Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Used Cnc Milling Machine
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for used cnc milling machine for sale
In an increasingly competitive global manufacturing landscape, the demand for precision and efficiency has led to a surge in the market for used CNC milling machines. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, investing in pre-owned machinery not only offers significant cost savings but also provides access to high-quality equipment that can enhance production capabilities. As companies strive to optimize their operations, understanding the nuances of the used CNC milling machine market becomes essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of sourcing used CNC milling machines, exploring various types, materials, and manufacturing standards. It provides insights into quality control measures, helping buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the condition of potential purchases. Additionally, the guide covers essential factors such as pricing strategies, market trends, and the intricacies of logistics and installation, ensuring that international buyers are well-equipped to navigate this complex market.
By addressing frequently asked questions and offering actionable tips, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs. Whether you are a manufacturer in Brazil seeking to upgrade your machinery or a UK-based supplier looking to expand your offerings, understanding the dynamics of the used CNC milling machine market will position you for success in today’s global economy.
Understanding used cnc milling machine for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical CNC Milling Machines | Upright spindle orientation, often smaller footprint | Aerospace, Automotive, General Manufacturing | Pros: Space-efficient, versatile; Cons: Limited depth of cut compared to horizontal. |
| Horizontal CNC Milling Machines | Horizontal spindle, ideal for heavy-duty tasks | Heavy Manufacturing, Aerospace, Tooling | Pros: Greater cutting capacity; Cons: Requires larger setup space. |
| 5-Axis CNC Milling Machines | Ability to move the cutting tool along five axes | Complex parts in Aerospace, Medical Devices | Pros: High precision, complex geometries; Cons: Higher initial cost and complexity. |
| CNC Bed Mills | Large, flat worktable, suitable for heavy materials | Large-scale production, Metal Fabrication | Pros: Stability for heavy workpieces; Cons: Less versatile than other types. |
| CNC Router Machines | Uses a rotating bit to cut hard materials | Woodworking, Sign Making, Composite Materials | Pros: Ideal for non-metal materials; Cons: Limited to lighter applications. |
Vertical CNC Milling Machines
Vertical CNC milling machines feature an upright spindle orientation, making them ideal for a variety of applications, particularly in aerospace and general manufacturing. Their compact size allows for efficient use of space, which is beneficial for smaller workshops. Buyers should consider the machine’s speed, tooling options, and overall versatility. While vertical mills are generally cost-effective, their limited depth of cut may restrict certain applications.
Horizontal CNC Milling Machines
Horizontal CNC milling machines are designed for heavy-duty machining tasks, with a spindle that operates horizontally. They are particularly suitable for industries requiring robust cutting capabilities, such as heavy manufacturing and aerospace. When purchasing, B2B buyers should evaluate the machine’s load capacity, tooling options, and maintenance requirements. Although they provide significant cutting power, the need for a larger footprint can be a drawback for some operations.
5-Axis CNC Milling Machines
5-axis CNC milling machines allow for intricate and complex machining by moving the cutting tool along five different axes. This capability is essential for industries that require high precision, such as aerospace and medical devices. Buyers should assess the machine’s software compatibility and precision capabilities when making a purchase. While they offer unparalleled flexibility and accuracy, the higher initial investment and operational complexity may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
CNC Bed Mills
CNC bed mills provide a stable platform for machining larger workpieces, making them suitable for large-scale production and metal fabrication. Their design allows for heavy materials to be processed with stability, which is crucial in high-volume environments. B2B buyers should focus on the machine’s bed size, rigidity, and ease of setup. However, their less versatile nature compared to other milling types may limit their use in diverse applications.
CNC Router Machines
CNC router machines use a rotating bit to cut through various materials, primarily non-metallic ones such as wood, plastics, and composites. They are commonly employed in woodworking and sign-making industries. When considering a purchase, buyers should evaluate the machine’s cutting speed, material compatibility, and software interface. While they excel in non-metal applications, their limitations in handling heavier materials may restrict their use in more demanding environments.
Related Video: Affordable Small 5 Axis CNC Milling Machine for Metal
Key Industrial Applications of used cnc milling machine for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of used cnc milling machine for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy and reduced waste in production | Certification of machines for aerospace standards |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission part production | Cost savings through efficient machining | Compatibility with existing production lines |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Enhanced precision for patient safety | Compliance with health regulations and standards |
| Energy | Turbine and generator component fabrication | Improved operational efficiency and reliability | Supplier reliability and service support availability |
| Consumer Products | Prototype development for various consumer goods | Faster time to market for new products | Availability of spare parts and maintenance history |
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, used CNC milling machines are essential for manufacturing precision components such as brackets, housings, and structural parts. These components require high tolerances and minimal waste to ensure safety and performance in flight. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing machines that meet stringent aerospace standards and may require certifications to validate their quality. This is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulatory compliance is critical.
Automotive
The automotive sector extensively utilizes used CNC milling machines for producing engine and transmission parts. These machines enable manufacturers to achieve cost-effective solutions while maintaining quality. International B2B buyers, especially from South America and Africa, should consider the machines’ compatibility with existing production systems and the availability of technical support. This ensures seamless integration into their manufacturing processes, resulting in better efficiency and reduced production costs.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, precision is paramount. Used CNC milling machines are used to create custom surgical instruments and implants, where even the slightest deviation can affect patient safety. Buyers must ensure that the machines comply with health regulations and standards, which can vary significantly across regions. For international buyers, particularly from Africa and Europe, sourcing machines with documented maintenance histories and reliable service support is vital to ensure ongoing compliance and operational efficiency.
Energy
The energy sector benefits from used CNC milling machines in the fabrication of turbine and generator components. These machines help improve operational efficiency and reliability, vital for maintaining energy production standards. B2B buyers in this industry should focus on the machine’s operational history and the availability of spare parts, as downtime can be costly. This is particularly important for buyers from South America and the Middle East, where energy demands are rapidly growing.
Consumer Products
Used CNC milling machines play a crucial role in the prototype development phase for various consumer goods, allowing companies to accelerate time-to-market for new products. By utilizing these machines, businesses can produce high-quality prototypes that facilitate testing and iteration. International B2B buyers should assess the availability of spare parts and the machines’ maintenance history to ensure long-term usability. This is essential for companies in Europe and Africa looking to innovate and stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
Related Video: A Cheap But Impressive Hobby CNC Router Machine: Two Trees TTC450 Review
Strategic Material Selection Guide for used cnc milling machine for sale
When selecting a used CNC milling machine, the material composition is critical to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Below, we analyze four common materials used in CNC milling machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to dampen vibrations, making it ideal for precision machining. It typically has a high temperature rating, allowing it to withstand significant heat generated during milling operations.
Pros & Cons:
Pros: Durable, stable, and provides excellent machining accuracy.
Cons: Heavier than other materials, which can complicate transportation and installation. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not properly maintained.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is suitable for heavy-duty applications and can handle various media, including metals and plastics. Its vibration-damping properties enhance the quality of the finished product.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for material quality. In regions like Europe, where environmental regulations are stringent, understanding the recycling and disposal protocols for cast iron is essential.
2. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel, particularly alloy steel, is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio and versatility. It can withstand high pressure and temperature, making it suitable for various machining tasks.
Pros & Cons:
Pros: Strong, durable, and relatively cost-effective.
Cons: Can be susceptible to rust if not treated, requiring regular maintenance. Manufacturing complexity can increase with specific alloy compositions.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of materials, including metals and composites, making it versatile for different machining applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify the steel grade and its compliance with international standards. In regions like South America and Africa, where sourcing may vary, ensuring the availability of spare parts is crucial.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance. It has a lower melting point than steel and cast iron, which can facilitate easier machining.
Pros & Cons:
Pros: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to machine.
Cons: Less durable than steel or cast iron, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is ideal for applications requiring lightweight components, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries. Its compatibility with various media, including non-ferrous metals, enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the specific alloy used, as different alloys have varying properties. Compliance with local standards, particularly in Europe, is vital for ensuring quality and safety.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials, often a combination of resins and fibers, offer unique properties such as high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Pros: Lightweight, customizable properties, and resistant to environmental degradation.
Cons: Generally more expensive and may require specialized machining techniques.
Impact on Application:
Composites are suitable for applications in aerospace and automotive sectors where weight savings are critical. Their compatibility with various media is often superior to traditional materials.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Understanding the specific composite material’s properties is crucial. Compliance with industry standards and certifications is essential, especially in regulated markets like the EU.
| Material | Typical Use Case for used cnc milling machine for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty machining | Excellent vibration damping | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Steel | Versatile machining applications | Strong and cost-effective | Susceptible to rust, requires maintenance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight components in aerospace/automotive | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable for heavy-duty applications | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace and automotive lightweight parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and requires specialized machining | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for used cnc milling machine for sale
In the competitive landscape of international B2B transactions, particularly in the market for used CNC milling machines, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is vital for buyers. This section delves into the key stages of manufacturing, relevant quality control standards, and actionable insights for verifying supplier quality, tailored specifically for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
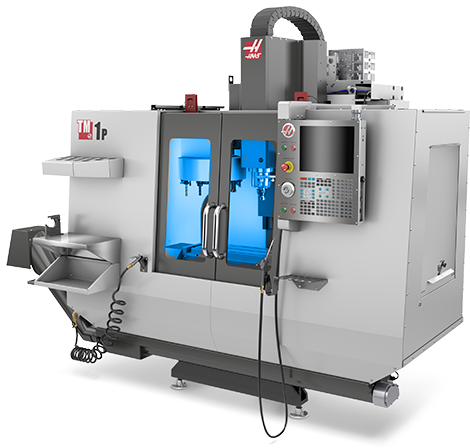
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes of Used CNC Milling Machines
The manufacturing of CNC milling machines, even those that are used, involves several critical stages. Each stage is crucial to ensure that the machine can perform reliably and meet the specific needs of various industries.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing CNC milling machines involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. High-quality steel and aluminum alloys are typically used for the machine frames and components. The preparation stage includes:
- Material Selection: Ensuring that materials meet specific mechanical properties required for durability and performance.
- Cutting and Shaping: Initial cuts are made to the raw materials using saws and other cutting tools, which are then shaped into components such as the base, column, and spindle.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage takes place. This includes:
- Machining: Components undergo machining processes, including turning, milling, and drilling. CNC machines are often employed here to achieve high precision.
- Welding and Joining: Components are welded or bolted together to form the machine structure. This process must ensure structural integrity and alignment.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves combining all the machined parts into a functional CNC milling machine. Key activities include:
- Integration of Components: Installing the spindle, axes, and control systems. Attention is paid to ensure that all components fit together perfectly to avoid issues during operation.
- Calibration: After assembly, machines are calibrated to ensure they can operate within specified tolerances. This step is crucial for maintaining accuracy.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which enhances the machine’s appearance and protects its components. This may involve:
- Surface Treatment: Applying coatings such as paint or anodization to protect against corrosion.
- Quality Checks: Conducting final inspections to ensure that all components meet specified standards and that the machine operates correctly.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of used CNC milling machines. It ensures that the machines meet international standards and are capable of performing as expected. Here are some key standards and practices to consider:
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is a widely recognized quality management standard that sets out criteria for a quality management system. Adherence to ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer maintains consistent quality in production and service.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking is required for machines to indicate compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It assures buyers that the machines meet EU regulations.
Industry-Specific Standards
- API (American Petroleum Institute): For CNC machines used in the oil and gas sector, compliance with API standards ensures safety and performance in critical applications.
- ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers): For machines used in pressure-related applications, ASME standards may apply, ensuring safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are critical in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Here are key stages of quality control:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor the machining processes and assembly. This helps identify any defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the complete machine undergoes rigorous testing to verify functionality, precision, and safety.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure that used CNC milling machines meet quality standards, various testing methods are employed:
- Functional Testing: Machines are operated under normal conditions to ensure all components function correctly.
- Dimensional Inspection: Precision measuring tools are used to verify that the machine meets specified tolerances.
- Load Testing: Machines are subjected to operational loads to assess their durability and performance under stress.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and quality control systems in place. This can help verify compliance with international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality inspections and testing results. Buyers should request these reports to ensure transparency.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the machine’s quality before purchase. This is especially valuable for buyers unfamiliar with local suppliers.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with international suppliers, buyers must be aware of potential nuances in quality control:
-
Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality control. Understanding these differences can aid in communication and expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the supplier understands and complies with both local and international regulations relevant to the buyer’s market.
-
Logistics and Support: Consider how the supplier handles logistics and post-purchase support, including spare parts availability and service options.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for used CNC milling machines is critical for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, as well as adhering to international quality standards, buyers can ensure they make informed purchasing decisions. Implementing thorough verification processes will further enhance the likelihood of a successful transaction, minimizing risks associated with buying used machinery.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for used cnc milling machine for sale Sourcing
In the global market for used CNC milling machines, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for international B2B buyers, especially those operating from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis breaks down the essential components that influence pricing, alongside actionable insights for effective sourcing.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The materials used in CNC milling machines, such as metals and electronic components, significantly affect the overall cost. Machines made from high-quality, durable materials typically command higher prices but offer better longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs are an important factor in the pricing of used machines, especially if they have undergone extensive refurbishing. Sellers may factor in the labor used for maintenance or upgrades, which could reflect in the final price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses incurred during the production of CNC machines. A manufacturer with higher overhead may price their machines at a premium.
-
Tooling: The condition and availability of tooling associated with the CNC machine can also influence pricing. Machines sold with additional tooling may be priced higher but offer more value to buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Sellers who implement rigorous quality control processes may charge more for their machines, as these typically come with certifications or guarantees regarding their performance and reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling are crucial components, especially for international transactions. Costs vary based on distance, mode of transport, and the complexity of shipping procedures. It’s essential to understand these costs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on their business model and market positioning. Larger suppliers might operate on lower margins due to higher volume sales, while smaller, niche suppliers may have higher margins reflecting their specialized offerings.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities often results in discounted pricing. Buyers should consider pooling orders with other companies to reach MOQ thresholds.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific manufacturing needs can incur additional costs. Understanding the necessity for customization versus off-the-shelf options can help buyers make informed decisions.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the price. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between cost and the expected performance of different materials.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines that come with quality certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may be priced higher but offer peace of mind regarding reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but their machines often come with better support and warranty options.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This can significantly impact the total cost.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Always engage in negotiations. Understanding the cost structure can empower buyers to negotiate better deals, especially if they can demonstrate knowledge of the market.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and potential downtime costs. This will help in evaluating the true value of a used machine.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For example, machines sourced from Europe may come with higher initial costs but offer superior technology and reliability compared to those from other regions.
-
Documentation: Ensure all agreements are thoroughly documented, especially regarding warranties and service agreements. This can mitigate risks associated with purchasing used machinery.
-
Expert Consultation: Consider consulting with industry experts or experienced machinists who can provide insights into specific models and brands, potentially guiding better purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for used CNC milling machines can vary widely based on condition, specifications, and market demand. This analysis provides indicative pricing and cost structures; actual prices may differ based on real-time market conditions and individual negotiations. Always conduct thorough due diligence and market research before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential used cnc milling machine for sale Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘used cnc milling machine for sale’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for used cnc milling machine for sale
When purchasing a used CNC milling machine, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making an informed decision. This knowledge helps in evaluating machine performance, ensuring compatibility with existing operations, and negotiating effectively. Below are key specifications and terms relevant to B2B buyers in international markets.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– This refers to the type and quality of materials used in the machine’s construction, such as cast iron or steel. Higher-grade materials typically enhance durability and precision. For B2B buyers, understanding material grades is essential for assessing the machine’s longevity and suitability for specific applications. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the permissible limits of variation in a manufactured part. It is critical in CNC machining, as it directly impacts the precision of the components produced. For buyers, knowing the tolerance levels can help determine if the machine meets their production standards and quality requirements. -
Spindle Speed
– Measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), spindle speed affects how quickly and efficiently a machine can operate. Higher spindle speeds can increase productivity but may also require more robust tooling and workpieces. Buyers should assess spindle speed to align it with their production needs and material types. -
Feed Rate
– The feed rate is the speed at which the workpiece is moved through the cutting tool, typically measured in inches per minute (IPM). This property influences productivity and the quality of the finished product. Understanding feed rates allows buyers to estimate processing times and adapt their workflows accordingly. -
Working Envelope
– This specification defines the maximum size of the workpiece that the machine can accommodate. Buyers must consider the working envelope to ensure it matches their production requirements, especially for larger components or complex geometries. -
Controller Type
– CNC machines can be equipped with various types of controllers, including Fanuc, Siemens, or proprietary systems. The controller impacts programming capabilities and ease of use. B2B buyers should ensure the controller’s compatibility with their existing software and workforce skill levels.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking reliable replacement parts and support for their used CNC machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For international buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory planning, particularly when sourcing parts or components for their CNC machines. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is crucial for comparing offers from different vendors, ensuring competitive pricing, and securing favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms used in international contracts to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations and minimize risk in cross-border transactions. -
CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
– CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through computer programming, enabling precise control of machining processes. Buyers should be aware of CNC technology’s capabilities and limitations to evaluate the machine’s suitability for their needs. -
Refurbished
– This term describes used machines that have been restored to a like-new condition, often including upgrades or replacement of worn parts. Buyers should inquire about refurbishment processes to ensure the machine’s reliability and performance.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the used CNC milling machine market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the used cnc milling machine for sale Sector
Global drivers are shaping the landscape of the used CNC milling machine market, offering unique opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The rising cost of new machinery, coupled with the need for immediate production capabilities, has led many businesses to consider second-hand options. Additionally, advancements in technology have improved the reliability and performance of used machines, making them an attractive choice for cost-conscious companies looking to maintain competitiveness.
Emerging sourcing trends are also noteworthy. Online marketplaces and digital platforms have transformed how buyers and sellers connect, facilitating easier access to a broader range of equipment and suppliers. This shift not only enhances transparency but also allows buyers to compare prices and specifications more effectively. Furthermore, the growing focus on automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is influencing the demand for CNC machines with advanced features, even in the used market. Buyers are increasingly looking for machines that offer compatibility with modern software and automation systems, ensuring they can integrate seamlessly into their existing operations.
Market dynamics are influenced by regional factors as well. In Africa and South America, where manufacturing capabilities are expanding, there is a rising demand for affordable machinery that can support local production initiatives. Meanwhile, in Europe and the Middle East, sustainability and energy efficiency are becoming critical considerations, prompting buyers to seek out machines that align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a key concern for B2B buyers in the used CNC milling machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal practices has prompted a shift towards more sustainable sourcing strategies. By purchasing used machines, companies can significantly reduce waste, contributing to a circular economy that emphasizes the reuse of materials and resources.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, as buyers increasingly seek suppliers who prioritize responsible sourcing practices. This includes verifying the origin of machines, ensuring they are not sourced from manufacturers with poor labor practices, and confirming that the machines meet environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Additionally, buyers should consider machinery that has been refurbished or retrofitted with energy-efficient components. This not only reduces the carbon footprint of operations but can also lead to long-term cost savings through lower energy consumption. Establishing partnerships with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices will enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The used CNC milling machine market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, the focus was primarily on the affordability of second-hand machinery; however, as manufacturing technologies advanced, so did the quality and capabilities of used machines. The introduction of digital platforms for sourcing and selling has further transformed the market, making it easier for buyers to find high-quality, reliable equipment. Today, the emphasis is not only on cost-effectiveness but also on sustainability, ethical sourcing, and technological compatibility, reflecting broader shifts in the manufacturing industry.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of used cnc milling machine for sale
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of used CNC milling machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Look for reviews and testimonials from previous clients, and consider their track record in international trade. Verify that they have a reliable supply chain and can provide documentation such as maintenance records and certifications. Engaging in direct communication can also help you assess their responsiveness and willingness to address your concerns. -
Can I customize a used CNC milling machine to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for used CNC milling machines. This can include modifications to the machine’s software, tooling, or even physical alterations to meet your production requirements. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier upfront, and ensure that any customization is documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for purchasing used CNC milling machines?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers. Some may allow single-unit purchases, while others may require larger orders, particularly for bulk purchases or specific machine models. Lead times also depend on the supplier’s inventory and your location. Always clarify these details upfront to align your production schedule with the supplier’s capabilities. -
How can I ensure the quality and certification of the used CNC milling machine?
Request comprehensive quality assurance documentation from the supplier, including inspection reports and certifications. Additionally, ask about the machine’s service history and previous usage. If possible, arrange for an in-person inspection or request a video demonstration to validate its condition. Reputable suppliers should be willing to provide this information to ensure buyer confidence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What logistics should I consider when importing a used CNC milling machine?
Logistics can be complex when importing machinery. Consider shipping costs, customs duties, and insurance coverage. Work with a logistics partner familiar with heavy machinery to navigate these challenges effectively. Additionally, confirm that the supplier can support the logistics process, including packaging and documentation for customs clearance. -
How can I handle disputes with the supplier after the purchase?
Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing to minimize disputes. If a disagreement arises, first try to resolve it amicably through discussion. If that fails, refer to the contract terms, particularly regarding warranties and return policies. In some cases, involving a third-party mediator or legal counsel may be necessary, especially for significant investments. -
Are there specific payment methods recommended for international purchases of used CNC milling machines?
For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services, which provide protection for both buyer and seller. Wire transfers are common but carry risks, so ensure that you have verified the supplier’s legitimacy. Discuss payment terms upfront, including deposit amounts and timelines for the remaining balance upon delivery. -
What are the advantages of purchasing used CNC milling machines compared to new ones?
Purchasing used CNC milling machines can offer significant cost savings, allowing you to access high-quality equipment at a fraction of the price of new models. Additionally, used machines often have a proven track record of performance, reducing the risk of unexpected issues. The availability of immediate stock can also shorten lead times, helping you ramp up production more quickly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for used cnc milling machine for sale
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of used CNC milling machines offers significant advantages for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By focusing on quality, proven performance, and cost-effectiveness, businesses can enhance their manufacturing capabilities without the substantial financial burden of new equipment.
Key takeaways include the importance of thoroughly evaluating machine conditions, maintaining open communication with reputable suppliers, and understanding the specific needs of your operations. Additionally, leveraging online marketplaces and local networks can lead to fruitful sourcing opportunities, ensuring that you find the best deals available.
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve, the demand for efficient, reliable machinery will only increase. Now is the time for businesses to act—explore your options, conduct diligent research, and seize the opportunity to invest in high-quality used CNC milling machines. By doing so, you will position your company for growth and sustainability in a competitive global market. Embrace the future of manufacturing by making informed purchasing decisions today.