Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Cnc Wheel Machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cnc wheel machine
In the rapidly evolving landscape of manufacturing, CNC wheel machines stand out as pivotal tools that enhance precision and efficiency in wheel production. These machines are not just equipment; they are integral to optimizing operations, ensuring quality, and maintaining competitiveness in the global market. For international B2B buyers—especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding the intricacies of CNC wheel machines is essential to making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of CNC wheel machines, including different types and materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. It also explores key suppliers and cost considerations, providing buyers with a well-rounded perspective on the market landscape. By addressing frequently asked questions, the guide aims to demystify the complexities surrounding CNC technology and its application in wheel manufacturing.
With the right information at their fingertips, international buyers can navigate the global market with confidence, identify reliable suppliers, and negotiate better deals. Whether you are a manufacturer looking to upgrade your machinery or a business aiming to enter the wheel production sector, this guide empowers you to leverage CNC technology effectively, ensuring that your operations are not only efficient but also aligned with global standards. Embrace the potential of CNC wheel machines and elevate your manufacturing capabilities in today’s competitive environment.
Understanding cnc wheel machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Vertical Wheel Machine | Vertical configuration, high rigidity, and precision | Automotive wheel manufacturing | Pros: High accuracy, efficient for mass production. Cons: Limited to specific wheel sizes. |
| CNC Horizontal Wheel Machine | Horizontal setup, versatile tooling options | Aerospace and industrial wheel production | Pros: Flexibility in design, accommodates larger wheels. Cons: Requires more floor space. |
| CNC 5-Axis Wheel Machine | Multi-axis capabilities for complex geometries | Custom wheel designs, luxury automotive | Pros: Exceptional precision for intricate designs. Cons: Higher investment cost. |
| CNC Grinding Wheel Machine | Specialized for grinding and finishing processes | Precision engineering, high-performance wheels | Pros: Superior surface finish, ideal for high-tolerance parts. Cons: Slower production rates. |
| CNC Wheel Lathe | Combines turning and milling functions | Wheel refurbishment, repair services | Pros: Cost-effective for repairs, versatile. Cons: Limited in producing new wheels. |
CNC Vertical Wheel Machine
CNC Vertical Wheel Machines are characterized by their vertical configuration, which offers high rigidity and precision during machining. These machines are primarily used in automotive wheel manufacturing, where mass production and accuracy are critical. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s ability to handle specific wheel sizes and the overall production capacity, as these factors directly impact efficiency and return on investment.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
CNC Horizontal Wheel Machine
The CNC Horizontal Wheel Machine features a horizontal setup that allows for versatile tooling options, making it suitable for various applications, including aerospace and industrial wheel production. This type is advantageous for manufacturers looking to produce larger wheels or multiple designs in one setup. Buyers should consider the floor space required for installation and the machine’s adaptability to different production needs, which can enhance operational flexibility.
CNC 5-Axis Wheel Machine
CNC 5-Axis Wheel Machines are designed for complex geometries, enabling the production of custom wheel designs, particularly in the luxury automotive sector. The multi-axis capabilities of these machines provide exceptional precision, allowing for intricate designs that meet high-quality standards. However, the initial investment cost can be significant, so B2B buyers should assess the potential for high-value projects that justify the expense.
CNC Grinding Wheel Machine
Specialized for grinding and finishing processes, CNC Grinding Wheel Machines excel in producing precision-engineered wheels that require high tolerances and superior surface finishes. They are commonly used in high-performance wheel applications. While these machines provide excellent results, they tend to have slower production rates, which could impact throughput. Buyers must weigh the benefits of quality against the potential need for increased production speed.
CNC Wheel Lathe
The CNC Wheel Lathe combines turning and milling functions, making it a versatile option for wheel refurbishment and repair services. This machine is particularly cost-effective for businesses looking to extend the life of existing wheels rather than producing new ones. Buyers should consider the machine’s versatility and the types of repairs it can perform, as this can significantly enhance service offerings and customer satisfaction.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of cnc wheel machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cnc wheel machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Precision wheel manufacturing for vehicles | High accuracy and consistency in wheel production, reducing defects | Supplier reliability, machine capabilities, and after-sales support |
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight, high-strength wheel components | Enhanced performance and fuel efficiency in aircraft | Material sourcing, compliance with aviation standards, and lead times |
| Rail Transportation | Fabrication of railway wheelsets | Improved safety and durability of rail vehicles | Certification requirements, production volume capabilities, and cost |
| Heavy Machinery | Custom wheel designs for construction and mining equipment | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Customization options, material quality, and service agreements |
| Sporting Goods | Manufacturing of specialized wheels for bicycles and skateboards | Enhanced performance and user experience for athletes | Innovation in design, material properties, and market trends |
Automotive Industry Applications
In the automotive sector, CNC wheel machines are essential for producing precision wheels that meet stringent safety and performance standards. These machines allow manufacturers to create wheels with exact specifications, which reduces defects and enhances vehicle safety. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers who can demonstrate reliability and provide robust after-sales support is crucial. Consideration should also be given to the machine’s capabilities in handling various materials, as different vehicle types may require unique wheel specifications.
Aerospace Industry Applications
CNC wheel machines play a pivotal role in the aerospace industry by enabling the production of lightweight yet strong wheel components. These components contribute significantly to overall aircraft performance and fuel efficiency. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers that comply with aviation industry standards and have a proven track record in delivering high-quality components. Additionally, sourcing considerations must include the availability of advanced materials and the ability to meet tight production schedules.
Rail Transportation Applications
In rail transportation, CNC wheel machines are utilized to fabricate wheelsets, which are critical for the safety and durability of trains. The precision offered by CNC technology ensures that wheelsets can withstand the rigors of rail travel while minimizing wear and tear. B2B buyers in regions like Turkey and South Africa should focus on suppliers that can provide certified products and demonstrate high production volume capabilities. Cost considerations are also vital, as rail projects often operate within strict budget constraints.
Heavy Machinery Applications
The heavy machinery sector benefits from CNC wheel machines through the customization of wheels for construction and mining equipment. These machines allow manufacturers to design wheels that enhance operational efficiency and reduce equipment downtime. For international buyers, it’s essential to evaluate suppliers based on their customization options and the quality of materials used. Service agreements that include maintenance and support can also provide added value, ensuring that the machinery remains operational over its lifecycle.
Sporting Goods Applications
In the sporting goods industry, CNC wheel machines are used to manufacture specialized wheels for bicycles and skateboards. The precision and innovation offered by these machines lead to enhanced performance, catering to the needs of athletes. Buyers should consider the latest trends in wheel design and material properties when sourcing. Understanding the competitive landscape and consumer preferences can help in selecting suppliers that align with market demands, particularly in Europe and South America.
Related Video: The World’s Largest Bevel Gear CNC Machine- Modern Gear Production Line. Steel Wheel Manufacturing
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cnc wheel machine
When selecting materials for CNC wheel machines, it is crucial to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we explore four common materials used in the manufacturing of CNC wheel machines, analyzing their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum Alloys
Key Properties:
Aluminum alloys are lightweight, with excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. They typically have a temperature rating up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum alloys are favored for their low weight, which enhances machine speed and efficiency. They are relatively easy to machine, leading to lower manufacturing complexity. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications due to lower tensile strength compared to steel.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oil-based coolants, making it versatile for different machining environments. However, it may not perform well in highly abrasive conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or ISO, particularly for aerospace or automotive applications. Preference for aluminum can vary based on regional availability and cost fluctuations.
Steel Alloys
Key Properties:
Steel alloys offer high tensile strength and durability, with temperature ratings exceeding 500°C. They exhibit excellent wear resistance and can handle high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of steel alloys is their robustness, making them ideal for heavy-duty machining tasks. However, they are heavier than aluminum, which can impact machine speed. The manufacturing complexity is higher due to the need for advanced machining techniques.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including aggressive coolants and lubricants. Its wear resistance makes it suitable for high-abrasion applications, such as in automotive or heavy machinery sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
In Europe and the Middle East, compliance with DIN and JIS standards is crucial for quality assurance. Buyers should also consider the availability of steel alloys in their region, as sourcing can affect lead times and costs.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often a blend of resin and reinforcement fibers, provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. They can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and are often tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of composites can significantly enhance machine performance. They are resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity. However, they can be more expensive than metals and may require specialized machining techniques.
Impact on Application:
Composites are particularly effective in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace or automotive industries. They are often compatible with various coolants but may not perform well under extreme temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Turkey and South Africa should be aware of the specific standards for composite materials, as they can vary significantly. Understanding local regulations regarding composites is essential for compliance and safety.
Titanium Alloys
Key Properties:
Titanium alloys are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance. They can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and are suitable for high-pressure environments.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of titanium is its durability and resistance to fatigue, making it ideal for demanding applications. However, titanium is more challenging to machine, leading to higher manufacturing costs and complexity.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is compatible with various media, including aggressive chemicals, making it suitable for specialized applications in the aerospace and medical fields.
Considerations for International Buyers:
When sourcing titanium alloys, buyers must consider compliance with international standards, particularly for aerospace applications. The higher cost of titanium may be a limiting factor for some buyers, especially in developing regions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for cnc wheel machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight components | Low weight enhances speed | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Steel Alloys | Heavy-duty machining | High durability | Heavier, impacts speed | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace and automotive applications | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost, specialized machining | High |
| Titanium Alloys | Specialized aerospace applications | Exceptional corrosion resistance | High manufacturing complexity | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cnc wheel machine
Manufacturing a CNC wheel machine involves a multi-stage process that ensures precision and quality at every step. For B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing CNC wheel machines is the preparation of raw materials. Common materials used include high-grade steel and aluminum alloys due to their strength and durability. Material preparation involves:
- Material Selection: Choosing the right type of metal based on the wheel’s intended application, which can affect weight, strength, and cost.
- Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes using saws or laser cutting, followed by initial shaping through processes like forging or casting.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, forming techniques are employed to create the desired shape of the wheel. This stage includes:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is the primary method used. It allows for high precision in shaping the wheel, including milling, turning, and drilling operations.
- Heat Treatment: After machining, the wheels may undergo heat treatment to enhance hardness and resistance to wear.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves integrating various components of the CNC wheel machine. Key aspects include:
- Component Integration: Assembling the wheel with other essential components, such as bearings, axles, and electronic controls.
- Alignment and Calibration: Ensuring that all parts are aligned correctly for optimal performance, which is critical for maintaining precision in operations.
4. Finishing
The final stage focuses on improving aesthetics and functionality:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like anodizing, powder coating, or painting are applied to protect against corrosion and wear, as well as to provide a finished look.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that the wheel meets all specifications and standards before delivery.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of CNC wheel machines is vital for ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of various international standards that govern manufacturing quality:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in products.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
Different industries may have specific quality standards, such as:
- API Standards: Relevant for CNC machines used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring they meet operational and safety requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during manufacturing ensure that processes remain within quality parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished product undergoes a final inspection to verify that it meets all design specifications and quality standards.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with common testing methods used in quality assurance, which include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying that the dimensions of the CNC wheel machine meet the specified tolerances using tools like calipers and gauges.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the operational performance of the machine under simulated working conditions.
- Non-destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection help identify internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International buyers can take several steps to verify the QC processes of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facility to assess compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline the results of inspections and tests conducted at various stages of production.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturing process and product quality before shipment.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
When sourcing CNC wheel machines, international B2B buyers must consider specific QC nuances:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and practices, which can impact quality. Understanding these differences is crucial for ensuring compliance.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is essential. Buyers should ensure that all specifications and quality requirements are documented in a language that both parties understand.
- Local Partnerships: Establishing relationships with local agents or consultants can help navigate the complexities of international procurement, particularly in emerging markets.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for CNC wheel machines is critical for B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality machines that meet their operational needs and comply with international standards. This knowledge not only aids in making informed decisions but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
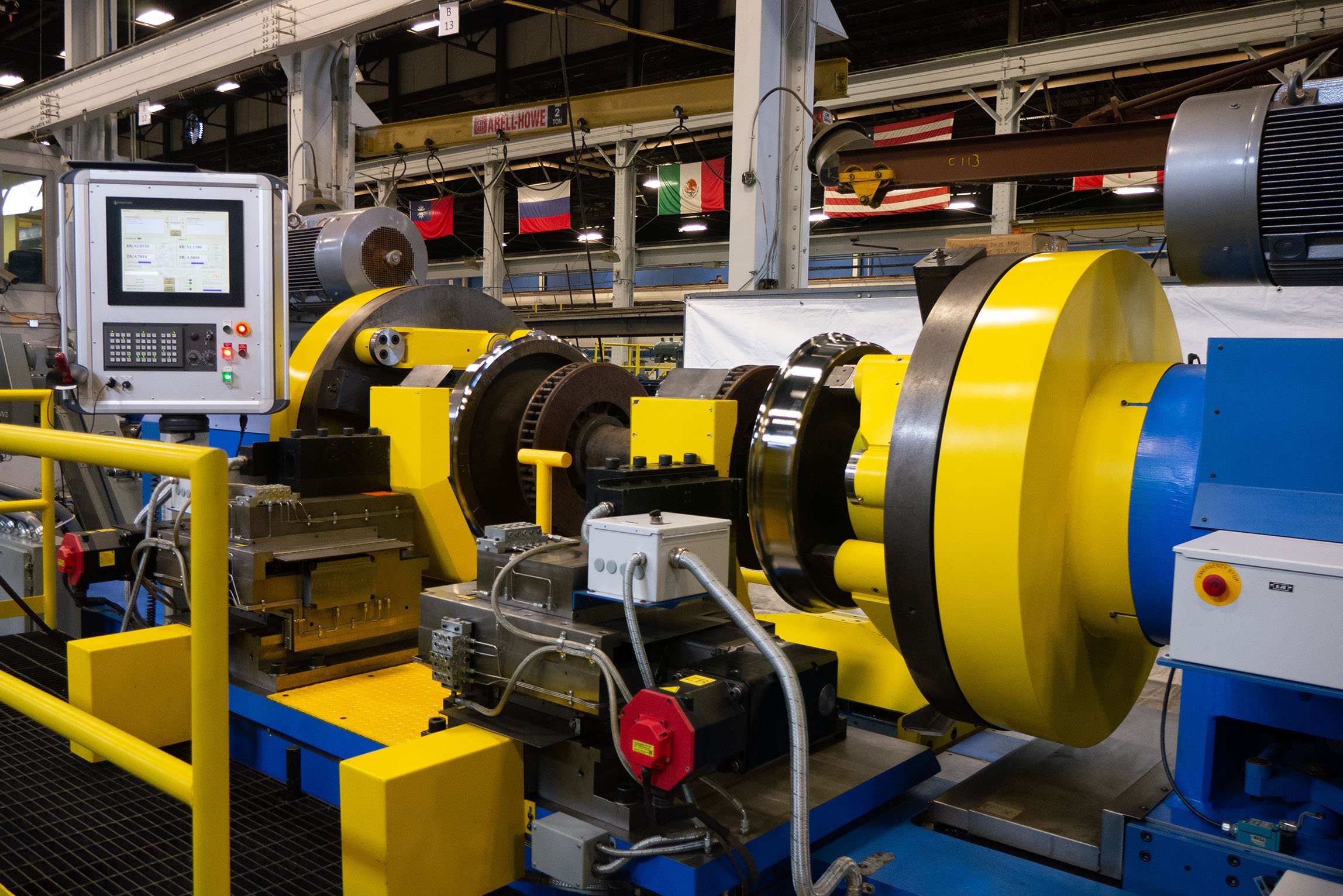

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cnc wheel machine Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing for CNC wheel machine sourcing is crucial for international B2B buyers. The analysis below breaks down the key components of cost, identifies factors that influence pricing, and offers strategic tips for making informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing CNC wheel machines significantly impact the overall cost. High-strength alloys or specialized composites may lead to increased material costs but can improve the machine’s performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be a substantial part of the total cost. Countries with higher wage standards, such as those in Europe, may have higher labor costs compared to regions like Africa or South America, where labor might be less expensive.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient factories with advanced technology may have lower overhead costs, translating to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling requirements can add to the initial investment. The complexity of the design and the need for specialized equipment will affect both the cost and lead time for production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investment in quality assurance processes is essential. Machines that undergo rigorous QC processes may have higher upfront costs but can lead to long-term savings through reduced failure rates and maintenance needs.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can be significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, method of transport, and customs duties should be considered when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers assess whether a quoted price is fair.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for better pricing. Buyers should assess their needs and potential for bulk purchasing to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features will likely lead to increased costs. Clearly defining specifications upfront can prevent misunderstandings and additional costs later in the process.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the price but also the machine’s performance. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between cost and quality based on their specific application needs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines with certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may be priced higher due to the assurance of quality. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can impact the final price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers. Highlight your long-term purchasing intentions to leverage better pricing or terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), not just the purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime when evaluating options.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, sourcing from suppliers in Europe may include higher labor costs but could offer advanced technology and reliability, while suppliers in Africa or South America may provide more competitive pricing.
Disclaimer
Pricing for CNC wheel machines can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cnc wheel machine
Key Technical Properties of CNC Wheel Machines
Understanding the essential technical properties of CNC wheel machines is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those involved in manufacturing and precision engineering. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used in the construction of the CNC wheel machine, such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials.
– Importance: Material grade affects durability, performance, and the machine’s ability to withstand operational stress. Buyers must select machines made from high-grade materials to ensure longevity and reliability, particularly in demanding environments like those often found in Africa and South America. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value, typically expressed in millimeters or microns.
– Importance: Tolerance is critical for ensuring that parts manufactured meet exact specifications. High tolerance levels are essential for precision engineering, impacting the quality of the end product and reducing waste, which is particularly important for cost-conscious buyers. -
Spindle Speed
– Definition: The speed at which the spindle of the CNC machine rotates, usually measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
– Importance: Higher spindle speeds can lead to increased production rates and improved surface finishes. Buyers should evaluate their specific manufacturing needs to select a machine with appropriate spindle speed capabilities, especially when working with various materials. -
Feed Rate
– Definition: The speed at which the tool moves through the material, often measured in millimeters per minute.
– Importance: The feed rate influences productivity and surface finish. An optimal feed rate helps achieve balance between speed and quality, enabling manufacturers to meet tight deadlines without compromising on quality, which is essential in competitive markets. -
Axis Configuration
– Definition: The number of axes the machine can operate on, typically ranging from 3 to 5 axes for CNC wheel machines.
– Importance: More axes allow for complex shapes and features to be machined in a single setup. This capability is particularly beneficial for manufacturers looking to produce intricate designs efficiently, reducing setup times and improving overall productivity.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms relevant to CNC wheel machines:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers should understand whether they are dealing with OEMs or resellers to ensure they are receiving genuine products and support, which can impact maintenance and warranty services. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and inventory. For international buyers, especially in markets with fluctuating demand, understanding MOQ can assist in cost management and logistics planning. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to solicit price offers for specific goods or services.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers gather multiple price points and terms, facilitating informed decision-making. This process is vital for budget management and ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping of goods.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand the implications of shipping costs, insurance, and risk. This knowledge is essential for negotiating contracts and managing international shipments efficiently. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time that passes from the initiation of a process until its completion, particularly in manufacturing and delivery.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is critical for planning production schedules and meeting market demands. Buyers should inquire about lead times to avoid delays and ensure timely delivery of CNC wheel machines.
By grasping these technical properties and terminologies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, streamline their procurement processes, and enhance their operational efficiency in the competitive landscape of CNC machining.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the cnc wheel machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global CNC wheel machine market is experiencing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting buyer preferences. Key market drivers include the increasing demand for precision manufacturing, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where high-quality wheel production is critical. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is propelling innovation in wheel design and manufacturing processes, creating opportunities for suppliers who can adapt quickly to new specifications.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, which enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize suppliers that leverage these technologies to reduce downtime and improve production speed. Furthermore, the trend toward automation is reshaping sourcing strategies, with many companies opting for CNC machines that incorporate automated loading and unloading systems to streamline operations.
For international buyers, understanding regional dynamics is crucial. In Africa, for instance, local manufacturers are increasingly collaborating with global suppliers to enhance their technological capabilities. Meanwhile, European buyers are focusing on local sourcing to mitigate supply chain disruptions, a trend that is also gaining traction in South America and the Middle East. Navigating these dynamics effectively requires a keen awareness of both global and regional market conditions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a central theme in the CNC wheel machine sector, with increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to adopt environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting buyers to seek out sustainable solutions. For B2B buyers, prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can enhance brand reputation and align with corporate social responsibility goals.
Ethical sourcing is equally important in today’s market. Buyers should evaluate their suppliers’ supply chains for transparency and sustainability, ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and ethically. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to standards like REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals) are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In terms of materials, the use of recycled metals and eco-friendly coatings can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of CNC wheel production. Buyers should actively seek suppliers who utilize these materials and who have implemented processes to minimize waste, thereby contributing to a circular economy. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, international buyers can foster innovation and enhance competitiveness in their respective markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of CNC wheel machines traces back to the late 20th century when the introduction of computer numerical control revolutionized machining processes. Initially, CNC technology was limited to larger manufacturers with substantial capital investments. However, as technology became more accessible and affordable, smaller firms began to adopt CNC machining, leading to increased precision and efficiency in wheel production.
Over the years, advancements in software and hardware have further enhanced CNC capabilities, allowing for more complex designs and faster production times. Today, the focus has shifted towards integrating sustainable practices within the manufacturing process, addressing the growing demand for environmentally friendly products. This evolution highlights the importance of continuous innovation and adaptation for suppliers and buyers alike, emphasizing the need to stay informed about technological advancements and market shifts.
Related Video: Is global trade transforming? | Counting the Cost
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cnc wheel machine
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for CNC wheel machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and financial stability. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Request references and case studies to assess their past performance. Additionally, consider their production capacity and technological capabilities to ensure they can meet your demands. Engaging in virtual meetings can also help gauge their professionalism and communication skills. -
Can CNC wheel machines be customized to my specifications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for CNC wheel machines to meet specific production needs. When discussing customization, clearly outline your requirements regarding dimensions, materials, and features. Inquire about the design process and the ability to prototype before full-scale production. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and consider the implications on lead times and costs when customizing. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for CNC wheel machines?
MOQs for CNC wheel machines can vary significantly based on the supplier and machine type, often ranging from 1 to 10 units. Lead times typically depend on the complexity of the machine and the supplier’s production schedule, ranging from a few weeks to several months. Always clarify these details during negotiations and consider how your order size may influence pricing and delivery timelines. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing CNC wheel machines internationally?
International B2B transactions often involve various payment methods, including letters of credit, bank transfers, or escrow services. Payment terms may vary, with options like 30% upfront and 70% upon delivery being standard. Ensure that you understand the payment terms fully and negotiate favorable conditions, considering the currency exchange risks and any applicable international tariffs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance?
Request detailed quality assurance (QA) processes from your supplier, including testing procedures and inspection reports. Ask for relevant certifications that confirm compliance with international standards, such as CE marking for Europe or ANSI for the United States. Consider conducting factory audits or utilizing third-party inspection services to verify quality before shipment, ensuring that the machines meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC wheel machines?
Logistics is crucial when importing CNC wheel machines. Evaluate shipping options, including freight forwarders that specialize in machinery transport, to ensure safe delivery. Be aware of customs regulations in your country, and prepare all necessary documentation to avoid delays. Additionally, consider insurance coverage for potential damages during transport to protect your investment. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements to minimize misunderstandings. In the event of a dispute, attempt to resolve it amicably through direct negotiations. If necessary, involve a mediator or arbitration service to facilitate a resolution. Ensure that your contracts include clauses regarding dispute resolution, specifying jurisdiction and applicable laws to streamline the process. -
What role do cultural differences play in international B2B transactions?
Cultural differences can significantly impact negotiations and relationship-building in international B2B transactions. Understanding the local business etiquette, communication styles, and decision-making processes of your suppliers can enhance collaboration. Invest time in research or engage local consultants to navigate cultural nuances effectively, fostering stronger partnerships and reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cnc wheel machine
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of CNC wheel machines presents a pivotal opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of understanding regional supply chains, fostering relationships with reliable manufacturers, and leveraging technological advancements. By focusing on a comprehensive sourcing strategy, buyers can mitigate risks, reduce costs, and ultimately improve their competitive positioning in the market.
For stakeholders in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly Turkey and South Africa, the emphasis should be on exploring local suppliers who can offer not only cost-effective solutions but also insights into regional market dynamics. Engaging in dialogues with manufacturers can reveal opportunities for customization and innovation, which are essential in a rapidly evolving industry.
Looking ahead, the landscape for CNC wheel machines is poised for growth, driven by advancements in automation and sustainability. International buyers are encouraged to remain proactive, invest in supplier partnerships, and continually assess the technological landscape to stay ahead. Embrace this moment to refine your sourcing strategies and unlock new avenues for growth and success in your operations.