Unlocking r.t.d. Meaning: The Complete Guide for Buyers (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for r.t.d. meaning
Navigating the complexities of sourcing RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) technology can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With varying standards, applications, and suppliers, understanding the nuances of RTD meaning is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide aims to demystify the intricacies surrounding RTDs, exploring their types, applications in various industries, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
International buyers face unique challenges, such as differing regulatory standards and market dynamics. This comprehensive resource will provide insights into the cost structures associated with RTDs, helping you identify budget-friendly options without compromising quality. Additionally, we will cover how to evaluate suppliers effectively, ensuring that your procurement process aligns with your operational needs and compliance requirements.
By equipping yourself with the knowledge from this guide, you will be empowered to make confident decisions that enhance your operational efficiency and product reliability. Whether you are sourcing RTDs for industrial applications or for specialized scientific research, understanding their meaning and implications will position your business for success in the global market.
Understanding r.t.d. meaning Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) | Uses resistance change to measure temperature; typically platinum-based | Industrial temperature measurement | Pros: High accuracy, stability. Cons: Higher cost than thermocouples. |
| Ready to Drink (RTD) | Pre-mixed beverages, often alcoholic; convenient packaging | Food and beverage distribution | Pros: Convenience, variety. Cons: Shorter shelf life. |
| Returned to Duty (RTD) | Military terminology for personnel returning to active duty | Defense and government sectors | Pros: Clear communication of status. Cons: May require extensive documentation. |
| Real-Time Data (RTD) | Data that is available immediately as it is generated | Data analytics, IoT applications | Pros: Timely insights, improved decision-making. Cons: High infrastructure costs. |
| Research and Technology Development (RTD) | Focus on advancing technology and scientific research | R&D departments across industries | Pros: Innovation-driven, potential for patents. Cons: Requires substantial investment. |
What are the Key Features of Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)?
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are widely recognized for their accuracy and stability in temperature measurement. Typically made from platinum, they operate on the principle that a material’s resistance changes predictably with temperature. RTDs are commonly used in industrial applications where precise temperature control is essential, such as manufacturing and HVAC systems. When purchasing RTDs, B2B buyers should consider the required accuracy, environmental conditions, and compatibility with measurement instruments. While they may have a higher initial cost compared to thermocouples, their long-term reliability often justifies the investment.
How Do Ready to Drink (RTD) Products Benefit B2B Buyers?
Ready to Drink (RTD) products represent a significant segment within the food and beverage industry, offering convenience and diverse options for consumers. These pre-mixed beverages, which include alcoholic and non-alcoholic varieties, are designed for immediate consumption and typically come in portable packaging. For B2B buyers, such as distributors and retailers, the appeal lies in the growing consumer demand for convenience. However, considerations regarding shelf life and storage conditions are crucial, as these products may have a shorter viability period compared to traditional beverages.
What is the Importance of Returned to Duty (RTD) Terminology in Military Contexts?
In military and defense sectors, the term Returned to Duty (RTD) is essential for tracking personnel status. It indicates that a service member is back in active service after a period of absence. This terminology is critical for maintaining operational readiness and ensuring that all personnel are accounted for. B2B buyers in defense contracting and personnel management should be aware of the documentation and processes involved in RTD statuses, as these can affect project timelines and resource allocation.
How Does Real-Time Data (RTD) Impact Business Decisions?
Real-Time Data (RTD) is increasingly vital in today’s data-driven business landscape. It refers to information that is collected and made available instantly as it is generated, enabling timely analysis and decision-making. Industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and finance leverage RTD for operational efficiency and responsiveness. B2B buyers must consider the infrastructure and technology investments needed to implement real-time data solutions, as these can entail significant costs but also provide a competitive edge through improved insights and agility.
What Role Does Research and Technology Development (RTD) Play in Innovation?
Research and Technology Development (RTD) focuses on advancing scientific and technological innovations across various sectors. This area encompasses activities aimed at creating new products, processes, or services that can lead to significant market advantages. For B2B buyers involved in R&D, understanding the landscape of RTD is crucial for identifying potential partnerships and investment opportunities. While the potential for innovation is high, the associated costs and risks of R&D projects should be carefully evaluated to ensure alignment with business objectives.
Key Industrial Applications of r.t.d. meaning
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of r.t.d. meaning | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Temperature Monitoring in Production Lines | Enhances product quality and operational efficiency | Ensure compatibility with existing systems and required accuracy |
| Food and Beverage | Quality Control in Food Processing | Maintains food safety standards and compliance | Look for RTDs with certifications relevant to food safety |
| Oil and Gas | Process Temperature Control | Prevents equipment failure and optimizes energy use | Focus on durability and resistance to harsh environments |
| Pharmaceuticals | Environmental Monitoring in Labs | Ensures compliance with regulatory standards | Consider RTDs that provide high accuracy and stability over time |
| Automotive | Engine Temperature Regulation | Improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions | Evaluate RTDs for responsiveness and reliability under dynamic conditions |
How is ‘r.t.d. meaning’ Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) are crucial for temperature monitoring in production lines. They help maintain optimal temperatures for various processes, ensuring product quality and enhancing operational efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing RTDs that are compatible with existing systems and meet specific accuracy requirements is essential. This guarantees that the manufacturing processes remain uninterrupted and efficient.
What Role Does ‘r.t.d. meaning’ Play in Food and Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage industry, RTDs are employed for quality control during food processing. They monitor temperatures to ensure that food safety standards are met, thereby preventing spoilage and ensuring compliance with health regulations. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing RTDs with relevant food safety certifications is critical. These devices must be reliable and capable of operating in environments that may vary widely in temperature.

A stock image related to r.t.d. meaning.
How are ‘r.t.d. meaning’ Applications Relevant in Oil and Gas?
The oil and gas industry utilizes RTDs for process temperature control, which is vital for preventing equipment failure and optimizing energy use. Accurate temperature readings can significantly reduce operational costs and enhance safety measures. Buyers in regions with extreme climates, such as parts of Africa and the Middle East, should focus on sourcing RTDs that offer durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions to ensure long-term reliability.
Why are ‘r.t.d. meaning’ Devices Important in Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceuticals, RTDs are employed for environmental monitoring in laboratories. They are essential for ensuring that temperature-sensitive materials are stored and handled correctly, thus maintaining compliance with regulatory standards. International B2B buyers, particularly from Europe, should prioritize RTDs that provide high accuracy and stability over time, ensuring that their operations meet stringent pharmaceutical regulations.
How Does ‘r.t.d. meaning’ Enhance Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, RTDs are used for engine temperature regulation, which plays a significant role in improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Accurate temperature monitoring helps in optimizing engine performance, which is crucial for manufacturers looking to meet environmental standards. Buyers should evaluate RTDs for their responsiveness and reliability under dynamic conditions, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of automotive applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘r.t.d. meaning’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Confusion Around RTD Definitions
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter confusion when trying to understand the various meanings of “RTD.” With applications ranging from “Ready to Drink” beverages to “Resistance Temperature Detectors,” the ambiguity can lead to miscommunication and incorrect sourcing decisions. For businesses, this can mean wasted time and resources in procuring the wrong products or technologies, especially when working across different industries and regions like Africa, Europe, and the Middle East.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this confusion, B2B buyers should develop a clear understanding of the specific context in which “RTD” is being used. This involves conducting thorough research and asking clarifying questions during discussions with suppliers. For instance, when dealing with temperature measurement devices, it is crucial to specify that you are interested in “Resistance Temperature Detectors.” Buyers should also create a glossary of terms relevant to their industry, ensuring all team members are on the same page regarding terminology. Additionally, leveraging platforms that provide industry-specific insights and educational resources can help demystify the term and its applications.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality and Compliance in RTD Sensors
The Problem: When sourcing RTD sensors for temperature measurement, B2B buyers often face challenges related to product quality and compliance with international standards. In regions like South America and Africa, where local suppliers may not always meet stringent quality controls, buyers risk receiving subpar products that can lead to inaccurate measurements and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, it is essential for B2B buyers to establish a robust supplier evaluation process. This includes verifying that suppliers adhere to international standards such as those set by DIN for RTD sensors. Buyers should request documentation that proves compliance, such as certificates of calibration and test results. Additionally, conducting site visits or audits can provide deeper insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Forming partnerships with reputable suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry can also enhance product reliability and performance.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Technical Integration Challenges with RTD Technology
The Problem: B2B buyers often experience technical challenges when integrating RTD technology into existing systems. In industries such as manufacturing or energy, where precise temperature control is critical, buyers may struggle with compatibility issues between RTD sensors and their data acquisition systems, leading to delays and increased costs.
The Solution: To overcome these integration challenges, it is crucial for buyers to engage in detailed planning and consultation with both their internal technical teams and suppliers. Before procurement, buyers should clearly outline their system requirements and discuss them with sensor manufacturers to ensure compatibility. It may also be beneficial to invest in training for staff on how to properly install and calibrate RTD sensors. Furthermore, buyers should consider working with suppliers who offer technical support and integration services, as this can provide valuable assistance during the implementation phase. Regularly updating software and firmware related to temperature measurement systems can also enhance compatibility and performance, ensuring a smoother integration process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for r.t.d. meaning
What Are the Common Materials for RTD Sensors and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), it is crucial to consider the properties that will directly impact performance, durability, and application suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in RTD sensors.
How Does Platinum Perform as an RTD Material?
Key Properties: Platinum is the most widely used material for RTD sensors due to its excellent thermal stability and linear resistance-temperature relationship. It typically has a base resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C and a temperature coefficient of 0.00385 ohm/ohm/°C, making it highly reliable for precise temperature measurements.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of platinum include high durability, excellent corrosion resistance, and a well-established standardization (DIN). However, it is relatively expensive and can be more challenging to manufacture compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: Platinum RTDs are suitable for a wide range of applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical industries, where accuracy is paramount. They are compatible with various media, including gases and liquids.
Considerations for International Buyers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Platinum RTDs are often preferred in regulated industries due to their reliability and accuracy.
What Are the Advantages of Nickel as an RTD Material?
Key Properties: Nickel RTDs typically feature a base resistance of 120 ohms at 0°C and a temperature coefficient of 0.00672 ohm/ohm/°C. They are known for their good thermal stability, although not as stable as platinum.
Pros & Cons: Nickel is less expensive than platinum, making it a cost-effective choice for applications where extreme accuracy is not critical. However, its susceptibility to oxidation can limit its use in harsh environments.
Impact on Application: Nickel RTDs are often used in applications such as HVAC systems and automotive industries, where moderate accuracy is acceptable. They are generally suitable for air and non-corrosive liquids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that nickel RTDs meet local standards and regulations, especially in industries like automotive, where safety and compliance are critical.
How Does Copper Compare as an RTD Material?
Key Properties: Copper RTDs have a base resistance of 10 ohms at 25°C and a temperature coefficient of 0.00427 ohm/ohm/°C. They offer a fast response time and are suitable for applications requiring quick temperature changes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its low cost and good conductivity. However, copper is less stable over time and can be affected by oxidation, which may lead to inaccuracies.
Impact on Application: Copper RTDs are often used in applications such as refrigeration and HVAC systems. Their quick response time makes them ideal for monitoring rapidly changing temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be cautious about the environmental conditions where copper RTDs will be used, as they may not be suitable for corrosive environments.
What Are the Benefits of Using Thermistors in RTD Applications?
Key Properties: Thermistors are not traditional RTDs but are often used in similar applications. They have a non-linear resistance-temperature relationship, offering high sensitivity in a limited temperature range.
Pros & Cons: Thermistors are cost-effective and provide high accuracy in specific temperature ranges. However, their non-linear characteristics make them less suitable for applications requiring linearity.
Impact on Application: They are ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control, such as in medical devices and consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that thermistors meet specific industry standards, particularly in medical applications, where compliance is critical.
Summary Table of Material Selection for RTD Sensors
| Material | Typical Use Case for r.t.d. meaning | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platinum | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | High durability and accuracy | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Nickel | HVAC systems, automotive | Cost-effective | Susceptible to oxidation | Medium |
| Copper | Refrigeration, HVAC | Low cost and fast response time | Less stable and prone to oxidation | Low |
| Thermistor | Medical devices, consumer electronics | High sensitivity in limited range | Non-linear characteristics | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of materials used in RTD sensors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions based on specific application needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for r.t.d. meaning
What Are the Typical Manufacturing Processes for RTD Devices?
Manufacturing Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final product meets the required performance and accuracy standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
How is Material Prepared for RTD Manufacturing?
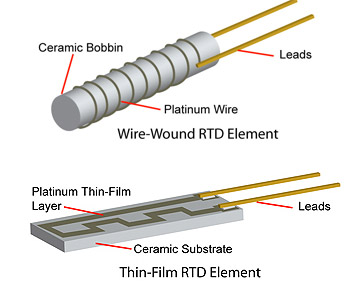
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of high-quality materials, primarily platinum, nickel, or copper, as they exhibit stable resistance properties. For platinum RTDs, which are the most common, the material is sourced in wire form. The wire undergoes a purification process to eliminate impurities that could affect resistance readings. Additionally, the wire is cut to specified lengths for different RTD configurations, such as 2-wire, 3-wire, or 4-wire setups.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in RTD Production?
Once the materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This typically involves winding the metal wire around a ceramic or glass core, which provides insulation and protection. The winding process must be precise to ensure consistent resistance readings. Advanced techniques, such as laser cutting and precision machining, are employed to shape the components accurately. The forming stage is crucial as it directly influences the sensitivity and accuracy of the RTD.
How is the Assembly of RTDs Conducted?
The assembly stage involves attaching the formed sensor to a protective housing. This can include various materials depending on the intended application—stainless steel for industrial environments or plastic for less demanding settings. During assembly, careful attention is paid to the electrical connections, ensuring that they are secure and free of contaminants. This stage may also involve the integration of additional components like terminals or connectors, which are essential for interfacing with measurement devices.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for RTDs?
After assembly, the finishing stage is critical for durability and performance. This includes applying coatings or treatments that enhance resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The finished products undergo visual inspections and functional testing to ensure they meet specified tolerances. This stage is vital, especially for international buyers who may require certifications for specific applications.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for RTD Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of RTDs. International standards such as ISO 9001, which focus on quality management systems, are commonly adopted by manufacturers. Compliance with these standards assures buyers that the supplier maintains consistent quality throughout the production process.
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
In addition to general quality standards, certain industry-specific certifications may be crucial. For example, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, API standards may be relevant for RTDs used in the oil and gas industry. Buyers should inquire about these certifications to ensure the products meet their specific regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in RTD Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each RTD meets the required specifications.
How Does Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Work?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) is the first checkpoint, where raw materials are inspected upon delivery. This includes verifying material specifications and conducting tests to ensure they meet predetermined standards. Suppliers should provide documentation proving that materials have passed IQC, giving buyers confidence in the quality of inputs.
What Role Does In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) Play?
During the manufacturing process, In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) is implemented to monitor key parameters such as temperature, resistance, and mechanical integrity. Regular sampling and testing are conducted to identify any deviations from standards. Buyers should ask suppliers about their IPQC procedures and the frequency of testing to understand how quality is maintained during production.
How Important is Final Quality Control (FQC)?
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last checkpoint before products are shipped. This includes comprehensive testing to ensure that each RTD operates within specified tolerances. Common testing methods involve temperature calibration and resistance checks using precise measurement instruments. B2B buyers should request FQC reports, which detail the results of these tests, to ensure that the products meet their specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for mitigating risks associated with substandard products.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Audits?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers is a critical step. Buyers should inquire about the frequency and scope of internal audits conducted by the supplier to assess compliance with quality standards. Additionally, buyers can request third-party audit reports, which provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management practices.
How Can Buyers Utilize Quality Reports?
Quality reports from suppliers should be scrutinized for details on testing methodologies, results, and adherence to standards. These reports can provide insights into the reliability and consistency of the supplier’s products. Buyers should ensure that reports are up-to-date and relevant to the specific RTDs they are sourcing.
What Are the Benefits of Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in product quality. These services can conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing process and product performance. This is especially beneficial for buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, where local suppliers may not have established quality assurance practices.
Conclusion: Navigating Quality Assurance in RTD Sourcing
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for RTDs is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and implementing robust quality control measures, suppliers can produce reliable and accurate temperature sensors. Buyers should leverage knowledge of industry standards and verification processes to ensure they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘r.t.d. meaning’
To effectively procure products or services related to the term “RTD” (Resistance Temperature Detector), international B2B buyers must follow a structured approach. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions while navigating the complexities of this market.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Understanding the specific application of RTDs—whether for industrial, scientific, or commercial use—will help narrow down your options. Key parameters to define include:
– Temperature Range: Identify the temperatures your RTD will measure.
– Accuracy Requirements: Specify the accuracy needed based on your application.
Step 2: Research Suppliers in Your Region
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers, especially those with a proven track record in your specific region. This is crucial as suppliers may have different levels of expertise and availability based on geographic location. Look for:
– Local Distributors: They can provide quicker support and services.
– Industry References: Seek suppliers with positive testimonials or case studies relevant to your industry.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
When sourcing RTDs, verifying supplier certifications is essential to ensure quality and compliance. Look for certifications that indicate adherence to international standards, such as:
– ISO 9001: Ensures quality management systems are in place.
– DIN Standards: Particularly relevant for RTDs, confirming the products meet specific technical criteria.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before finalizing any contracts, request samples of the RTDs you are considering. This step allows you to evaluate the product’s performance in your specific environment. When testing samples, consider:
– Compatibility: Ensure the RTD works with your existing systems and instruments.
– Performance Metrics: Assess the response time and accuracy during your testing phase.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, analyze their pricing structures and terms of service. It’s vital to understand:
– Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing for bulk purchases.
– Warranty and Support: Review the warranty terms and available technical support post-purchase.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms of Purchase
Negotiation can significantly impact the overall cost and terms of your procurement. Engage in discussions around:
– Payment Terms: Establish clear payment schedules that align with your financial planning.
– Delivery Schedules: Confirm timelines for delivery to avoid disruptions in your operations.
Step 7: Finalize Your Supplier Relationship
After selecting a supplier, formalize the relationship with a contract that outlines all agreed terms. Ensure that the contract includes:
– Performance Expectations: Clearly define the expectations for product quality and delivery.
– Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Establish procedures for addressing any potential issues that may arise during the partnership.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring RTDs effectively, ensuring they select the right products and suppliers that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for r.t.d. meaning Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in r.t.d. Sourcing?
When sourcing for r.t.d. (Resistance Temperature Detector) components, it’s essential to understand the cost structure involved. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of materials used significantly affects pricing. Platinum, commonly used in RTDs, tends to be more expensive than alternatives like nickel or copper. Suppliers often provide different grades of materials, which can influence both performance and cost.
-
Labor: The manufacturing process for RTDs requires skilled labor, especially when precision is crucial. Labor costs can vary based on geographical location; for instance, labor may be more expensive in Europe compared to South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities may charge a premium, but this can lead to better quality and reliability.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specific designs or configurations, which adds to the initial investment. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability of RTDs involves rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. Suppliers with robust QC protocols may charge higher prices but can offer greater confidence in product performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance, weight, and shipping method. International buyers should consider these logistics costs as part of the total purchase price.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can help you negotiate better.
How Do Price Influencers Impact r.t.d. Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing of RTDs, which are crucial for international B2B buyers to consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their demand to negotiate favorable pricing based on volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized RTDs may require additional design and manufacturing efforts, impacting the price. Clearly defining specifications can help streamline the sourcing process and control costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or RoHS compliance) can lead to higher prices but may be necessary for certain applications. Buyers must weigh the benefits of quality against costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand and reliability, while newer suppliers may offer competitive pricing to build their market presence.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly impact total costs. Understanding who bears the risk and costs at various stages of shipping is essential for calculating the total landed cost.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient r.t.d. Sourcing?
For international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are actionable tips to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices based on your understanding of market rates and the supplier’s cost structure. Building a relationship can lead to better long-term pricing.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime costs associated with lower-quality RTDs.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Familiarize yourself with regional pricing trends and fluctuations in raw material costs. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and sourcing decisions.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize procurement platforms and tools that allow for efficient sourcing and supplier comparisons. These tools can provide insights into pricing trends and supplier performance.
-
Build Long-Term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service levels. Suppliers often reward loyalty with discounts or improved terms.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing r.t.d. meaning With Other Solutions
In the world of industrial measurement and control, understanding the various options available is crucial for B2B buyers. This section explores the concept of ‘r.t.d. meaning’, specifically referring to Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), and compares it with alternative temperature measurement solutions. By evaluating different technologies, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational requirements and budget constraints.
Comparison Table of Temperature Measurement Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | R.T.D. Meaning (RTD) | Thermocouple | Infrared Temperature Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy and repeatability | Fast response but less accurate | Non-contact, quick measurements |
| Cost | Moderate (higher than thermocouples) | Low (cost-effective) | High (due to advanced technology) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific wiring and calibration | Simple installation | Easy installation; no contact required |
| Maintenance | Low (requires periodic calibration) | Low (generally robust) | Low (no maintenance needed) |
| Best Use Case | Precision applications (e.g., labs) | General-purpose, quick readings | Surface temperature measurement |
Understanding the Alternatives
What Are Thermocouples and Their Advantages?
Thermocouples are widely used temperature sensors that consist of two different metals joined at one end. When heated, they produce a voltage that correlates with temperature. Their primary advantages include lower costs and faster response times compared to RTDs. However, thermocouples generally have lower accuracy and can be affected by electromagnetic interference. They are ideal for applications requiring quick temperature changes but may not be suitable for precision measurement tasks.
What Are Infrared Temperature Sensors and When Should They Be Used?
Infrared temperature sensors measure the thermal radiation emitted from an object to determine its temperature. The key benefits of infrared sensors include their ability to take measurements without direct contact, making them ideal for hazardous or moving objects. However, they come with a higher price tag due to the advanced technology involved. Infrared sensors are best suited for situations where fast readings are needed, and contact measurement is impractical, such as in manufacturing processes or HVAC systems.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a temperature measurement solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including accuracy, cost, and ease of use. If precision is paramount and the budget allows, RTDs are an excellent choice. For applications where speed is critical and budget constraints are significant, thermocouples may be more appropriate. On the other hand, if the environment is hazardous or the object is difficult to reach, infrared temperature sensors offer a practical solution. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to select the most suitable technology for their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for r.t.d. meaning
What Are the Key Technical Properties of RTDs?
When considering the procurement of Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), understanding their essential technical properties is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here are some of the most critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Most RTDs are made with platinum, known for its stability and repeatability. The material choice affects the sensor’s accuracy and durability.
– B2B Importance: Selecting high-grade materials ensures longer lifespan and reliability, reducing replacement costs and downtime. -
Tolerance Classes
– Definition: Tolerance is defined by standards such as the DIN Class A, B, and C, which specify the allowable deviation from the specified resistance.
– B2B Importance: Understanding tolerance is vital for applications requiring precise temperature measurements. Choosing the right class can impact product quality and operational efficiency. -
Temperature Range
– Definition: This refers to the operational limits within which the RTD can accurately measure temperature. Common ranges for platinum RTDs are from -200°C to +850°C.
– B2B Importance: Buyers must ensure that the selected RTD can operate within the specific environmental conditions of their applications, preventing potential failures. -
Resistance Value
– Definition: The most common resistance value for RTDs is 100 ohms at 0°C, with temperature coefficients that dictate how resistance changes with temperature.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the resistance value helps in compatibility with existing measurement systems and instrumentation, ensuring seamless integration. -
Lead Wire Configuration
– Definition: RTDs can be configured with two, three, or four wires, affecting measurement accuracy.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate configuration based on accuracy requirements can significantly enhance measurement reliability, especially in industrial applications. -
Self-Heating Effect
– Definition: This is the increase in temperature of the RTD due to the electrical current passing through it, which can affect measurement accuracy.
– B2B Importance: Understanding and mitigating self-heating effects is essential for applications where precise temperature readings are critical, such as in pharmaceuticals and food processing.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to RTDs?
Navigating the procurement of RTDs also involves familiarity with industry-specific jargon. Here are some common terms that international B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Identifying OEMs can help buyers source high-quality RTDs that meet specific application requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses looking to minimize upfront investment. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and other details for a specific product or service.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare prices and terms across multiple suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping costs, insurance, and liability, which can significantly affect the overall cost of procurement. -
Calibration
– Definition: The process of adjusting the accuracy of a measurement device to ensure it produces accurate readings.
– Importance: Regular calibration is necessary for maintaining the reliability of RTDs, impacting product quality in industries such as manufacturing and healthcare. -
Compatibility
– Definition: The ability of an RTD to work seamlessly with other devices and systems.
– Importance: Ensuring compatibility with existing systems is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring accurate measurements.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing RTDs, leading to better operational outcomes and cost efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the r.t.d. meaning Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the r.t.d. Sector?
The market for r.t.d. (ready-to-drink) products is experiencing robust growth, driven by a combination of changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. Key drivers include an increasing demand for convenience, particularly in urban areas across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Consumers are seeking on-the-go beverage solutions that do not compromise on quality or flavor, leading to a surge in innovative product offerings.
Emerging trends such as health-conscious formulations and premiumization are reshaping the landscape. B2B buyers are now more inclined to source products that cater to specific dietary needs, such as low-sugar or organic options. This shift is accompanied by the adoption of digital sourcing platforms, which enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency. Technologies such as blockchain are increasingly being utilized to track product origins, ensuring quality and safety, which is vital for international trade.
Moreover, the influence of social media cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in shaping brand perceptions and consumer choices. B2B buyers must stay attuned to social trends and consumer feedback to align their sourcing strategies effectively. By leveraging data analytics, companies can anticipate market shifts and adjust their offerings to meet evolving demands.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the r.t.d. Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount in the r.t.d. sector, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental impact and social responsibility among consumers and businesses alike. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as reduced carbon footprints and eco-friendly packaging.
The environmental impact of beverage production is significant, from water usage to waste generation. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who have received certifications like Fair Trade or Rainforest Alliance, as these credentials often indicate a commitment to ethical sourcing and sustainable agricultural practices. Furthermore, the use of biodegradable or recyclable materials in packaging is gaining traction, aligning with consumer preferences for greener options.
Adopting sustainable practices not only enhances brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in the long run. For instance, optimizing supply chains to reduce waste can improve operational efficiency and profitability. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing methods and actively work towards sustainability goals, as this can lead to a competitive advantage in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What Is the Historical Context of the r.t.d. Sector’s Development?
The r.t.d. sector has evolved significantly over the last few decades, transitioning from traditional beverage options to a diverse array of ready-to-drink products that cater to various consumer preferences. Initially, r.t.d. beverages were primarily limited to soft drinks and juices. However, the late 1990s and early 2000s saw a rapid expansion into categories such as alcoholic beverages, functional drinks, and health-oriented options.
This evolution can be attributed to changing lifestyles, particularly among urban populations in emerging markets. As consumers sought convenience and variety, manufacturers began innovating, introducing products that combined flavors, health benefits, and unique packaging solutions. The rise of e-commerce has further transformed the landscape, allowing B2B buyers to access a broader range of products and suppliers globally.
As the market continues to grow, understanding the historical context provides valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities. B2B buyers can leverage this knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions that align with market demands and consumer expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of r.t.d. meaning
-
How do I source reliable suppliers for RTD sensors in international markets?
To source reliable suppliers for RTD sensors, start by researching manufacturers and distributors with a proven track record in your target region, such as Africa, South America, or Europe. Utilize platforms like Alibaba, Global Sources, or industry-specific trade shows to identify potential vendors. Vet suppliers by checking their certifications, customer reviews, and production capabilities. Establish communication to discuss your specific needs and request samples to assess quality. Additionally, consider leveraging local trade associations or chambers of commerce for recommendations. -
What are the common applications of RTD sensors in various industries?
RTD sensors are widely used across multiple industries for temperature measurement and control. Common applications include food and beverage processing, HVAC systems, petrochemical plants, and manufacturing processes. They are favored for their accuracy and stability, making them suitable for critical processes where precise temperature control is vital. By understanding the specific needs of your industry, you can identify the right RTD type and configuration to optimize performance and compliance with industry standards. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for RTD sensors from suppliers?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for RTD sensors can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific product configuration. Generally, MOQs can range from 10 to 100 units for standard models. For customized sensors, suppliers may require higher MOQs to justify production costs. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to find a mutually agreeable MOQ that aligns with your project requirements and budget. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with RTD sensor suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms with RTD sensor suppliers, consider industry standards such as a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining 70% before shipment. For first-time orders, you may negotiate more favorable terms based on your relationship with the supplier. Additionally, explore options for letters of credit or escrow services for added security. Ensure that payment terms are clearly documented in the contract to avoid misunderstandings later on. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for RTD sensors?
To ensure quality assurance for RTD sensors, request detailed product specifications, including compliance with international standards such as ISO or IEC. Implement a quality control process that includes inspections of incoming materials, in-process checks, and final product testing. Consider arranging for third-party inspections or certifications to validate the quality. Additionally, establish a clear return policy in case the products do not meet your standards, ensuring you have recourse if issues arise.

A stock image related to r.t.d. meaning.
- What customization options are available for RTD sensors?
Many suppliers offer customization options for RTD sensors, allowing you to tailor specifications such as resistance values, temperature ranges, and lead wire configurations to meet your specific application needs. You can also request special coatings for harsh environments or specific connectors for compatibility with your existing systems. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and ask for samples of custom configurations to evaluate performance before making a larger purchase.
A stock image related to r.t.d. meaning.
-
What are the logistics considerations when importing RTD sensors?
When importing RTD sensors, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a shipping method that balances cost and speed; air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Ensure that your supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes in your country to avoid unexpected costs and delays upon arrival. -
How can I assess the reliability of RTD sensor manufacturers?
Assessing the reliability of RTD sensor manufacturers involves several steps. Look for manufacturers with established reputations, positive customer testimonials, and relevant industry certifications. Conduct factory visits or request virtual tours to evaluate production capabilities and quality control processes. Additionally, review their history of fulfilling orders on time and their responsiveness to customer inquiries. Engaging with other businesses in your industry can also provide insights into a manufacturer’s reliability and service quality.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for r.t.d. meaning
What Are the Key Takeaways for Strategic Sourcing in RTD?
In conclusion, understanding the various meanings of RTD—whether it pertains to resistance temperature detectors or ready-to-drink products—can significantly enhance strategic sourcing decisions for international B2B buyers. By leveraging the precise applications of RTDs, businesses can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they select the right suppliers and technologies that align with their operational needs.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Benefit International Buyers?
Strategic sourcing not only drives cost efficiencies but also fosters supplier relationships that enhance product quality and reliability. This is particularly critical for buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics can vary widely. By adopting a methodical approach to sourcing RTD solutions, businesses can mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging trends.
What Should International B2B Buyers Do Next?
Looking forward, international B2B buyers are encouraged to evaluate their sourcing strategies in light of the insights gathered about RTDs. Engaging with suppliers who understand regional challenges and can offer tailored solutions will be vital in navigating the complexities of global markets. As the demand for innovative RTD products continues to rise, proactive sourcing will be a key differentiator in achieving competitive advantage.