitigate logistics challenges and reduce lead times, ultimately enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
What Does the Future Hold for Electrical Motor Procurement?
A stock image related to electrical motor.
Looking ahead, the demand for energy-efficient and high-performance electric motors is set to rise, driven by sustainability initiatives and technological advancements. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about emerging trends and innovations in the electrical motor sector. Engaging with industry experts and participating in trade shows can provide valuable insights that inform purchasing decisions.
By embracing a strategic sourcing approach, B2B buyers can position themselves for success in the evolving marketplace of electrical motors. Take action today to explore partnerships that will empower your business for tomorrow.